Deze handleiding is bedoeld als leidraad bij het gebruik van de RFlex Travel Extreme. Volg de aanbevelingen en specificaties nauwkeurig op voor optimale prestaties van uw lasapparaat.
Inhoudsopgave
- Hoofdstuk 1: Beoogd gebruik
- Hoofdstuk 2: Veiligheidstekens en pictogrammen
- Hoofdstuk 3: Technische gegevens
- Hoofdstuk 4: Technische beschrijving
- Hoofdstuk 5: Montage en installatie
- Hoofdstuk 6: Werking
- Hoofdstuk 7: Selectie van lasparameters
- Hoofdstuk 8: Onderhoud
- Hoofdstuk 9:
Gezondheid en veiligheid op het werk
- Hoofdstuk 10: Elektrische documentatie
- Hoofdstuk 11: Pneumatische documentatie
- Hoofdstuk 12: Algemene instructies
- Hoofdstuk 13: Bijlagen
- Hoofdstuk 14: Aanvullende machinedocumenten
Bel voor meer technische informatie over deze machine ons Resolution Center op 1-855-888-WELD of stuur een e-mail naar service@weldmaster.com.
1.0 Machineoverzicht/bedoeld gebruik
Miller Weldmaster is een toonaangevend bedrijf op het gebied van hoogfrequent lasmachines met meereizende kop. Reizende kop RFlex lasser is speciaal ontworpen voor de productie van grootformaat dekzeilen, tenten, zonweringssystemen, vrachtwagenafdekkingen, zwembadafdekkingen, vliegtuighangars, reclameborden, zijgordijnen en vele andere algemene technische stofverbindingen. De machine kan worden uitgerust met speciale gebogen elektroden voor het lassen van ronde raamprofielen van doorzichtig PVC en andere vormen die een nauwkeurige afdichting vereisen.
RFlex Het model is uitgerust met speciale lineaire precisiebewegingen, geregeld door een frequentieomvormer en een glide-on railing om een perfecte doorlopende rechte naad te verkrijgen. De werktafel heeft een goot voor eenvoudige materiaalhantering. De optionele vacuümwerktafel met een lengte tot 12 meter en lasergeleiders maken het mogelijk om materialen van groot formaat te verwerken en de lasnaden nauwkeurig te positioneren voor een snelle productie-instelling.
Met behulp van touchscreen HMI en programmeerbare PLC kan de operator eenvoudig meerdere las-/naadrecepten invoeren. RFlex Reislasmachine heeft RF-vermogenuitgangen voor zware productielast en versterkte zware stoffen.
Automatisch lassen cycli, pneumatisch aangedreven lassen bar, elektronische beweging teller regelen de lengte, afgelegde afstand en lascyclus aantal maken deze machine een perfect hulpmiddel voor high-end product waar precisie, duurzaamheid en sterkte de sleutel is.
RFlex Travel kan eenvoudig worden opgewaardeerd en omgebouwd tot een Keder-productiemachine met behulp van een speciaal hulpstuk en een laselektrode.
DE BELANGRIJKSTE MACHINEKENMERKEN:
- het routineonderhoud van de machine is zeer eenvoudig;
- kan het persen nauwkeurig worden aangepast;
- de fabrikant de noodknop op het bedieningspaneel heeft geïnstalleerd;
- de machine is uitgerust met een signaallichtkolom om de veiligheid van de machinist te verhogen wanneer de machine ingeschakeld is;
- dankzij het aanraakgevoelige HMI-paneel kan de machinist de inschakelduur van de machine programmeren en regelen;
- Met de programmeertool kan de operator in het systeem parameters invoeren zoals: de lastijd en het vermogen samen met de koeltijd;
- Met behulp van het HMI-paneel op de machine kan de operator vele lasprogramma's opslaan voor verschillende soorten materialen, laat staan de programma's die gebruikt worden voor het werken met verschillende soorten elektroden;
- Voor het gemak van de operator is de machine uitgerust met een elektrodehouder die speciaal ontworpen is voor het snel verwisselen van de laselektrode;
- de machine is uitgerust met de extra aardelektrode om de gebruiker te beschermen tegen het verhoogde niveau van HF niet-ioniserende straling die door de machine wordt uitgezonden;
- ZTG RF AutoTuning System™ - de machine is uitgerust met het automatische regelsysteem voor het uitgangsvermogen om de veiligheid van de operator te verhogen;
- ZTG SafeDOWN™ - de machine is uitgerust met het systeem dat de operator effectief moet beschermen tegen de elektrode wanneer deze omlaag wordt gebracht;
- ZTG Flash™ - een ander systeem van de machine dat verondersteld wordt de elektrode en het ruwe materiaal dat gelast wordt te beschermen tegen mogelijke schade veroorzaakt door een boogoverslag;
- Alle machines hebben CE-conformiteitscertificaten ontvangen.
HOOGFREQUENTE TECHNOLOGIE:
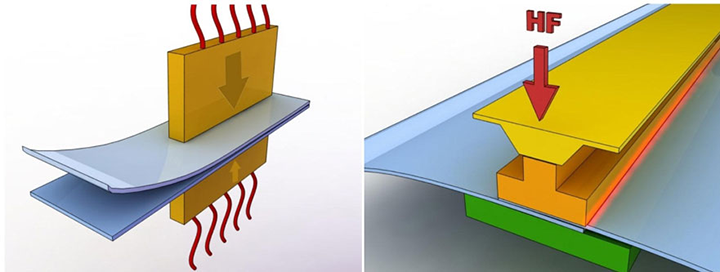
Hoogfrequent lassen, ook bekend als radiofrequentie (RF) of diëlektrisch lassen, is het proces waarbij materialen samensmelten door radiofrequentie-energie toe te passen op het te verbinden gebied. De resulterende las kan net zo sterk zijn als de oorspronkelijke materialen.
HF-lassen vertrouwt op bepaalde eigenschappen van het te lassen materiaal om warmte te genereren in een snel wisselend elektrisch veld. Dit betekent dat alleen bepaalde materialen met deze techniek kunnen worden gelast. Het proces houdt in dat de te verbinden delen worden blootgesteld aan een elektromagnetisch veld met een hoge frequentie (meestal 27,12 MHz), dat normaal gesproken tussen twee metalen staven wordt aangebracht. Deze staven dienen ook als drukmiddel tijdens het verhitten en afkoelen. Het dynamische elektrische veld zorgt ervoor dat de moleculen in polaire thermoplasten gaan oscilleren. Afhankelijk van hun geometrie en dipoolmoment kunnen deze moleculen een deel van deze oscillerende beweging omzetten in thermische energie en verwarming van het materiaal veroorzaken. Een maat voor deze interactie is de verliesfactor, die afhankelijk is van temperatuur en frequentie.
Polyvinylchloride (PVC) en polyurethanen zijn de meest voorkomende thermoplasten die met het RF-proces kunnen worden gelast. Het is mogelijk om andere polymeren RF te lassen, waaronder nylon, PET, PET-G, A-PET, EVA en sommige ABS-harsen, maar hiervoor zijn speciale omstandigheden vereist. Nylon en PET zijn bijvoorbeeld lasbaar als er naast het RFvermogen ook voorverwarmde lasstaven worden gebruikt.
HF-lassen is over het algemeen niet geschikt voor PTFE, polycarbonaat, polystyreen, polyethyleen of polypropyleen. Vanwege de dreigende beperkingen in het gebruik van PVC is er echter een speciale soort polyolefine ontwikkeld die wel geschikt is voor RF-lassen.
De primaire functie van HF-lassen is het vormen van een verbinding in twee of meer diktes plaatmateriaal. Er zijn een aantal optionele mogelijkheden. Het lasgereedschap kan worden gegraveerd of geprofileerd om het gehele gelaste gebied een decoratief uiterlijk te geven of het kan een reliëftechniek bevatten om belettering, logo's of decoratieve effecten op de gelaste delen aan te brengen. Door een snijkant naast het lasoppervlak te plaatsen, kan het proces tegelijkertijd lassen en snijden. De snijkant drukt de hete kunststof voldoende samen zodat het overtollige materiaal kan worden afgescheurd, vandaar dat dit proces vaak tear-seal lassen wordt genoemd.
 LET OP: De fabrikant kan niet aansprakelijk worden gesteld voor schade of letsel als gevolg van onjuist gebruik van dit apparaat.
LET OP: De fabrikant kan niet aansprakelijk worden gesteld voor schade of letsel als gevolg van onjuist gebruik van dit apparaat.
 LET OP: Lees alle instructies in deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding zorgvuldig door en volg ze op om het apparaat optimaal en veilig te kunnen gebruiken.
LET OP: Lees alle instructies in deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding zorgvuldig door en volg ze op om het apparaat optimaal en veilig te kunnen gebruiken.
 OPGELET: Alle arbeiders die opgeleid zijn in operationele veiligheid, werkprocedures en lasmachinerisico's, alsook zij die bevoegd zijn om de lasmachine te bedienen, worden door de Aannemer verzocht om het bijgevoegde formulier met leesbare handtekening te ondertekenen.
OPGELET: Alle arbeiders die opgeleid zijn in operationele veiligheid, werkprocedures en lasmachinerisico's, alsook zij die bevoegd zijn om de lasmachine te bedienen, worden door de Aannemer verzocht om het bijgevoegde formulier met leesbare handtekening te ondertekenen.
 LET OP: Het hoogfrequent lasapparaat is ontworpen en geproduceerd in een uitvoering die ongeschikt is voor personen met een handicap. Wanneer de machine bediend moet worden door personen met een handicap, moet de machine na overleg met de fabrikant op de juiste manier worden aangepast.
LET OP: Het hoogfrequent lasapparaat is ontworpen en geproduceerd in een uitvoering die ongeschikt is voor personen met een handicap. Wanneer de machine bediend moet worden door personen met een handicap, moet de machine na overleg met de fabrikant op de juiste manier worden aangepast.
2.0 Veiligheidstekens en pictogrammen
2.1 Algemene informatie
Om het lasapparaat op een optimale en veilige manier te gebruiken, dient u alle instructies in deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding zorgvuldig te lezen en op te volgen, met name ook alle waarschuwingen, verbods-, beperkings- en beveligingsinformatie en -tekens.
Op basis van de informatie in deze Operation & Maintenance Manual moet de klant Werkplekhandleidingen voor werknemers opstellen.
De Klant is volledig, wettelijk en materieel aansprakelijk voor alle gebeurtenissen die het gevolg zijn van onvoldoende kennis van deze Bedienings- & Onderhoudshandleiding of het niet naleven van de principes van de Arbo.
 WAARSCHUWINGEN OP DE APPARATEN EN/OF BESCHREVEN IN ONDERHANDLEIDENDE BEDIENINGS- EN ONDERHOUDSHANDLEIDINGEN WORDEN UITSLUITEND VERPLICHT.
WAARSCHUWINGEN OP DE APPARATEN EN/OF BESCHREVEN IN ONDERHANDLEIDENDE BEDIENINGS- EN ONDERHOUDSHANDLEIDINGEN WORDEN UITSLUITEND VERPLICHT.  LET OP: Voordat iemand met een HF-lasmachine gaat werken, is het verplicht om kennis te nemen van de volgende Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding.
LET OP: Voordat iemand met een HF-lasmachine gaat werken, is het verplicht om kennis te nemen van de volgende Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding.
 LET OP: Elke ontvanger of persoon die door de ontvanger is geautoriseerd op basis van deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding en de juiste karakteristieken van de productietechnologie is verplicht verschuldigd om een HANDLEIDING VOOR WERKSTANDEN uit te geven voor operators.
LET OP: Elke ontvanger of persoon die door de ontvanger is geautoriseerd op basis van deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding en de juiste karakteristieken van de productietechnologie is verplicht verschuldigd om een HANDLEIDING VOOR WERKSTANDEN uit te geven voor operators.
 LET OP: Het hoogfrequent lasapparaat mag ALLEEN bediend worden door werknemers die getraind zijn in het onderhoud van het apparaat en in INDUSTRIËLE VEILIGHEID met speciale aandacht voor de mogelijke risico's die het apparaat met zich meebrengt.
LET OP: Het hoogfrequent lasapparaat mag ALLEEN bediend worden door werknemers die getraind zijn in het onderhoud van het apparaat en in INDUSTRIËLE VEILIGHEID met speciale aandacht voor de mogelijke risico's die het apparaat met zich meebrengt.
 ATTENTIE: Gedurende de gehele levensduur van het apparaat raadt de fabrikant de koper aan om gebruik te maken van getraind onderhoudspersoneel dat door de fabrikant is geleverd of een serviceteam dat door de fabrikant is geautoriseerd.
ATTENTIE: Gedurende de gehele levensduur van het apparaat raadt de fabrikant de koper aan om gebruik te maken van getraind onderhoudspersoneel dat door de fabrikant is geleverd of een serviceteam dat door de fabrikant is geautoriseerd.
 ATTENTIE: De fabrikant raadt sterk aan om het lasapparaat alleen in een industriële omgeving te installeren.
ATTENTIE: De fabrikant raadt sterk aan om het lasapparaat alleen in een industriële omgeving te installeren.
 ATTENTIE: De machine moet goed waterpas staan en moet een vaste bedieningsplaats hebben.
ATTENTIE: De machine moet goed waterpas staan en moet een vaste bedieningsplaats hebben.
 LET OP: Onzorgvuldig gebruik van het apparaat tijdens transport (verplaatsing) kan leiden tot ernstig letsel of ongevallen.
LET OP: Onzorgvuldig gebruik van het apparaat tijdens transport (verplaatsing) kan leiden tot ernstig letsel of ongevallen.
 LET OP: De generator wordt gevoed door de levensgevaarlijke spanning van het elektriciteitsnet 3 x 480 VAC; 50 Hz. Het apparaat heeft een hoog voltage tot 8000 VDC. Alle service- en preventiewerkzaamheden mogen alleen worden uitgevoerd door getraind personeel met de wettelijk vereiste bevoegdheden.
LET OP: De generator wordt gevoed door de levensgevaarlijke spanning van het elektriciteitsnet 3 x 480 VAC; 50 Hz. Het apparaat heeft een hoog voltage tot 8000 VDC. Alle service- en preventiewerkzaamheden mogen alleen worden uitgevoerd door getraind personeel met de wettelijk vereiste bevoegdheden.
 OPGELET: De koper moet zorgen voor een correcte uitvoering en regelmatige preventieve controle van de installatie van de bescherming tegen elektrische schokken voor elk apparaat dat in gebruik is. Alle verantwoordelijkheid hiervoor ligt bij de koper.
OPGELET: De koper moet zorgen voor een correcte uitvoering en regelmatige preventieve controle van de installatie van de bescherming tegen elektrische schokken voor elk apparaat dat in gebruik is. Alle verantwoordelijkheid hiervoor ligt bij de koper.
 ATTENTIE: De lampspanning moet dezelfde zijn als gespecificeerd in het gegevensblad van het product - het is mogelijk om deze aan te passen met behulp van aftakkingen aan de primaire zijde van de gloeilamptransformator.
ATTENTIE: De lampspanning moet dezelfde zijn als gespecificeerd in het gegevensblad van het product - het is mogelijk om deze aan te passen met behulp van aftakkingen aan de primaire zijde van de gloeilamptransformator.
 ATTENTIE: De lamp moet na de installatie ongeveer een uur worden voorverwarmd.
ATTENTIE: De lamp moet na de installatie ongeveer een uur worden voorverwarmd.
 ATTENTIE: Alle werkzaamheden binnen de zone van de actieve perseenheid van de pers, d.w.z. het vervangen van het apparaat, kunnen alleen worden uitgevoerd met speciale voorzorgsmaatregelen door een getraind serviceteam.
ATTENTIE: Alle werkzaamheden binnen de zone van de actieve perseenheid van de pers, d.w.z. het vervangen van het apparaat, kunnen alleen worden uitgevoerd met speciale voorzorgsmaatregelen door een getraind serviceteam.
 LET OP: De machine kan op elk moment noodstop worden gezet door op de NOODSTOPknop te drukken. STOP-knop (de rode knop op gele achtergrond).
LET OP: De machine kan op elk moment noodstop worden gezet door op de NOODSTOPknop te drukken. STOP-knop (de rode knop op gele achtergrond).
 ATTENTIE: De werkomgeving van de machine, de vloer en de handmatige houders en handgrepen moeten altijd schoon en vrij van verontreiniging, vet of modder zijn om het risico van uitglijden of vallen tot een minimum te beperken.
ATTENTIE: De werkomgeving van de machine, de vloer en de handmatige houders en handgrepen moeten altijd schoon en vrij van verontreiniging, vet of modder zijn om het risico van uitglijden of vallen tot een minimum te beperken.
 LET OP: Haal de stekker uit het stopcontact voordat u toegangspanelen verwijdert of deuren opent. Alle afschermingen en toegangspanelen moeten op hun plaats zitten voordat u deze machine bedient.
LET OP: Haal de stekker uit het stopcontact voordat u toegangspanelen verwijdert of deuren opent. Alle afschermingen en toegangspanelen moeten op hun plaats zitten voordat u deze machine bedient.
 LET OP: De temperatuur van de elektrode kan oplopen tot 100 °C. Daarom kan men zich bij aanraking verbranden.
LET OP: De temperatuur van de elektrode kan oplopen tot 100 °C. Daarom kan men zich bij aanraking verbranden.
 LET OP: De lamp bevat zeldzame aardmetalen en zeldzame aardmetaaloxiden die zeer giftig zijn. In geval van breuk moet de lamp met de grootste zorg en met behulp van gespecialiseerd diensten.
LET OP: De lamp bevat zeldzame aardmetalen en zeldzame aardmetaaloxiden die zeer giftig zijn. In geval van breuk moet de lamp met de grootste zorg en met behulp van gespecialiseerd diensten.

 LET OP: Hoogfrequent lasmachine is de bron van niet-ionische elektromagnetische straling. Na installatie van de machine bij de koper moet de niet-ionische straling worden gemeten. De stralingsmetingen moeten worden uitgevoerd door een erkend bedrijf.
LET OP: Hoogfrequent lasmachine is de bron van niet-ionische elektromagnetische straling. Na installatie van de machine bij de koper moet de niet-ionische straling worden gemeten. De stralingsmetingen moeten worden uitgevoerd door een erkend bedrijf.
 ATTENTIE: Hoogfrequent lasapparaat moet op een stevige werkplek werken, omdat voor omzetting een nieuwe meting van de intensiteit van niet-ionische straling nodig is..
ATTENTIE: Hoogfrequent lasapparaat moet op een stevige werkplek werken, omdat voor omzetting een nieuwe meting van de intensiteit van niet-ionische straling nodig is..
 LET OP: Het is verboden voor mensen met een geïmplanteerde pacemaker om in de zone met actieve straling te verblijven..
LET OP: Het is verboden voor mensen met een geïmplanteerde pacemaker om in de zone met actieve straling te verblijven..
 ATTENTIE: De fabrikant raadt zwangere vrouwen of vrouwen die borstvoeding geven af om te werken in de zone met actieve niet-ionische straling..
ATTENTIE: De fabrikant raadt zwangere vrouwen of vrouwen die borstvoeding geven af om te werken in de zone met actieve niet-ionische straling..
 ATTENTIE: Reinig het luchtfilter in de pneumatische installatie ten minste eenmaal per maand.
ATTENTIE: Reinig het luchtfilter in de pneumatische installatie ten minste eenmaal per maand.
 LET OP!!! Er zijn laser indicatoren in de apparaat. Onder geen omstandigheden moet de laser straal zijn gericht naar de ogen als het kan oorzaak tijdelijk blindheid of, in extreme gevallen, permanent zicht schade.
LET OP!!! Er zijn laser indicatoren in de apparaat. Onder geen omstandigheden moet de laser straal zijn gericht naar de ogen als het kan oorzaak tijdelijk blindheid of, in extreme gevallen, permanent zicht schade.
 HET IS VERBODEN om werkzaamheden aan het lasapparaat uit te voeren door personen die niet vooraf zijn opgeleid in het onderhoud van hoogfrequente machines en industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften met speciale aandacht voor mogelijke risico's afkomstig van de machine.
HET IS VERBODEN om werkzaamheden aan het lasapparaat uit te voeren door personen die niet vooraf zijn opgeleid in het onderhoud van hoogfrequente machines en industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften met speciale aandacht voor mogelijke risico's afkomstig van de machine.  HET IS VERBODEN om de machine aan te zetten door werknemers zonder voorafgaande training in service en industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften.
HET IS VERBODEN om de machine aan te zetten door werknemers zonder voorafgaande training in service en industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften.  HET IS VERBODEN om de machine aan te zetten door werknemers zonder voorafgaande training in service en industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften.
HET IS VERBODEN om de machine aan te zetten door werknemers zonder voorafgaande training in service en industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften.  Het IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN om onderhouds- of preventiewerkzaamheden uit te voeren zonder eerst de generator en de machine los te koppelen van de stroomvoorziening.
Het IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN om onderhouds- of preventiewerkzaamheden uit te voeren zonder eerst de generator en de machine los te koppelen van de stroomvoorziening. HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN om pogingen te ondernemen om elektroden of elementen van de perseenheid in de pers aanraken. Aanraken tijdens het lassen kan brandwonden veroorzaken door hoogfrequente stroom of hoge temperatuur ~ 100 oC.
HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN om pogingen te ondernemen om elektroden of elementen van de perseenheid in de pers aanraken. Aanraken tijdens het lassen kan brandwonden veroorzaken door hoogfrequente stroom of hoge temperatuur ~ 100 oC.  HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN om handelingen uit te voeren die de veiligheidsstatus van de machine kunnen verminderen, d.w.z. werken met geopende beschermkap, toetsen blokkeren, enz.
HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN om handelingen uit te voeren die de veiligheidsstatus van de machine kunnen verminderen, d.w.z. werken met geopende beschermkap, toetsen blokkeren, enz. HET IS VERBODEN voor zwangere vrouwen of vrouwen die borstvoeding geven om in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling te verblijven.
HET IS VERBODEN voor zwangere vrouwen of vrouwen die borstvoeding geven om in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling te verblijven. HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN voor mensen met een geïmplanteerde pacemaker om in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling te verblijven.
HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN voor mensen met een geïmplanteerde pacemaker om in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling te verblijven. HET IS VERBODEN voor mensen met metalen orthopedische implantaten om in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling te verblijven.
HET IS VERBODEN voor mensen met metalen orthopedische implantaten om in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling te verblijven. HET IS VERBODEN om metalen gereedschappen in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling te brengen.
HET IS VERBODEN om metalen gereedschappen in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling te brengen. HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN om elke brand bij de generator en machine te bestrijden met water of een andere vloeistof.
HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN om elke brand bij de generator en machine te bestrijden met water of een andere vloeistof. HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN beschermkappen te verwijderen terwijl het apparaat in werking is.
HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN beschermkappen te verwijderen terwijl het apparaat in werking is. HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN om de machine af te spuiten tijdens het gebruik of om het systeem af te tappen.
HET IS TEN STRENGSTE VERBODEN om de machine af te spuiten tijdens het gebruik of om het systeem af te tappen. HET IS VERBODEN om olie, oplosmiddelen of andere giftige vloeistoffen weg te gieten in de omgeving van de machine.
HET IS VERBODEN om olie, oplosmiddelen of andere giftige vloeistoffen weg te gieten in de omgeving van de machine. het is verboden om een mobiele telefoon te gebruiken in de omgeving van de werkende machine.
het is verboden om een mobiele telefoon te gebruiken in de omgeving van de werkende machine. Het is VERBODEN om vuur te gebruiken in de omgeving van de werkende machine.
Het is VERBODEN om vuur te gebruiken in de omgeving van de werkende machine. HET IS VERBODEN te roken in de omgeving van de werkende machine.
HET IS VERBODEN te roken in de omgeving van de werkende machine. HET IS VERBODEN om alcohol te drinken in de omgeving van de machine en alle apparaten te bedienen door dronken werknemers.
HET IS VERBODEN om alcohol te drinken in de omgeving van de machine en alle apparaten te bedienen door dronken werknemers. HET IS VERBODEN te consumeren in de omgeving van de werkende machine.
HET IS VERBODEN te consumeren in de omgeving van de werkende machine. HET IS VERPLICHT om elke persoon die werkzaamheden aan de generator en pers uitvoert, op te leiden in het onderhoud van de machine en de industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften, met speciale aandacht voor mogelijke risico's die van de machine uitgaan.
HET IS VERPLICHT om elke persoon die werkzaamheden aan de generator en pers uitvoert, op te leiden in het onderhoud van de machine en de industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften, met speciale aandacht voor mogelijke risico's die van de machine uitgaan. HET IS STRICTISCH VERPLICHT om ALLE ontworpen beschermhoezen en blokkerende toetsen te gebruiken.
HET IS STRICTISCH VERPLICHT om ALLE ontworpen beschermhoezen en blokkerende toetsen te gebruiken. HET IS VERPLICHT om de supervisor en/of het verkeerspersoneel te informeren over alle gevallen van onjuiste bediening van de machine.
HET IS VERPLICHT om de supervisor en/of het verkeerspersoneel te informeren over alle gevallen van onjuiste bediening van de machine. HET IS VERPLICHT om werkkleding te gebruiken met zo min mogelijk onderdelen die door de pers van een hoogfrequente machine gegrepen of meegesleurd kunnen worden.
HET IS VERPLICHT om werkkleding te gebruiken met zo min mogelijk onderdelen die door de pers van een hoogfrequente machine gegrepen of meegesleurd kunnen worden. HET IS VERPLICHT om alle werkzaamheden aan lasserelementen (elektrode, perseenheid) uit te voeren met speciale beschermende handschoenen.
HET IS VERPLICHT om alle werkzaamheden aan lasserelementen (elektrode, perseenheid) uit te voeren met speciale beschermende handschoenen. Het is verplicht voor werknemers om werkschoenen te gebruiken die bescherming bieden tegen uitglijden.
Het is verplicht voor werknemers om werkschoenen te gebruiken die bescherming bieden tegen uitglijden. HET IS VERPLICHT om gebruik hoofddeksels door werknemers.
HET IS VERPLICHT om gebruik hoofddeksels door werknemers. HET IS VERPLICHT om de vloer in de omgeving van de machine schoon te houden.
HET IS VERPLICHT om de vloer in de omgeving van de machine schoon te houden. HET IS UITSLUITEND VERPLICHT om het lasapparaat te laten bedienen door werknemers die getraind zijn in het bedienen van hoogfrequente machines en in industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften.
HET IS UITSLUITEND VERPLICHT om het lasapparaat te laten bedienen door werknemers die getraind zijn in het bedienen van hoogfrequente machines en in industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften. HET IS VERPLICHT om de machine onmiddellijk uit te schakelen in geval van onjuiste bediening met behulp van de NOODSTOP-knop.
HET IS VERPLICHT om de machine onmiddellijk uit te schakelen in geval van onjuiste bediening met behulp van de NOODSTOP-knop. HET IS STRIKT VERPLICHT de generator en machine los te koppelen van alle voedingsmedia voordat u onderhoud of preventiewerkzaamheden uitvoert.
HET IS STRIKT VERPLICHT de generator en machine los te koppelen van alle voedingsmedia voordat u onderhoud of preventiewerkzaamheden uitvoert. HET IS STRIKT VERPLICHT om keramische condensatoren in een hoogfrequentiegenerator te ontladen. Zelfs nadat ze zijn losgekoppeld, kunnen ze lading behouden bij een spanning van enkele duizenden Volt, wat levensgevaar kan opleveren.
HET IS STRIKT VERPLICHT om keramische condensatoren in een hoogfrequentiegenerator te ontladen. Zelfs nadat ze zijn losgekoppeld, kunnen ze lading behouden bij een spanning van enkele duizenden Volt, wat levensgevaar kan opleveren. De lamp moet altijd worden vervoerd of verplaatst in de originele verpakking van de fabrikant, in verticale positie, met de anode naar boven of naar beneden gericht, zonder de lamp te stoten of te schudden.
De lamp moet altijd worden vervoerd of verplaatst in de originele verpakking van de fabrikant, in verticale positie, met de anode naar boven of naar beneden gericht, zonder de lamp te stoten of te schudden.3.0 Technische gegevens
|
Machine type |
RFlex Reizen |
|
Lasmaterialen |
PVC, PVC-gecoate stoffen |
|
Stroomvoorziening |
3 x 220 V; 50/60 Hz |
|
PLC-stuurprogramma |
Delta |
|
Stuurspanning |
24 VDC |
|
Geïnstalleerde capaciteit |
22 kVA |
|
RF uitgangsvermogen |
15 kW |
|
Aanpassing uitgangscapaciteit |
handmatige/autotuner |
|
Werkfrequentie |
27,12 MHz |
|
Frequentiestabiliteit |
+/- 0,6 % |
|
Antivlotsysteem, ZEMAT TG |
ultrasnelle gevoelige ARC-sensor |
|
Persluchtverbruik |
70 nl/cyclus |
|
Persluchtdruk |
0,4-0,8 MPa |
|
Max. lengte elektrode |
1500 mm |
|
Afmeting werktafel |
1620 x 320 mm |
|
Slag van de aandrijving |
160 mm |
|
Aandrijving voor drukelektrode |
pneumatisch |
|
Drukkracht (max) |
1900 kG |
|
Generatorlamp |
ITL 12-1 |
|
Koelvloeistof |
lucht |
|
Gewicht machine |
~ 1600 kg |
|
Afmetingen |
ZIE BIJLAGEN |
4.0 Technische beschrijving
Radio Frequentie Lasser RFlex Reizen bestaat uit de volgende basiselementen:
- LASSEN KOP - met een ondersteuning frame gemaakt van gelast stalen platen en gevormde profielen. Het interne deel van de constructie kan worden verdeeld in drie zones:
- een achterste deel - waar een hoge frequentie generator is geplaatst met een anode transformator en een controle kast. Dit deel is beschermd door afneembare deksels uitgerust met eindschakelaars;
- een laszone - met werktafel. De las wordt gemaakt met een elektrode die op de werktafel wordt gedrukt door een geïsoleerde gereedschapshandgreep die via een tussenplaat en isolatoren verbonden is met een pneumatische aandrijving. De laszone wordt beschermd tegen niet-ioniserende straling door de beweegbare aardelektrode die tijdens de lasprocedure tegen de tafel wordt gedrukt , waardoor een soort condensator ontstaat die de niet-ioniserende straling moet beperken. Bijzondere aandacht moet worden besteed aan het feit dat het oppervlak van het te lassen materiaal gelijkmatig verdeeld is op de werktafel en niet gegolfd is. Let er vooral op dat er zich geen metalen voorwerpen in de buurt van en onder de aardelektrode bevinden . Het niet voldoen aan de voorwaarden in de twee bovenstaande waarschuwingen kan van invloed zijn op de emissie van het elektromagnetische veld. Boven de laszone bevindt zich een bedieningspaneel waar de meeste bedieningselementen zijn geplaatst. Daarnaast is de machine uitgerust met een extra elektrode, waardoor lassen zonder gebruik van een aardelektrode mogelijk is. Nadat zo'n elektrode in de houder is geplaatst en begint te zakken, wordt een extra eindschakelaar geactiveerd die de beweging van de aardelektrode blokkeert.
- de aandrijving van de machine is gelegen in het onderste deel van de contractie. Het bestaat uit een asynchrone motor verbonden met een rek via rek transmissie. De motor wordt bestuurd door een omvormer geplaatst in de schakelkast op de machine chassy. Het rek beweegt op een ketting vast op de tafel assemblage. Het traject van de machine wordt gecontroleerd door rails waarop schuivende of wielstellen bewegen.
|
|
- WERKTAFEL met trog - gemaakt van onderling verbonden aluminium profielen voor de nodige stijfheid. Aan de voorkant is de werktafel bevestigd op stalen profielen die de basis vormen voor de rails waarop de machine beweegt. Aan de achterkant wordt de werktafel ondersteund door inklapbare staanders die naar beneden klappen wanneer de machine over de rails beweegt. Aan beide uiteinden van de werktafel bevinden zich verstelbare bumperschakelaars die de eindschakelaars activeren die het begin en het einde van de werktafel markeren, evenals twee elastische buffers die, in geval van uitval, de machine aan het einde van de werktafel stoppen en beschermen tegen schade. Elektrische en pneumatische stroom wordt aan de HF laskop geleverd via kabels die in flexibele kabelgeleiders zijn geplaatst. De elektrische en pneumatische aansluitingen bevinden zich in het midden van de achterkant van de werktafel.
De volgende systemen van de machine kunnen worden onderscheiden:
- HET BESTURINGSSYSTEEM dat bestaat uit een PLC met een touch screen HMI, bedieningselementen op een bedieningspaneel en elektrische en elektronische assemblage in de schakelkast en in de machine.
- HET PERSLUCHTSYSTEEM dat onder andere bestaat uit een persluchtvoorbereidingsset, verdeelkleppen, reduceerventielen en pneumatische cilinders.
- HET RF GENERATIESYSTEEM bestaande uit een zelfactiverende, hoogfrequente generator met gedistribueerde constanten met een hoogkwalitatief LC circuit gericht op een resonantiefrequentie van 27,12 MHz. Het systeem bevat ook een triode, HF genererende buis, anode- en gloeidraadtransformatoren evenals een koelsysteem van de HF genererende buis.
De laselektrodehouder is uitgerust met een automatisch grijpsysteem dat wordt bediend via het HMI touchpanel. Hierdoor kunnen elektroden zonder gereedschap worden vervangen.
|
|
De machine heeft een ingebouwd systeem (ZTG AntiCRUSH) dat ontworpen is om de handen van de operator te beschermen tegen pletten. Wanneer een hand of een voorwerp met een andere hoogte dan die van het lasmateriaal onder de laselektrode wordt geplaatst, wordt de elektrode automatisch omhoog getrokken tijdens de persfase.
|
|
Bovendien zijn er laserindicatoren geïnstalleerd op het chassis van de machine om het gelaste materiaal gemakkelijk op de werktafel te kunnen positioneren.
 LET OP! Vermijd blootstelling naar de laser licht! Het is strikt verboden staren rechtstreeks op de laser straal! De laser veiligheid klasse is 3B (PN-EN 60825 1:2005).
LET OP! Vermijd blootstelling naar de laser licht! Het is strikt verboden staren rechtstreeks op de laser straal! De laser veiligheid klasse is 3B (PN-EN 60825 1:2005).
Montage tekeningen, samen met de afmetingen van de lasapparaat, zijn zijn opgenomen in de bijlagen bij dit gebruikershandleiding handleiding.
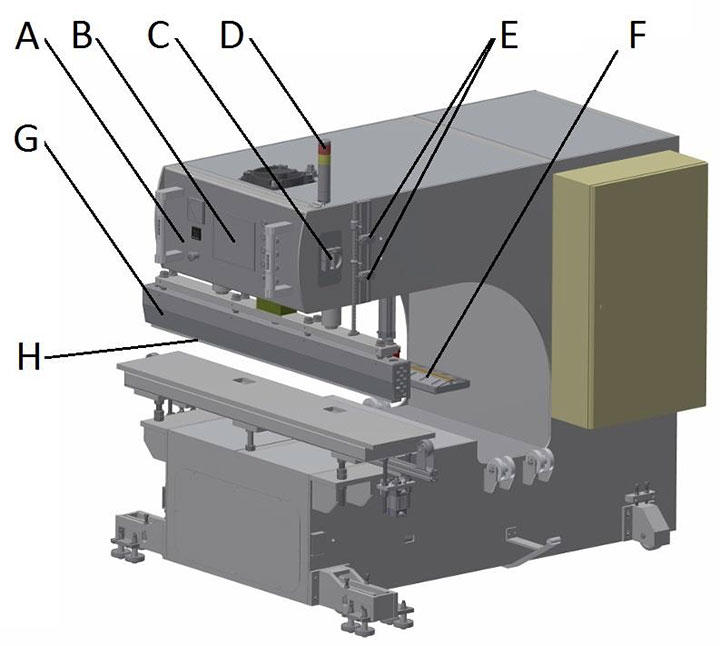
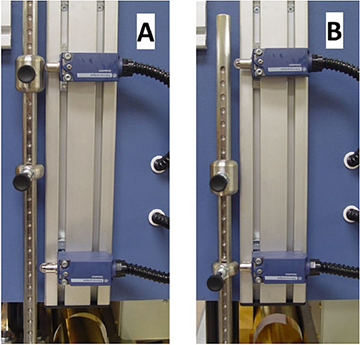
Laskop (zonder de werkbank) - basis elementen van de machine:
Een - behandeling en controle elementen geplaatst op de controle paneel;
B -HMI aanraakpaneel; C - hoofdschakelaar ;
D - signalering kolom;
E - grenswaarde schakelaars die de elektrode positie aangeven; F - aarding elektrode;
G - elektrode houder;
5.1 Informatie en tekenen van beperkingen en verplichtingen
De fabrikant zorgt voor een geschikte verpakking van het apparaat voor het moment van transport. Het type en de duurzaamheid van de verpakking zijn aangepast aan de afstand en het transportmiddel, en dus aan het potentiële risico van schade tijdens het transport. De Fabrikant stelt voor dat elke Klant de transportmiddelen en het technische servicepersoneel van de Fabrikant gebruikt.
Aan de opslag van de machine worden geen speciale eisen gesteld, behalve een geschikte opslagomgeving.
De opslagruimte moet voldoende bescherming bieden tegen weersinvloeden, moet zo droog mogelijk zijn en een aanvaardbaar vochtigheidsniveau hebben (minder dan 70%). Het is ook noodzakelijk om te zorgen voor de juiste bescherming tegen corrosie, vooral met betrekking tot metalen onderdelen die om technische redenen niet geverfd zijn.
Als de machine wordt geleverd in een doos en verpakt is in plastic dat een corrosiewerende atmosfeer genereert, moet de machine gedurende de hele opslagperiode verpakt en ingepakt blijven.
Ter bescherming tegen vochtigheid wordt aanbevolen om de machine niet rechtstreeks op de vloer van de opslagruimte op te slaan, maar op pallets.
Een onderdeel dat in elk stadium speciale aandacht en behandeling vereist - inclusief opslag - is de generatielamp (triode). De lamp moet worden opgeslagen in de originele verpakking, in verticale positie, met de anode naar boven of beneden gericht, in een droge ruimte. De lamp is een hoogvacuüm, metalen en keramisch onderdeel dat uiterst kwetsbaar is en niet geraakt of gevallen mag worden, zelfs niet van geringe hoogte.
Het slaan, laten vallen, schudden of voor langere tijd kantelen van de lamp kan leiden tot permanente en onomkeerbare schade aan de lamp. Met name de gloeidraad van de lamp - kathode kan breken, wat in de meest extreme gevallen kan leiden tot interne kortsluiting of lampbreuk.
 ATTENTIE: De fabrikant raadt zwangere vrouwen of vrouwen die borstvoeding geven af om te werken in de zone met actieve niet-ionische straling..
ATTENTIE: De fabrikant raadt zwangere vrouwen of vrouwen die borstvoeding geven af om te werken in de zone met actieve niet-ionische straling..
De bovenstaande bepalingen zijn bedoeld om alle personen en diensten die in contact kunnen komen met dit apparaat te instrueren en te waarschuwen voor zijn grote kwetsbaarheid voor alle impulsen en slagen. Tegelijkertijd zullen geen claims in verband met permanente schade zoals hierboven beschreven worden geaccepteerd in de loop van de klachtenprocedure.
Ook moet worden benadrukt dat de generatorlamp een erg duur onderdeel is.
In geval van twijfel is het raadzaam de gespecialiseerde medewerkers van de fabrikant te raadplegen.
5.2 Transport van de machine
De partij die verantwoordelijk is voor het transport en de installatie van de machine op de locatie van de besteller, dient te worden bepaald op het moment van ondertekening van het contract en niet later dan na de definitieve acceptatietest van de machine op de locatie van de fabrikant, voordat de machine aan de besteller wordt overgedragen.
 ATTENTIE: Onzorgvuldig gebruik van het apparaat tijdens transport/verplaatsing kan leiden tot ernstig letsel of ongevallen.
ATTENTIE: Onzorgvuldig gebruik van het apparaat tijdens transport/verplaatsing kan leiden tot ernstig letsel of ongevallen.
 HET IS VERBODEN om het apparaat te monteren, te demonteren of te transporteren door personeel zonder de juiste kwalificaties of zonder bekend te zijn met de veiligheidsvoorschriften die in deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding worden beschreven. Dergelijke handelingen kunnen ongelukken of materiële schade veroorzaken.
HET IS VERBODEN om het apparaat te monteren, te demonteren of te transporteren door personeel zonder de juiste kwalificaties of zonder bekend te zijn met de veiligheidsvoorschriften die in deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding worden beschreven. Dergelijke handelingen kunnen ongelukken of materiële schade veroorzaken.
Rekening houdend met het specifieke karakter van het apparaat, stelt de fabrikant voor dat elke besteller gebruik maakt van de transportmiddelen en het technische servicepersoneel van de fabrikant.
De voedingsbuis moet worden gedemonteerd voordat deze wordt vervoerd of verplaatst.
 De lamp moet altijd worden vervoerd of verplaatst in de originele verpakking van de fabrikant, in verticale positie, met de anode naar boven of naar beneden gericht, zonder de lamp te stoten of te schudden.
De lamp moet altijd worden vervoerd of verplaatst in de originele verpakking van de fabrikant, in verticale positie, met de anode naar boven of naar beneden gericht, zonder de lamp te stoten of te schudden.
 ATTENTIE: De machine moet in verticale positie worden vervoerd.
ATTENTIE: De machine moet in verticale positie worden vervoerd.
Door de grootte en structuur van de machine moeten sommige onderdelen en eenheden gedemonteerd en losgekoppeld worden tijdens transport of verplaatsing. Het is noodzakelijk om kwetsbare en dure componenten en gereedschappen te demonteren (deze moeten in een aparte koffer worden vervoerd). Het is absoluut noodzakelijk om de generatorlamp te demonteren.
De machine moet worden verplaatst met behulp van hefapparatuur - kranen, vorkheftrucks, palletwagens - met voldoende hefvermogen om de generator veilig te kunnen vervoeren, terwijl de mensen die deze hefapparatuur bedienen alle geldige licenties en kwalificaties moeten hebben die wettelijk vereist zijn.
Alle onderdelen van de machine die beschadigd kunnen raken tijdens het transport (als er geen duurzame verpakkingsdoos wordt gebruikt) of door hef- of verplaatsingsapparaten, moeten goed worden vastgezet (op voorwaarde dat ze gedemonteerd en apart verpakt worden).
Om een stabiele positie van het apparaat te garanderen, is het erg belangrijk om te zorgen voor de juiste bescherming van de machine tijdens lang transport (veiligheidsgordels, verankeringsbouten), evenals bescherming en hulp tijdens transport op locatie.
Als de machine niet is uitgerust met geschikte hulpstukken, kunnen andere beschikbare gaten of elementen van voldoende duurzaamheid worden gebruikt om ervoor te zorgen dat de generator en andere onderdelen van de machine goed worden uitgebalanceerd en gestabiliseerd.
Bij het plannen van het transport moet zeker rekening worden gehouden met het gewicht van de machine (ongeveer 1100 kg).
5.3 Installatie op de plaats van gebruik
Afhankelijk van de mate van complexiteit van de machine, moet de installatie op de plaats van gebruik worden uitgevoerd door personeel van de besteller, dat deze Bedienings- & Onderhoudshandleiding heeft gelezen, of technisch servicepersoneel van de fabrikant, in samenwerking met het personeel van de besteller.
Denk eraan dat de juiste positionering en installatie van het lasapparaat van vitaal belang zijn voor een optimale werking en voor het comfort en de veiligheid van de operator in de omgeving van het apparaat.
De besteller is verantwoordelijk voor de voorbereiding van de installatieplaats van het apparaat, de beschikbaarheid en voorbereiding van de elektrische aansluitingen en de realisatie van de bijzondere eisen van het technisch ontwerp en de technische acceptatietests waarmee het complete aggregaat wordt goedgekeurd voor gebruik.
De fabrikant zal de besteller in dit verband alle vereiste instructies en informatie verstrekken.
 LET OP: Zorg ervoor dat de vloer/het oppervlak/de fundering waarop het apparaat wordt geplaatst voldoende duurzaam is, rekening houdend met het gewicht, het oppervlak en de verdeling van het gewicht van het apparaat over de steunpunten (meestal de poten).
LET OP: Zorg ervoor dat de vloer/het oppervlak/de fundering waarop het apparaat wordt geplaatst voldoende duurzaam is, rekening houdend met het gewicht, het oppervlak en de verdeling van het gewicht van het apparaat over de steunpunten (meestal de poten).
 ATTENTIE: Het apparaat moet goed waterpas staan en moet een vaste bedieningsplaats hebben.
ATTENTIE: Het apparaat moet goed waterpas staan en moet een vaste bedieningsplaats hebben.
De optimale plaats om het HF lasapparaat te gebruiken is het betonnen oppervlak dat niet bedekt is of bedekt is met een zeer dunne laag niet-geleidend materiaal.
Het oppervlak moet worden gemaakt in overeenstemming met het specifieke ontwerp volgens de constructie- en veiligheidsnormen en volgens de vereisten met betrekking tot parallelle, loodrechte en vlakke posities.
 OPGELET: De besteller is als enige verantwoordelijk voor de naleving van de hierboven vermelde voorwaarden.
OPGELET: De besteller is als enige verantwoordelijk voor de naleving van de hierboven vermelde voorwaarden.
Na het plaatsen van het lasapparaat op de gekozen plaats is het noodzakelijk om het apparaat waterpas te zetten, de technische staat te controleren en alle defecten die tijdens het transport kunnen zijn opgetreden te verwijderen. Vervolgens de generator uitpakken, plaatsen, waterpas zetten en bevestigen. De lamp van de hoogfrequente generator moet helemaal aan het einde van het installatieproces worden gemonteerd. Deze taak moet met bijzondere aandacht worden uitgevoerd, zowel bij het monteren van de lamp in de fitting/voet als bij het aansluiten van de elektrische contacten van de lamp. Sluit de connectors van de bedieningsconsole aan op de juiste gemarkeerde bussen op de pers. Het wordt aanbevolen om de installatie van de machine na transport uit te voeren onder direct toezicht van een vertegenwoordiger van de fabrikant.
 LET OP: Als de bovengenoemde taken worden uitgevoerd door een vertegenwoordiger van de klant, moeten ze strikt worden uitgevoerd in overeenstemming met de beschrijving in deze Bedienings- & Onderhoudshandleiding en/of instructies van de fabrikant tijdens de technische acceptatietest.
LET OP: Als de bovengenoemde taken worden uitgevoerd door een vertegenwoordiger van de klant, moeten ze strikt worden uitgevoerd in overeenstemming met de beschrijving in deze Bedienings- & Onderhoudshandleiding en/of instructies van de fabrikant tijdens de technische acceptatietest.
Vanwege het gegenereerde magnetische veld mogen grote metalen voorwerpen niet in de buurt van het apparaat worden geplaatst. De machine kan de werking van elektronische apparaten (radio, tv, computer) in de buurt van de machine beïnvloeden, als gevolg van de hoge ingangsgevoeligheid van voornoemde apparaten. De beste plaats om de machine te gebruiken is het betonnen oppervlak dat niet bedekt is of bedekt is met een zeer dunne laag niet-geleidend materiaal.
5.4 Installatie op de plaats van gebruik
5.4.1 Algemene informatie
 ATTENTIE: De fabrikant raadt ten zeerste aan om het apparaat alleen in een industriële omgeving te installeren.
ATTENTIE: De fabrikant raadt ten zeerste aan om het apparaat alleen in een industriële omgeving te installeren.
De machine waarop deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding betrekking heeft, is ontworpen en gebouwd voor gebruik in een industriële omgeving voor het verwerken van transportbanden.
De ontwerpers van de machine hebben rekening gehouden met specifieke werkingsomstandigheden van de apparaten, d.w.z. hoge luchtvochtigheid, hoge temperatuur, stoom en stof, die geen invloed hebben op de werking van de machine, maar die strengere eisen stellen aan de uitvoering van preventieve programma's.
Het apparaat mag niet worden gebruikt in een explosiegevaarlijke omgeving, een zeer stoffige omgeving, een omgeving met een hoge vochtigheid en/of hoge temperatuur en de aanwezigheid van agressieve dampen (zuur, basisch, organisch of anorganisch, met een mogelijk of feitelijk bijtende werking).
De temperatuur van de werkomgeving moet tussen +10º C en +40º C liggen en de relatieve vochtigheid tussen 30% en 90%. Condensatie van vocht of agressieve stoffen op het oppervlak van de machine (of een van de onderdelen ervan) is niet toegestaan.
Het is vereist dat de amplitude van de temperatuur op lange termijn gedurende de dag in de werkruimte van de generator niet hoger is dan 10 ºC en in het geval van relatieve vochtigheid: 10%.
De bovenstaande clausule is niet van toepassing op de media of stoffen die worden gebruikt voor smering, conservering of niet-agressieve stoffen die worden gebruikt tijdens de productie/werking van het apparaat.
 ATTENTIE: Als er een groot verschil is tussen de buitentemperatuur en de temperatuur in de ruimte waar het apparaat is geïnstalleerd, moet het apparaat na 24 uur na montage in de ruimte worden opgestart.
ATTENTIE: Als er een groot verschil is tussen de buitentemperatuur en de temperatuur in de ruimte waar het apparaat is geïnstalleerd, moet het apparaat na 24 uur na montage in de ruimte worden opgestart.
5.4.2 Verlichting
De vereisten voor de minimale lichtsterkte stellen dat op het horizontale werkgebied een verlichtingssterkte van 300 lx aanvaardbaar moet zijn in ruimten waar mensen langere tijd verblijven, ongeacht of er visuele activiteiten worden uitgevoerd.
In het geval van visuele activiteiten met een hogere moeilijkheidsgraad dan gemiddeld en wanneer zeer comfortabel zicht vereist is, en wanneer de meerderheid van de gebruikers ouder is dan 40 jaar, moet de vereiste lichtsterkte hoger zijn dan het minimum, d.w.z. ten minste 500 lx.
5.4.3 Geluid
De machine produceert geen geluid van een niveau waarbij het gebruik van middelen of apparaten ter bescherming van het personeel vereist is.
We mogen echter niet vergeten dat alle werkomgevingen hun eigen geluidsemissies hebben, die van invloed kunnen zijn op het geluidsniveau dat de machine tijdens het gebruik produceert.
5.5 Verbindingsparameters
5.5.1 Elektrisch vermogen
Aansluiting: 3 x 480V; 50Hz (3P+N+PE), overstroombeveiliging met vertraagde eigenschappen. De installatie van de klant moet maatregelen voor bescherming tegen elektrische schokken conform EN 60204-1:2001 garanderen.
 ATTENTIE: Controleer altijd de gloeispanning na installatie van de buis - zie de technische gegevens van de buis.
ATTENTIE: Controleer altijd de gloeispanning na installatie van de buis - zie de technische gegevens van de buis.
5.5.2 Perslucht
Druk: 0,4 - 0,8 MPa, vereiste reinheidsklasse volgens ISO8573-1 4-4-4, verbruik: 70 nl per één cyclus.
 LET OP: Als de druk in het systeem van de eindgebruiker hoger is dan 0,8 MPa, moet deze worden verlaagd tot ongeveer 0,6 MPa met een reduceerventiel dat op de lasmachineaansluiting is gemonteerd.
LET OP: Als de druk in het systeem van de eindgebruiker hoger is dan 0,8 MPa, moet deze worden verlaagd tot ongeveer 0,6 MPa met een reduceerventiel dat op de lasmachineaansluiting is gemonteerd.
5.6 Verbindingsparameters
Afhankelijk van de complexiteit van het systeem en de kwalificaties en vergunningen van de medewerkers, wordt het aansluiten van de lasmachine op de plaats van gebruik uitgevoerd door door de besteller geselecteerde personen of door medewerkers van de technische dienst van de fabrikant, in samenwerking met het personeel van de besteller, tegen een meerprijs of kosteloos, hetgeen altijd wordt geregeld voordat de machine vanaf de locatie van de fabrikant aan de besteller wordt overgedragen.
Het is altijd nodig om te controleren of alle aansluitingen zijn uitgevoerd in overeenstemming met de documentatie van het apparaat.
Er moet worden vermeld dat voor de bovengenoemde taken de juiste kwalificaties van het personeel vereist zijn, waaronder toepasselijke licenties die door de juiste instanties zijn afgegeven.
Het is van toepassing op zowel gespecialiseerde kwalificaties als op afgeronde en geldige trainingen op het gebied van gezondheid en veiligheid op het werk, waaronder met name de risico's die deze taken met zich meebrengen.
6.0 Werking
6.1 De machine voorbereiden op gebruik - Eerste inbedrijfstelling
 ATTENTIE: Om het apparaat optimaal en veilig te gebruiken, moet u alle instructies in deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding zorgvuldig lezen en opvolgen.
ATTENTIE: Om het apparaat optimaal en veilig te gebruiken, moet u alle instructies in deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding zorgvuldig lezen en opvolgen.
 HET IS VERBODEN om werkzaamheden aan de lasmachine uit te voeren door personen die niet vooraf zijn opgeleid in het onderhoud van hoogfrequente machines en industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften met speciale aandacht voor mogelijke risico's die van de machine uitgaan.
HET IS VERBODEN om werkzaamheden aan de lasmachine uit te voeren door personen die niet vooraf zijn opgeleid in het onderhoud van hoogfrequente machines en industriële veiligheidsvoorschriften met speciale aandacht voor mogelijke risico's die van de machine uitgaan.
Als aan alle installatievereisten is voldaan en de in punt 5 beschreven taken zijn uitgevoerd, zijn wij gereed om de lasmachine voor het eerst in gebruik te nemen in de productieomgeving van de locatie van de besteller.
 ATTENTIE: De eerste inbedrijfstelling van de machine moet worden uitgevoerd in aanwezigheid van en onder toezicht van de vertegenwoordigers van de fabrikant.
ATTENTIE: De eerste inbedrijfstelling van de machine moet worden uitgevoerd in aanwezigheid van en onder toezicht van de vertegenwoordigers van de fabrikant.
6.2 Operationele vereisten - Algemene instructies en richtlijnen
Alle afstellingen en kalibraties die nodig zijn voor de correcte werking van de apparaatparameters zijn door de fabrikant uitgevoerd tijdens de montage en interne testprocedures. De algemene conformiteit met de contractuele technische eisen en de correcte werking van de machine worden bevestigd tijdens de technische oplevering, die plaatsvindt op de locatie van de fabrikant, in aanwezigheid van een vertegenwoordiger van de besteller en met gebruikmaking van originele, door de besteller geleverde grondstoffen voor het testen.
 LET OP: Vanwege de specifieke eigenschappen van de apparaten die hoogfrequente energie afgeven, is het noodzakelijk om bepaalde metingen uit te voeren op de plaats waar het apparaat op de locatie van de besteller in werking is. Om dezelfde reden is het zeer belangrijk dat het apparaat een vaste plaats van werking heeft.
LET OP: Vanwege de specifieke eigenschappen van de apparaten die hoogfrequente energie afgeven, is het noodzakelijk om bepaalde metingen uit te voeren op de plaats waar het apparaat op de locatie van de besteller in werking is. Om dezelfde reden is het zeer belangrijk dat het apparaat een vaste plaats van werking heeft.
VOOR DE BEDIENING ABSOLUUT NOODZAKELIJK IS OM TE CONTROLEREN:
- Effectiviteit van maatregelen ter bescherming tegen elektrische schokken;
- Voedingsspanning - waarde en juistheid van faseverbinding;
- Draairichting van de motor (indien van toepassing);
- Spanning gloeilamp;
 ATTENTIE: De lampspanning moet dezelfde zijn als gespecificeerd in het gegevensblad van het product - het is mogelijk om deze aan te passen met behulp van aftakkingen aan de primaire zijde van de gloeilamptransformator.
ATTENTIE: De lampspanning moet dezelfde zijn als gespecificeerd in het gegevensblad van het product - het is mogelijk om deze aan te passen met behulp van aftakkingen aan de primaire zijde van de gloeilamptransformator.
 ATTENTIE: Vanwege het specifieke karakter van het apparaat moet het personeel altijd worden gewaarschuwd en geïnformeerd over de hoge voedingsspanning van de anode van de lamp en het potentiële risico op dodelijke elektrische schokken door elektrische stroom met een spanning tot 8000 VDC.
ATTENTIE: Vanwege het specifieke karakter van het apparaat moet het personeel altijd worden gewaarschuwd en geïnformeerd over de hoge voedingsspanning van de anode van de lamp en het potentiële risico op dodelijke elektrische schokken door elektrische stroom met een spanning tot 8000 VDC.
 ATTENTIE: De lamp moet na de installatie ongeveer een uur worden voorverwarmd.
ATTENTIE: De lamp moet na de installatie ongeveer een uur worden voorverwarmd.
- Positie van de houder op de basis van de werktafel;
- Uitstoot van elektromagnetisch veld - na het instellen van de lasparameters, tijdens het lasproces;

 LET OP: Hoogfrequent lasmachine is de bron van niet-ionische elektromagnetische straling. Na installatie van de machine bij de koper moet de niet-ionische straling worden gemeten. De stralingsmetingen moeten worden uitgevoerd door een erkend bedrijf.
LET OP: Hoogfrequent lasmachine is de bron van niet-ionische elektromagnetische straling. Na installatie van de machine bij de koper moet de niet-ionische straling worden gemeten. De stralingsmetingen moeten worden uitgevoerd door een erkend bedrijf.
 ATTENTIE: De machine moet op een stevige werkplek werken, omdat bij omzetting een nieuwe meting van de niet-ionische stralingsintensiteit nodig is.
ATTENTIE: De machine moet op een stevige werkplek werken, omdat bij omzetting een nieuwe meting van de niet-ionische stralingsintensiteit nodig is.
 LET OP: Het is verboden voor mensen met een geïmplanteerde pacemaker om in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling te verblijven.
LET OP: Het is verboden voor mensen met een geïmplanteerde pacemaker om in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling te verblijven.
 ATTENTIE: De fabrikant raadt zwangere vrouwen of vrouwen die borstvoeding geven af om te werken in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling.
ATTENTIE: De fabrikant raadt zwangere vrouwen of vrouwen die borstvoeding geven af om te werken in de zone van actieve niet-ionische straling.
 BELANGRIJK: Als de hoogspanningscircuits per ongeluk zijn aangesloten terwijl de anode is losgekoppeld of als de generatorlamp defect is, moeten de hoogspanningsfiltercondensatoren worden ontladen door ze zeer kortstondig kort te sluiten met de behuizing.
BELANGRIJK: Als de hoogspanningscircuits per ongeluk zijn aangesloten terwijl de anode is losgekoppeld of als de generatorlamp defect is, moeten de hoogspanningsfiltercondensatoren worden ontladen door ze zeer kortstondig kort te sluiten met de behuizing.
 ATTENTIE: Alle activiteiten tijdens het opstarten en de metingen, wanneer het veiligheidsniveau lager is (geopende beveiligingsschermen, geblokkeerde sleutelschakelaars), moeten zo weinig mogelijk tijd in beslag nemen en het veiligheidsniveau van de volledige werking van de machine moet zo snel mogelijk worden gegarandeerd.
ATTENTIE: Alle activiteiten tijdens het opstarten en de metingen, wanneer het veiligheidsniveau lager is (geopende beveiligingsschermen, geblokkeerde sleutelschakelaars), moeten zo weinig mogelijk tijd in beslag nemen en het veiligheidsniveau van de volledige werking van de machine moet zo snel mogelijk worden gegarandeerd.
 ATTENTIE: Alle controle- en meetactiviteiten moeten worden uitgevoerd nadat is gecontroleerd of de schakelaars voor anodische spanningsaanpassing in de 0 - OFF positie staan (dit geldt niet voor het meten van de emissie van elektromagnetische velden).
ATTENTIE: Alle controle- en meetactiviteiten moeten worden uitgevoerd nadat is gecontroleerd of de schakelaars voor anodische spanningsaanpassing in de 0 - OFF positie staan (dit geldt niet voor het meten van de emissie van elektromagnetische velden).
 ATTENTIE: Alle controle- en meetactiviteiten mogen uitsluitend worden uitgevoerd door bevoegd personeel.
ATTENTIE: Alle controle- en meetactiviteiten mogen uitsluitend worden uitgevoerd door bevoegd personeel.
 HET IS ALTIJD VERBODEN om het lasproces te starten, d.w.z. de hoogspanning van de lamp in te schakelen, die de hoogfrequente spanning op de geïsoleerde houder van de elektrode initieert, wanneer het veiligheidsniveau van de werking van het apparaat is verlaagd.
HET IS ALTIJD VERBODEN om het lasproces te starten, d.w.z. de hoogspanning van de lamp in te schakelen, die de hoogfrequente spanning op de geïsoleerde houder van de elektrode initieert, wanneer het veiligheidsniveau van de werking van het apparaat is verlaagd.
De machine is aangepast om in de automatische cyclus te werken. De automatische modus is de standaardwerkwijze van het apparaat tijdens het productieproces.
Het hoogfrequent lasapparaat kan handmatig worden ingesteld.
Machinebedieners moeten altijd standaard werkkleding en antislipschoenen dragen.
De werkomgeving van het apparaat, de vloer en de handhouders en handgrepen moeten altijd schoon en vrij van verontreiniging, vet of modder zijn om het risico van uitglijden of vallen tot een minimum te beperken.
Gebruik de machine nooit zonder de vaste of mobiele beschermelementen. Controleer regelmatig of alle veiligheidsschermen en alle andere beschermingselementen goed gemonteerd zijn en goed functioneren.
Alleen bevoegde personen, die goed zijn opgeleid in de bediening van de machine en in Arbo & veiligheid, mogen direct contact hebben met de machine.
Elke bediener van het apparaat moet worden geïnstrueerd over de functies van de beveiligingselementen van de machine en het juiste gebruik ervan.
In de omgeving van het apparaat (ongeveer 1,5 m rond de generator en de pers) mogen zich geen voorwerpen bevinden die de werking van het apparaat kunnen verstoren. Dit gebied moet schoon worden gehouden en goed verlicht zijn.
Gebruik nooit de manipulators van het apparaat of flexibele buizen als houders. Onthoud dat elke onopzettelijke beweging van de manipulator van het apparaat per ongeluk het lasproces kan starten, parameters kan veranderen of zelfs kan leiden tot het uitvallen van de machine of beschadiging van de gereedschappen.
 HET IS VERPLICHT om de supervisor en/of het verkeerspersoneel op de hoogte te stellen van alle gevallen van onjuiste bediening van het apparaat.
HET IS VERPLICHT om de supervisor en/of het verkeerspersoneel op de hoogte te stellen van alle gevallen van onjuiste bediening van het apparaat.
6.3 Bedieningselementen en indicatoren beschikbaar voor de operator
Alle bedieningselementen en indicatoren van de lasser zijn gemakkelijk te vinden op de constructie of op het bedieningspaneel. Alvorens aan het werk te gaan, moet de bediener van de machine zich vertrouwd maken met de plaatsing van de bedieningselementen en indicatoren op de machine en met de functies die ze bedienen.
De volledige lijst van de bovengenoemde bedieningselementen en indicatoren die beschikbaar zijn voor de operator is hieronder bijgevoegd:
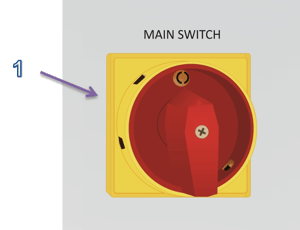
- HOOFDSCHAKELAAR - een schakelaar (Afb.3) voor het in- of uitschakelen van de elektriciteitsvoorziening. 1-AAN positie betekent dat de schakelaar is ingeschakeld, terwijl de 0-UIT betekent dat de schakelaar is uitgeschakeld.

Fig.5. De indeling van de bedieningselementen en indicatoren op het bedieningspaneel I: 2 - POWER; 3 - TWEEHANDSBEDIENING UIT/AAN; 4 - HF; 5 - HF UIT/AAN; 6 - USB; 7 - ETHERNET; 8 - RESTART; 9 - STOP; 10 - JOISTIC; 11 - START; 12 - elektrode omhoog; 13 - linksom draaien; 14 - rechtsom draaien; 14 - elektrode omlaag.
-
POWER - een indicator die wit knippert als het apparaat is aangesloten op de voeding (Fig.5).
-
TWEEHANDSBEDIENING UIT / AAN - een sleutelschakelaar (Afb.5) voor het activeren van de machinebedieningsmodus voor twee handen. De schakelaar heeft betrekking op de drukknoppen op de zwarte handgrepen en de elektrode voor de hef- en daalfuncties in de joystick. De schakelaar in de stand ON - betekent dat om de drukknoppen te activeren, beide drukknoppen voor dezelfde functie moeten worden ingedrukt, waarna de joystick zijn hef- en daalfunctie voor de elektrode verliest. De schakelaar in de OFF-stand geeft aan dat bediening met één drukknop mogelijk is en dat de elektrode met de joystick omhoog en omlaag wordt gebracht.
 LET OP!!! Schakelen uit de tweehandig controle stand maakt de werk operaties eenvoudiger; maar het aanzienlijk verhoogt ongeval risico. Alleen een geautoriseerd en correct getraind, verantwoordelijke persoon moeten hebben de sleutel voor de aan/uit-schakelaar.
LET OP!!! Schakelen uit de tweehandig controle stand maakt de werk operaties eenvoudiger; maar het aanzienlijk verhoogt ongeval risico. Alleen een geautoriseerd en correct getraind, verantwoordelijke persoon moeten hebben de sleutel voor de aan/uit-schakelaar. -
HF - als de indicator geel knippert, betekent dit dat het HF-lasproces is ingeschakeld (Fig.5).
- HF UIT/AAN - een schakelaar waarmee de HF-stroom kan worden vrijgegeven of vastgezet (als deze in UIT positie betekent dit dat de HF-las niet kan worden uitgevoerd)
 Zolang het de standaard lasprocedure betreft, is de HF UIT/AAN schakelaar moet in OP positie.Als de HF OFF/ON-schakelaar in de OFF-stand staat, betekent dit dat de duty cycle kan worden uitgevoerd zonder de HF-stroom vrij te geven.
Zolang het de standaard lasprocedure betreft, is de HF UIT/AAN schakelaar moet in OP positie.Als de HF OFF/ON-schakelaar in de OFF-stand staat, betekent dit dat de duty cycle kan worden uitgevoerd zonder de HF-stroom vrij te geven. -
USB-sleuf - een sleuf (Fig.5) waarin een USB-geheugenkaart voor de opslag van lasparameters en de geschiedenis van berichten kan worden geplaatst; hiermee kunnen ook de recepten worden opgeslagen die in het HMI-paneel zijn opgeslagen.
-
ETHERNET-sleuf - een sleuf (Afb.5) waarin de Ethernet-kabel wordt aangesloten als er een machinediagnose online moet worden uitgevoerd, zodat er internettoegang tot de machine mogelijk is.
-
RESTART - de blauwe drukknop (Afb.5) die moet worden gebruikt om het bedienings- en beveiligingssysteem van de machine opnieuw te starten wanneer het alarmbericht op het HMI-paneel wordt weergegeven.
-
STOP - de zwarte drukknop (Fig.5) is bedoeld voor het uitschakelen van het hoogfrequent lassen.
-
JOYSTIC - joystick (Afb.5, Afb.7) gebruikt voor het voor- en achteruit bewegen van de laselektrode en het naar links of rechts rijden van de machine met een langzame start voor eenvoudige positionering. Met de joystick kan de elektrode echter alleen omlaag of omhoog worden gebracht als de tweehandenmodus is geactiveerd. Er zijn twee rijsnelheden:
- "langzaam" - (Afb. 6 - A, C, E, G) de snelheidsverplaatsing wordt bepaald door de parameter in het servicemenupaneel HMI - Toerental aandrijving MANUAL - SLOW.
- Snel" - (Afb. 6 - B, D) snelheid wordt bepaald door de parameter op het servicemenupaneel HMI - Toerental aandrijving HANDMATIG - SNEL.
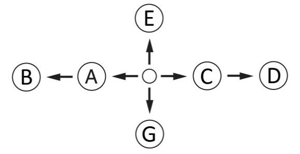
Fig. 6. Plaats de joystick:
A - langzaam verplaats van de hoofd naar de links, B - snel verplaats van de hoofd naar de links,
C - langzaam verplaats van het hoofd naar het rechts,
D - snel verplaats van de kop naar de rechts,
E - elektrode omhoog,
F - elektrode omlaag,
-
START - de groene drukknop (Fig.5) wordt gebruikt voor het inschakelen van het proces van hoogfrequent lassen.
-
 op pijl - twee drukknoppen op de zwart handgrepen op de bedieningspaneel (Fig. 5, Fig. 7) tweedehands voor activeren de elektrode in bovenste positie. Wanneer de tweehandig operatie stand is geactiveerd, beide drukknoppen moeten zijn tegelijkertijd ingedrukt
op pijl - twee drukknoppen op de zwart handgrepen op de bedieningspaneel (Fig. 5, Fig. 7) tweedehands voor activeren de elektrode in bovenste positie. Wanneer de tweehandig operatie stand is geactiveerd, beide drukknoppen moeten zijn tegelijkertijd ingedrukt -
 links pijl - twee drukknoppen op de zwart handgrepen op de bedieningspaneel (Fig. 5, Fig. 7) waardoor de machine naar verplaatsen links. Wanneer de twee handen operatie stand is geactiveerd, beide drukknoppen moet zijn tegelijkertijd ingedrukt.
links pijl - twee drukknoppen op de zwart handgrepen op de bedieningspaneel (Fig. 5, Fig. 7) waardoor de machine naar verplaatsen links. Wanneer de twee handen operatie stand is geactiveerd, beide drukknoppen moet zijn tegelijkertijd ingedrukt. -
 rechts pijl - twee drukknoppen op de zwart handgrepen op de bedieningspaneel (Fig. 5, Fig. 7) vereist waardoor de machine naar verplaatsen rechts. Wanneer de tweehandig operatie stand is geactiveerd, beide drukknoppen moet tegelijkertijd worden ingedrukt.
rechts pijl - twee drukknoppen op de zwart handgrepen op de bedieningspaneel (Fig. 5, Fig. 7) vereist waardoor de machine naar verplaatsen rechts. Wanneer de tweehandig operatie stand is geactiveerd, beide drukknoppen moet tegelijkertijd worden ingedrukt. -
 naar beneden pijl - twee drukknoppen op de zwart handgrepen op de operator paneel (Fig. 5, Fig. 7) tweedehands voor activeren de elektrode in lagere positie. Wanneer de tweehandig operatie stand is geactiveerd, beide drukknop moet zijn persen bij de dezelfde tijd.
naar beneden pijl - twee drukknoppen op de zwart handgrepen op de operator paneel (Fig. 5, Fig. 7) tweedehands voor activeren de elektrode in lagere positie. Wanneer de tweehandig operatie stand is geactiveerd, beide drukknop moet zijn persen bij de dezelfde tijd.
Fig. 7. De opstelling van de bedieningselementen en indicatoren een het bedieningspaneel:
12 - elektrode omhoog;
13. draai naar links; 14. draai naar rechts;
14. elektrode omlaag
15. ANODE STROOM;
16. ELEKTRODETEMPERATUUR;
17. NOODSTOP;
-
ANODE STROOMMETER - de paneelampèremeter (Fig.5) wordt verondersteld de waarde van de stroomsterkte in het anodecircuit aan te geven en moet de operator in staat stellen het lasproces visueel te inspecteren (de vollastkarakteristieken van de generator).
-
ELECTRODE TEMPERATUUR - een thermoregulator (Fig.6 ) gebruikt voor de regeling van de temperatuur van de elektrode . Deze regelt het systeem dat de temperatuur van de elektrode stabiliseert. Een drukknop, Temp Regulation in het Hoofdscherm venster van het touch-panel wordt gebruikt om de temperatuur stabilisatie functie te activeren. De handleiding die verwijst naar de E5CC temperatuur is te vinden in de bijlage.

Afb. 8 Bedieningspaneel;
18.- NOODSTOP;
19. - HMI; - NOODGEVALLEN STOP - de rood paddestoelhoofd drukknop (Afb.5) het is a knop dat moet zijn ingedrukt alleen wanneer de functies van de machine nodig naar zijn stopgezet onmiddellijk of wanneer alles met betrekking tot de machine functies of de operator omgeving houding a bedreiging naar de productie of veiligheid.
 De NOODGEVALLEN STOP knop moet niet zijn overmatig gebruikt, het is vermeend naar zijn tweedehands alleen in geval van noodgevallen.
De NOODGEVALLEN STOP knop moet niet zijn overmatig gebruikt, het is vermeend naar zijn tweedehands alleen in geval van noodgevallen. -
HMI PANEL - het aanraakgevoelige paneel (Fig.5) moet gebruikt worden voor het wijzigen van de instelparameters van de machine en moet een betrouwbare informatiebron worden over de huidige toestand van de lasmachine. Zie hoofdstuk 6.6. voor meer informatie over het uitvoeren van de onderhoudsprocedure die van toepassing is op het aanraakgevoelige paneel.
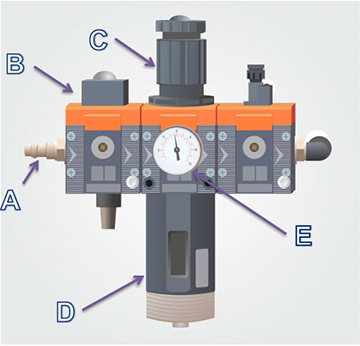
Fig.9. HET GEcomPROMPSEERDE LUCHT VOORBEREIDING SYSTEEM.
-
VOORBEREIDINGCOMPRESSED AIR SYSTEEM (Afb.9) - bestaat uit:
A. De persluchtaansluiting waarop de persluchtslang moet worden aangesloten. De slang moet het systeem voorzien van perslucht van 0,4 tot 0,8 MPa;
B. De handmatig bediend gecomprimeerd lucht uitschakeling ventiel (in bestel om de klep te openen - draaien het naar de links en stel naar AAN-stand; a naar rechts - de OFF-stand - de klep gesloten is);
C. De gecomprimeerd lucht terminal in die de gecomprimeerd lucht slang moet zijn verbonden. De slang is vermeend naar bieden de systeem met de perslucht bereik van 0,4 tot 0.8 MPa; 0,6 M
 Het drukniveau in het pneumatische systeem is nooit hoger dan het drukniveau dat de machine aandrijft.
Het drukniveau in het pneumatische systeem is nooit hoger dan het drukniveau dat de machine aandrijft.
D. Het persluchtfilter samen met het condenswatervrijgavemechanisme;
E. De manometer die het drukniveau in het persluchtsysteem van de machine aangeeft;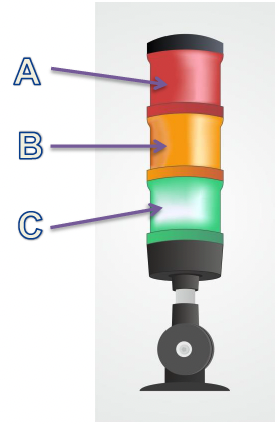
Fig.10. De seinlampkolom:
Een - rode kleur;
B - oranje kleur;
C - kleur groen
21. SIGNAALLICHT COLUMN (Afb.10):
A. De rode kleur wijst op een storing en op de dezelfde tijd het alarm bericht moet worden weergegeven op het HMI aanraakgevoelige paneel.
 De alarm massages zijn verwijderd en de rood licht op de signaallichtkolom stopt met knipperen wanneer de RESTART knop wordt ingedrukt.
De alarm massages zijn verwijderd en de rood licht op de signaallichtkolom stopt met knipperen wanneer de RESTART knop wordt ingedrukt.
In als de inspanningen tevergeefs en het alarm bericht niet is verwijderd op de RESTART knop had is geweest ingedrukt dus het zou kunnen betekenen dat de oorzaak van storing optreden had niet nog niet verwijderd.
Zie hoofdstuk 6.6.2. voor meer informatie toepassen op de alarmmassages.
B. De oranje kleur geeft aan dat het lasapparaat met hoge frequentie begint te werken.
C. De groene kleur geeft aan dat de machine klaar is om te werken.
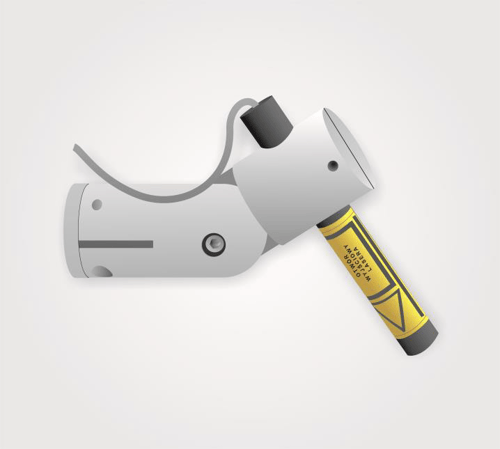

Afb. 11. Een van de laser indicatoren geplaatst op de rechter zijde van de laskop .
22. Lasers geïnstalleerd op de laskop (Fig. 11) gebruikt voor de projectie van de laslijn op het gelaste/afgedichte materiaal. Handig voor het plaatsen en positioneren het materiaal langs de laslijn . Ze worden rechtstreeks vanaf het HMI touchpanel ingeschakeld.
|
|
|
De laser is om te markeren de lijn OP de MATERIAAL in de positie van de elektrode en zijn houder omhoog. De laser DOET NIET / MOET NIET schijnen op de voorkant of achterkant van de elektrode xml-ph-003
Laserregulatieprocedure:
1. Leg het materiaal op tafel en laat de houder met de elektrode op tafel zakken,
2. Trek met een markeerstift een lijn langs de voorkant en eventueel de achterkant van de elektrode (als er twee lasers aan één kant zijn gemonteerd),
3. Til de elektrode op en stel de laser(s) in op de getekende lijnen, eventueel met een zodanige afwijking van deze lijnen als de operator de folie wil positioneren,
4. Zorg ervoor dat het materiaal niet beweegt.
|
|
|

Fig. 12 De bumper
23. De zijbumpers geïnstalleerd op beide zijden van de laskop (Fig.9 ), voorkomen dat de machine in botsing komt met iemand of iets. Elke schok op een bumper zal resulteren in de onmiddellijke uitschakeling van het aandrijfsysteem van de machine ; dit zal worden aangegeven door de boodschap: OPEN xml-ph-

Fig. 13 Noodbeweging
23.Noodverplaatsing - de schakelaar wordt gebruikt om te wijzigen de bedrijfsmodus . In het geval van een obstakel en stoppen op het. De schakelaar deactiveert de zijbumpers en maakt het mogelijk de verlaten van een obstakel Na het schakelen van de schakelaar naar positie I op de HMI, de "noodgevallen trips" venster verschijnt in die de gebruiker heeft de optie van met behulp van de navigatie pijlen naar passeren de hoofd links of Door de schakelaar in de stand 0 te zetten activeert de stootranden aan de zijkant en herstelt de correcte werking van de machine .
|
|
|
 LET OP! Aangezien het bovengenoemde systeem feilloos moet werken, wordt sterk aanbevolen om de hoogtebegrenzer zo in te stellen dat deze de onderste positie van de elektrode aangeeft. Een onjuiste instelling van de hoogteregelingsschuif van de eindschakelaar kan leiden tot zowel een zelfgeactiveerde noodheffing van de elektrode als het verschijnen van de volgende alarmmelding op het display van de HMI: NOODELEKTRODE OMHOOG.
LET OP! Aangezien het bovengenoemde systeem feilloos moet werken, wordt sterk aanbevolen om de hoogtebegrenzer zo in te stellen dat deze de onderste positie van de elektrode aangeeft. Een onjuiste instelling van de hoogteregelingsschuif van de eindschakelaar kan leiden tot zowel een zelfgeactiveerde noodheffing van de elektrode als het verschijnen van de volgende alarmmelding op het display van de HMI: NOODELEKTRODE OMHOOG.Eindschakelaars voor de hoogte van de elektrode:
- bovengrens schakelaar - wanneer ingeschakeld (Afb. 14-) A) geeft de bovenste elektrode positie aan. Aanpassing van de schuif , die de schakelaar activeert, moet gedaan worden wanneer de maximale bovenste positie van de elektrode te veranderd is. Als de grenswaarde schakelaar te hoog wordt gezet, zal niet op in de bovenste elektrodepositie - de lascyclus zal niet worden afgerond en de machine aandrijving cyclus niet mogelijk zijn. Als aan de andere hand, het is te laag - zal de elektrode niet worden verhoogd tot een voldoende hoogte na de las cyclus en kan het gelaste materiaal tijdens de aandrijving vangen, wat schade veroorzaakt.
- Onderste grenswaarde schakelaar - wanneer uitgeschakeld (Afb. 14-)B) geeft de onderste elektrode positie boven de werk tafel. Instelling van de schuif op deze schakelaar moet worden uitgevoerd elke keer als de elektrode is vervangen (wanneer de nieuwe elektrode is van een hoogte anders van de vorige 1 ) en wanneer er een significante verandering is in de dikte van het gelaste materiaal. De onderste eindschakelaar is ook een element van het systeem dat de handen van de operator beschermt tegen verplettering . Als de afstelling niet correct wordt uitgevoerd, zal de antikreukfunctie (ZTG Anti-CRUSH) geactiveerd worden waardoor de automatisch van de elektrode in de bovenste positie wordt getild. De eindschakelaar moet op een hoogte worden geplaatst die ervoor zorgt dat het rolwiel van de schakelaar wordt ingedrukt door de onderste schuifknop van de hoogte van de elektrode die zich bevindt op de staaf vanaf het moment dat de elektrode het lasmateriaal raakt. (Afb. 14- B).
Afb. 14 Eindschakelaars die de positie van de elektrode aangeven:
A - bovenste positie;
B - lagere positie.
Aanpassing procedure en het bepalen van de juiste hoogte van de onderste eindschakelaar:
- plaats het te lassen materiaal op de werktafel,
- plaats de elektrode in de gereedschapshouder en zet vast,
- laat de elektrode houder met de elektrode op het materiaal zakken, zodanig dat de elektrode net het raakt zonder enige druk (laat een ruimte van maximaal 5mm / 1/8inch); laat in deze positie staan.
- zet de onderste metalen schuif op de stang in de stand waarbij de onderste eindschakelaar wordt uitgeschakeld (de schakelwals zit direct op de schuif (Fig. 14- B),
- als het niet mogelijk is om de metalen geleider op de juiste hoogte in te stellen vanwege de trapsgewijze instelling (elke 15 mm), draai dan de twee schroeven los die de eindschakelaar vasthouden en breng deze in een vergrendelpositie met de rol naar de onderste metalen geleider van de elektrodehoogte (Afb. 14-B), draai vervolgens de schroeven vast.
- til de handgreep met de elektrode naar boven,
- Als het niet mogelijk is om de indicator op de juiste hoogte in te stellen vanwege de trapsgewijze instelling (om de 15 mm), draai dan de twee schroeven los waarmee de schakelaar is bevestigd en verplaats hem in een zodanige positie dat de rol naar de onderste indicator van de elektrodehoogte gaat (Fig. 14- B), draai vervolgens de schroeven vast.
 LET OP! Manipulatie met de eindschakelaar die de onderste positie van de elektrode aangeeft, is strikt verboden. Het negeren van de waarschuwing van de fabrikant kan leiden tot ernstige machine-uitval en als gevolg daarvan tot ernstig lichamelijk letsel.
LET OP! Manipulatie met de eindschakelaar die de onderste positie van de elektrode aangeeft, is strikt verboden. Het negeren van de waarschuwing van de fabrikant kan leiden tot ernstige machine-uitval en als gevolg daarvan tot ernstig lichamelijk letsel.
Op bovendien de machine heeft geweest uitgerust met een extra elektrode, waardoor lassen zonder de gebruik van aarding elektrode. Na installatie dit soort van elektrode in de houder en beginnen naar te laten zakken te laten zakken, een extra limiet schakelaar geactiveerd die de beweging van de aardings elektrode.
6.5 Bedrijfstemperatuurregelaar E5CC
Temperatuurregeling eenheid wordt gebruikt om controle de temperatuur van de elektrode. Het programmeren van de juiste temperatuur van de elektrode is nodig om het verloop van het lasproces te corrigeren. De temperatuur moet experimenteel gekozen worden. Hieronder staat een beschrijving van het display en bedieningspaneel temperatuurregeling (Afb. 15).

Fig. 15. Display en bedieningspaneel thermoregulerend.
- Display met vier cijfers (wit) waarop de werkelijke temperatuur waarde wordt weergegeven. In de parameterinstellingen modus wordt het huidige teken van de bewerkte parameter weergegeven.
- Display met vier cijfer (groen) die weergegeven werkelijke bestelde temperatuurwaarde. In parameter instelling modus display huidige werkelijke waarde van bewerkte parameter.
- Bedieningsknoppen:
 verplaatsen knop. Druk op deze knop oorzaak naar bewerken volgende cijfer van bewerkt nummer.
verplaatsen knop. Druk op deze knop oorzaak naar bewerken volgende cijfer van bewerkt nummer.
 - knop "DOWN oorzaak laag bewerkt cijfer per één.
- knop "DOWN oorzaak laag bewerkt cijfer per één.
 - toets "UP" om het bewerkte cijfer te verhogen door één.
- toets "UP" om het bewerkte cijfer te verhogen door één.
 In de parameter bewerken ga naar de volgende parameter
In de parameter bewerken ga naar de volgende parameter
 Lang druk op deze knop (min 3sec.) oorzaak pas naar editie stand van verlaten parameter. Als systeem werk in editie modus, druk op knop oorzaak terugkeer naar de hoofdvenster
Lang druk op deze knop (min 3sec.) oorzaak pas naar editie stand van verlaten parameter. Als systeem werk in editie modus, druk op knop oorzaak terugkeer naar de hoofdvenster
BESTURINGSINSTELLINGEN - GERANGSCHIKT TEMPERATUURWAARDE
Naar veranderen besteld waarde nodig naar korte druk op knop (Fig. 15)  of
of  . Hierdoor wordt de parametereditiemodus geactiveerd. Het beschikbare nummer dat wordt bewerkt, wordt aangegeven door snel knipperen. Met de knoppen "UP" (Omhoog)
. Hierdoor wordt de parametereditiemodus geactiveerd. Het beschikbare nummer dat wordt bewerkt, wordt aangegeven door snel knipperen. Met de knoppen "UP" (Omhoog)  of "DOWN
of "DOWN  stel de waarde van dit getal in en druk vervolgens op de knop "move
stel de waarde van dit getal in en druk vervolgens op de knop "move  , die naar de volgende positie op editie gaat.
, die naar de volgende positie op editie gaat.
6.6 Het aanraakgevoelige paneel van de HMI programmeren en bedienen
 LET OP! Elke waarde van de parameter afgebeeld op de afbeeldingen van deze handleiding is willekeurig genomen en moet door de operator van de machine genegeerd worden. De waarden van de parameters moeten worden afgeleid uit de praktijkervaring van de gebruiker, omdat ze sterk kunnen variëren afhankelijk van het type lasmateriaal of de gebruikte instrumenten.
LET OP! Elke waarde van de parameter afgebeeld op de afbeeldingen van deze handleiding is willekeurig genomen en moet door de operator van de machine genegeerd worden. De waarden van de parameters moeten worden afgeleid uit de praktijkervaring van de gebruiker, omdat ze sterk kunnen variëren afhankelijk van het type lasmateriaal of de gebruikte instrumenten.
![]() In het HMI-paneel worden alle bewerkbare waarden van de parameters weergegeven op een witte achtergrond. Om een parameter weer te geven, moet de gebruiker op de waarde ervan drukken, waardoor het toetsenbord op het scherm wordt geopend. Gegevens kunnen worden opgeslagen door op de Enter-toets te drukken.
In het HMI-paneel worden alle bewerkbare waarden van de parameters weergegeven op een witte achtergrond. Om een parameter weer te geven, moet de gebruiker op de waarde ervan drukken, waardoor het toetsenbord op het scherm wordt geopend. Gegevens kunnen worden opgeslagen door op de Enter-toets te drukken.
6.6.1 Aansluiting op stroombron
Kort nadat de machine op een voedingsbron is aangesloten, verschijnt op het display van de HMI een alarmvenster met het volgende bericht:
#A001 NOODSTOP
#K001 DRUK OP DE HERSTARTKNOP
Volgens deze situatie moet de machine opnieuw worden opgestart, dus moet de blauwe RESTART-toets worden ingedrukt. Vervolgens moeten we 30 seconden wachten tot de machine klaar is voor het werk en in de stand-bymodus gaat die we kennen door de volgende feiten: een lampje in de lichtsignaalkolom knippert groen en de voortgangsbalk die wordt weergegeven in het hoofdvenster van de HMI knippert groen. Als de alarmmassage niet van het display van de HMI verdwijnt, zie hoofdstuk 0.
6.6.2 Alarmmeldingen
Als er een storing optreedt in de machine, als een van de beveiligingssystemen wordt ingeschakeld of als er andere afwijkingen in de werking van de machine worden gedetecteerd, wordt er een van de alarmberichten weergegeven op het aanraakgevoelige paneel van de HMI. Alle alarmmeldingen worden gewist met behulp van de RESTART-toets .De soorten alarmmassages:
#A001 NOODGEVAL STOP - dit soort bericht wordt weergegeven wanneer:
- de machine is ingeschakeld - het veiligheidscircuit van de machine moet altijd gecontroleerd worden wanneer de RESTART toets wordt ingedrukt,
- de rode paddestoelkop NOODOPSTELLING STOP drukknop werd ingedrukt en is vastgelopen . Het moet losmaken door zijn hoofd naar rechts te draaien.
#A002 TUBE TEMPERATURE - dit type van massage betekent dat ofwel de travelling-wave tube cooling niet bestaat of dat het koelsysteem defect is en het wordt weergegeven wanneer:
- de zekeringen die zijn worden verondersteld te beschermen de voeding voeding circuit van de ventilator die de loopgolf buis moet afkoelen, zijn losgekoppeld;
- de contactor die moet activeren de ventilator die moet afkoelen de buis is uitgeschakeld of beschadigd;
- de buis thermisch bescherming systeem wordt in operatie die betekent dat de reisgolf buis kreeg verwarmd op naar te hoog temperatuur en als een resultaat van de buis bandschoot pin die had zijn geweest aangesloten naar de grens schakelaar door een Het snoer is losgesoldeerd.
Fig.16. Het thermische beschermingssysteem van de buis.
Een splitpen wordt aan een buisband gesoldeerd met behulp van soldeer met een smeltpunt dat veel lager ligt dan het smeltpunt waarbij de buis oververhit raakte (beschadigd raakte). Als de temperatuur van de lamp te hoog oploopt, zal de splitpen uit de band vallen en als gevolg daarvan zal de eindschakelaar worden geactiveerd, tegelijkertijd zal de alarmmelding worden weergegeven en zal de voeding voor een gloed in de buis worden afgesneden. Vervolgens moet de oorzaak van de oververhitting worden weggenomen.
 LET OP! Het snoer mag aan geen enkel ander onderdeel van de machine worden bevestigd dan aan de splitpen van de band die op de buis is geschroefd. Het negeren van deze waarschuwing kan leiden tot een blokkering van de eindschakelaar, wat kan leiden tot oververhitting van de loopgolfbuis en daardoor tot beschadiging.
LET OP! Het snoer mag aan geen enkel ander onderdeel van de machine worden bevestigd dan aan de splitpen van de band die op de buis is geschroefd. Het negeren van deze waarschuwing kan leiden tot een blokkering van de eindschakelaar, wat kan leiden tot oververhitting van de loopgolfbuis en daardoor tot beschadiging.
![]() If the cotter pin gets separated from the band than the band should be taken off from the tube, the pin should be soldered to the band with the standard solder used in electronic engineering (Melting point < 190oC) zodat het gerepareerde deel weer aan de buis bevestigd kan worden.
If the cotter pin gets separated from the band than the band should be taken off from the tube, the pin should be soldered to the band with the standard solder used in electronic engineering (Melting point < 190oC) zodat het gerepareerde deel weer aan de buis bevestigd kan worden.
De oververhitting van de buis kan worden veroorzaakt door:
- het vuil in de generator of in de buisradiator;
- het uitvallen van de buiskoelventilator of het uitvallen van het voedingssysteem van de ventilator;
- door verstopping van de ventilatieopeningen van de machine of door te veel vuil dat wordt opgevangen door de filters in de ventilatieopeningen;
- de te hoge omgevingstemperatuur.
#A003 ANTIFLASH - dit type massage betekent dat het beschermingssysteem tegen een vlamboogoverslag tijdens het lassen in werking is getreden - controleer vanwege deze melding of de isolatiemat, het lasmateriaal of de laselektrode niet beschadigd zijn.
#A004 ANODE OVERLOAD - deze melding betekent dat de anodestijgingslimiet werd overschreden, zodat de parameters die van toepassing zijn op de stroom die vrijkomt bij het lassen moeten worden aangepast.
#A005 GRIDOVERLOAD - dit bericht betekent dat de netstijgingslimiet werd overschreden, zodat de parameters die van toepassing zijn op het vermogen dat in las wordt vrijgegeven, moeten worden aangepast.
#A006 LAGE LUCHTDRUK - deze melding betekent dat er te weinig luchtdruk is of dat het luchtdrukniveau te laag is in het pneumatische systeem. Zorg ervoor dat de slang die de perslucht levert is aangesloten op de machine of dat het niveau van de perslucht juist is en pas vervolgens met behulp van de drukreduceerventielregelaar die zich in het persluchtvoorbereidingssysteem bevindt de druk in de machine aan tot het juiste niveau.
#A008 ELECTRODE IS NIET IN BOVENSTE POSITIE -. het bericht wordt weergegeven als de laselektrode niet in de bovenste positie na inschakelen van de machine. Controleer de dichtheid van van het pneumatische systeem en de juiste instelling van de eindschakelaar die de bovenste positie aangeeft.
#A011 ELECTRODE TEMPERATUUR - dit bericht geeft aan dat de instelwaarde temperatuur van de elektrode op de thermoregulator is overschreden - de machine zal uitgeschakeld worden in de noodmodus . U moet 1 wachten tot de elektrode is afgekoeld en controleer dan of de instelling temperatuur op de temperatuurregelaar te hoog is. Een andere mogelijke optie is dat het warme circuit van de elektrode defect is geraakt . In zo'n geval moet contact worden opgenomen met de service van de fabrikant .
#A013 LASSEN PARAMETERS NIET GEREIKT - de besturingssoftware van de machine bevat een algoritme dat controleert of elke gedeeltelijke las correct is uitgevoerd . Als, tijdens het lassen, de parameters ingesteld uit niet zijn bereikt of als het lassen is gestopt voordat de taak is voltooid, zal het bovenstaande bericht worden weergegeven. De kwaliteit van de las wordt dan gecontroleerd en als niet voldoende is, moet de taak worden herhaald .
#A019 SENSOR / DRIVE ERROR - ELECTRODE OMLAAG - het alarmbericht zal worden weergegeven wanneer, na het bedienen van de klep spoel, de controller geen bevestiging ontvangt van de sensor die het bereiken van van de onderste positie binnen 15 seconden bevestigt. Controleer of de sensor niet heeft bewogen of controleer of het pneumatische systeem dicht bij de actuator is.
#A020 SENSOR / DRIVE ERROR - ELECTRODE OMHOOG - het alarmbericht zal worden weergegeven wanneer, na het bedienen van de klepspoel , de controller binnen 15 seconden geen bevestiging van de sensor ontvangt dat de bovenste positie is bereikt. Controleer of de sensor niet bewogen heeft of controleer of het pneumatische systeem zich dicht bij de actuator bevindt.
#A032 START CAPACITOR POSITION NOT ACHIVED - het bericht zal worden weergegeven als de condensatoren niet de vooraf ingestelde positie binnen 15 seconden bereiken. Controleer de aandrijving van de condensator .
#A034 NOODGEVAL ELECTRODE OMHOOG - deze melding wordt weergegeven toen de elektrode houder die was werd neergelaten op de werktafel stuitte op een obstakel op zijn weg en het beveiligingssysteem tegen knellend gevaar in praktijk werd gebracht. obstakel op zijn weg en het beveiligingssysteem tegen knellend gevaar in gebruik werd genomen . Zorg ervoor dat er niets tussen de elektrode en het werk tafel. Als de alarmmelding niet verdwijnt de aanpassing van de schakelaar limiet aangeeft de onderste elektrode positie moet worden uitgevoerd. Zie hoofdstuk 6.4. voor meer informatie het toepassen van op de afstelprocedure van de schakelaar grenswaarde .
#A035 CHECK RESET CIRCUIT IN SAFETY RELAY - betekent dat het veiligheidscircuit van de machine waarschijnlijk beschadigd is. In een dergelijk geval moet contact worden opgenomen met de service van fabrikant .
#A046 CURRENT NOT IN TOLERANCE DURING WELDING - dit bericht zal worden weergegeven als de huidige waarde niet kan worden bereikt operaties. Het algoritme controleert of de anode stroom is voldaan. De verkregen anode stroom moet zijn binnen +/- van de tolerantie bereik van de anode stroom waarde voor een gegeven percentage van de tijd voor de duur van het lassen, gespecificeerd in het servicevenster na het kiezen van Lasproces controle optie.
#A047 DOWN FORCE NOT IN TOLERANCE DURING THE WELDING -dit bericht wordt weergegeven als, tijdens lassen, de huidige neerwaartse kracht buiten het tolerantiebereik valt dat is opgegeven in het Service venster na het kiezen van Lasproces controle optie.
#A053 NOODGEVAL REMMEN - Dit bericht wordt weergegeven wanneer de veiligheidsschakelaar wordt ingedrukt. Wanneer de schakelaar paddenstoel in een noodgeval wordt geactiveerd, zal de kop plotseling - en met geweld - remmen.
#A054 VEILIGHEID VALVE SCHADE - Dit bericht wordt weergegeven wanneer de sensor (gemarkeerd met het symbool 10B1 op het elektrische diagram) van bevestiging zuiger klep in de juiste positie wordt geactiveerd . Deze sensor bevindt zich op de veiligheidsklep (aangeduid met het symbool 1V3 op het elektrisch schema). Als de zuiger van veiligheidsklep niet de juiste positie bereikt, betekent dit dat de klep niet werkt xml-ph-0030
#A055 SERVO ALARM - dit signaleert een fout in de Y-as aandrijving. Start de machine opnieuw op en, als de melding niet verdwijnt, controleer het alarm nummer dat op de servo weergeeft en controleer de beschrijving in de xml-ph-003
#A056 LAGE LUCHT DRUK IN ONDERSTEUNENDE CYLINDERS - betekent dat luchtdruk in de servomotoren die de elektrode ondersteunen te te laag is waardoor een snelle daling van de elektrode en het raken xml-ph-0030@dee kan veroorzaken Aanpassing van de persluchtdruk in het circuit van deze servomotoren moet worden uitgevoerd.
#A057 WELDING POSITIE NIET GEREIKT - het alarm bericht zal worden weergegeven wanneer, na het regelen van de klep spoel, de controller niet bevestiging ontvangt van de sensor bevestiging het bereiken van van de ingestelde positie binnen 8 seconden. Controleer of de sensor niet heeft bewogen of controleer de dichtheid van het pneumatische systeem bij de actuator.
#A058 DE ELEKTRODE IS NIET PLAATSEN IN EEN ONDERSTE POSITIE - het alarm bericht zal worden weergegeven als de START knop wordt ingedrukt en de elektrode is niet in de neerwaartse positie. Onderste xml-ph-0
#A059 TABEL - FOUT VAN SET DRIVE POSITION - De melding alarm wordt weergegeven als de controller geen bevestiging ontvangt van de sensor dat de gewenste positie is bereikt binnen seconden van xml-ph-0030@deepl.i Controleer dat de sensor in positie is en controleer ook de luchtdichtheid van de aandrijving.
#A060 NOODGEVAL REBOUND - AXIS X START/END - Het alarm bericht #A061 X-AXIS BASING ERROR wordt weergegeven, samen met het alarm, wanneer de schakelaar einde , gelegen op de kop, wordt geactiveerd. Op dat moment zal de kop doorbuigen en zal het systeem ontploffen.
#A061 AXIS X HOMING ERROR - Het bericht wordt weergegeven wanneer de eindschakelaar , bevindt op de kop , is geactiveerd. Deze kan zijn te wijten aan de operator heeft een onjuiste, tabel lengte va ingevoerd. een hoger dan de werkelijke lengte- in de Bewegingen instellingen in de service menu . Een basing error kan ook optreden in het geval van een actief eindpunt na basing.
#A062 SET PRESSURE HAS NOT BEEN ACHIEVED - Het bericht wordt weergegeven als de opgegeven waarde van de druk parameter is lager dan de lagere tolerantie bereik, gespecificeerd in het service venster in de controle parameters van het lasproces.
#A063 NOODGEVAL REBOUND - AXIS Y START/END - Het alarm bericht #A061 Y-AXIS BASING ERROR wordt weergegeven, samen met het alarm, wanneer de schakelaar einde , gelegen op de kop, wordt geactiveerd. Op dat moment zal de kop doorbuigen en zal het systeem ontploffen.
#A064 AXIS Y HOMING ERROR - Het bericht wordt weergegeven wanneer de eindschakelaar , op de kop , is geactiveerd. Dit kan zijn te wijten aan de operator een onjuiste "As Y omhoog xm" heeft ingevoerd. een hoger dan de werkelijke waarde- in de instellingen Bewegingen in het menu service . Een fout basing kan ook optreden bij een actief eindpunt na basing.
#A075 DRIVE ERROR - het alarm bericht zal worden weergegeven wanneer een alarm optreedt op de omvormer. Als het alarm kan niet worden verwijderd, controleer het alarm nummer dat wordt weergegeven op de omvormer display en controleer zijn uitleg in de technische documentatie van de fabrikant.
#A076 OPEN WAARSCHUWING - wordt weergegeven wanneer een van de schilden werd genomen uit - de schilden zijn uitgerust met de sleutel- schakelaars die draaien zelf op alleen als de schilden op de juiste manier worden geplaatst en worden vastgedraaid.
#A077 DRIVE COMMUNICATIE FOUT - het alarm wordt weergegeven als er geen communicatie is PLC = Omvormer. Controleer of de connectoren van de kabel niet verwijderd zijn.
#A080 INCORRECT LENGTE VAN LASSEN - een alarm bericht zal worden weergegeven als de las is onmogelijk te maken, omdat de lengte van de las groter is dan de lengte van de tabel het betekent als de operator wil start de cyclus in BA aandrijving modus maar heeft de laslengte voor AB modus ingevoerd. Controleer:
- het hoofd is op het begin van de tabel, of op het einde afhankelijk van de keuze van de AB-BA aandrijving modus,
- passeren parameters zijn correct ingevoerd in het venster HF HEAD DRIVE,
- de werkelijke tabel lengte is correct ingevoerd in het venster SERVICE MENU .
#A102 LINKER BUMPER - COLLISION - het bericht wordt weergegeven wanneer de linker bumper is geactiveerd. In geval van stoppen in een obstakel (bumper actief), draai de schakelaar NOODGEVALLEN MOVE deactiveer het nood systeem en gebruik de HMI om te bewegen het hoofd het obstakel te verlaten.
#A103 RECHTER BUMPER - COLLISION - het bericht wordt weergegeven wanneer de rechter bumper is geactiveerd. In het geval van stoppen in een obstakel (bumper actief), draait u de schakelaar EMERGENCY MOVE deactiveer het noodsysteem en gebruik de HMI om te bewegen het hoofd het obstakel te verlaten.
6.6.3 Alarmscherm - Noodbeweging
Het venster NOODGEVALLEN VERPLAATSEN wordt weergegeven wanneer de noodschakelaar in de stand I wordt gezet (afb. 13). Noodbeweging ). In het venster, heeft de operator de optie om de las kop rechts of links met langzame snelheid te passeren. De beweging van de kop wordt gedaan door middel van navigatie pijlen indicat

Fig. 17 Noodbeweging
 Operatie op de machine is alleen mogelijk wanneer de NOODVERHUIZING schakel is in positie 0.
Operatie op de machine is alleen mogelijk wanneer de NOODVERHUIZING schakel is in positie 0.
In het bovenste gedeelte van het aanraakgevoelige display van de HMI bevindt zich een menu waarmee de gebruiker een van de vijf virtuele hoofdvensters kan kiezen, zoals:
- Hoofdscherm
- Recepten database
- Vermogen instelling
- Werkgrafiek
- Servicemenu
6.6.5 Hoofdscherm
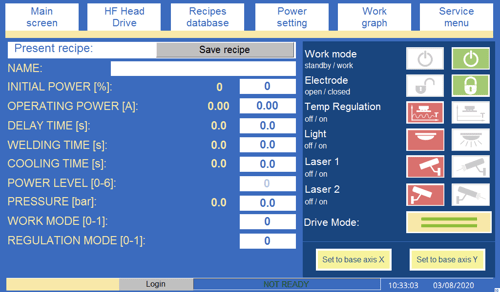
Fig.12. Hoofdscherm.
Recept - Onder deze naam is een groep parameters te vinden die van toepassing zijn op de inschakelduur. Zodra de lasparameters voor het specifieke soort product op basis van praktische ervaring zijn vastgesteld (de waarden van de parameters zijn sterk afhankelijk van de grootte van de las, de grootte van het gelaste materiaal en de vorm van de elektrode), moeten ze in het systeem worden ingevoerd en onder de naam van het recept worden opgeslagen.
 LET OP! Het is belangrijk naar denk aan dat in wrevel van de dat de boven vermeld parameters kan zijn opgeslagen onder de recepten naam in de HMI aanraakgevoelig paneel daar is ook een andere parameter - ELECTRODE TEMPERATUUR dat moet handmatig worden aangepast.
LET OP! Het is belangrijk naar denk aan dat in wrevel van de dat de boven vermeld parameters kan zijn opgeslagen onder de recepten naam in de HMI aanraakgevoelig paneel daar is ook een andere parameter - ELECTRODE TEMPERATUUR dat moet handmatig worden aangepast.
![]() Naast de naam van elke parameter staan ook twee waarden op het display van de HMI. De eerste (op de blauwe achtergrond) is de waarde van de huidige bedrijfsparameter die in de actuele tijd wordt weergegeven, de tweede (op de witte achtergrond) is de ingestelde waarde die afkomstig is van het productierecept of de gegevens van de operator.
Naast de naam van elke parameter staan ook twee waarden op het display van de HMI. De eerste (op de blauwe achtergrond) is de waarde van de huidige bedrijfsparameter die in de actuele tijd wordt weergegeven, de tweede (op de witte achtergrond) is de ingestelde waarde die afkomstig is van het productierecept of de gegevens van de operator.
![]() Als het nodig is, kan de operator altijd op het cijfer op de witte achtergrond drukken en de waarde wijzigen. De waarde van de huidige bedrijfsparameter wordt meteen bijgewerkt, maar de wijziging heeft geen invloed op het uitgevoerde recept.
Als het nodig is, kan de operator altijd op het cijfer op de witte achtergrond drukken en de waarde wijzigen. De waarde van de huidige bedrijfsparameter wordt meteen bijgewerkt, maar de wijziging heeft geen invloed op het uitgevoerde recept.
![]() Om de wijzigingen in een recept op te slaan die in het hoofdscherm zijn gemaakt, drukt u op de toets RECEPT OPSLAAN om de parameters van het hoofdscherm te kopiëren naar de balk Recept bewerken in het venster Receptendatabase. De gekopieerde parameters kunnen worden opgeslagen als een nieuw recept met de knop Maak nieuw of ze kunnen worden gebruikt om een bestaand recept bij te werken met de knop Bijwerken.
Om de wijzigingen in een recept op te slaan die in het hoofdscherm zijn gemaakt, drukt u op de toets RECEPT OPSLAAN om de parameters van het hoofdscherm te kopiëren naar de balk Recept bewerken in het venster Receptendatabase. De gekopieerde parameters kunnen worden opgeslagen als een nieuw recept met de knop Maak nieuw of ze kunnen worden gebruikt om een bestaand recept bij te werken met de knop Bijwerken.
Het rode teken op het HMI paneel in het hoofdvenster Fig. 19 geeft aan dat de machine niet klaar is voor gebruik. De knoppen op het HMI paneel en op het bedieningspaneel zijn inactief totdat de operator de machine opnieuw opstart met de blauwe RESTART-knop op het bedieningspaneel. Het selecteren van de RESTART-knop heeft hetzelfde effect als het veiligheidscircuit en het opstartproces van de opwekkingslamp gedurende 30 seconden. Tijdens deze tijd wordt de voortgangsbalk geleidelijk groen (Afb. 20 ), en de knoppen het hoofd toestaan te passeren op de X en Y assen terwijl de knoppen die het hoofd toestaan te laten vallen over de werkbank actief zijn ; echter, het is niet mogelijk om te schakelen naar xml-ph-00 Zodra de voortgangsbalk volledig groen is, zal een GEREED teken verschijnen op de voortgangsbalk en vanaf zullen alle knoppen, inclusief de hoge frequentie, activering knoppen, actief zijn.

Fig. 19 Informatie NOT READY weergegeven op HMI paneel

Afb. 20 Voortgangsbalk geleidelijk groen na selectie van RESTART knop op het bedieningspaneel
Naam: - de naam van het recept uitgevoerd voor productiedoeleinden.
Initieel vermogen - deze parameter geeft de positie (capaciteit) aan van de uitgangscondensator in de generator; de intensiteit van de anodestroom in de beginfase van hoogfrequent lassen hangt sterk af van de waarde van deze parameter. (Parameter uitgedrukt in procenten, waarbij 0% het laagste capaciteitsniveau aangeeft - het laagste niveau van anodestroomintensiteit en 100% het hoogste capaciteitsniveau - het hoogste niveau van anodestroomintensiteit).
![]() De parameterwaarde van het aanvangsvermogen en de waarde van de anodestroom (in het materiaal afgegeven vermogen) zijn niet lineair afhankelijk, waardoor de juiste voorzorgsmaatregelen moeten worden genomen bij het aanpassen van de waarden van deze parameter.
De parameterwaarde van het aanvangsvermogen en de waarde van de anodestroom (in het materiaal afgegeven vermogen) zijn niet lineair afhankelijk, waardoor de juiste voorzorgsmaatregelen moeten worden genomen bij het aanpassen van de waarden van deze parameter.
![]() De huidige waarde van de parameter Initieel vermogen en de waarde van de ingestelde parameter zijn alleen gelijk aan elkaar in de beginfase van de lasprocedure. Wanneer de procedure wordt gestart, wordt de positie van de uitgangscondensator automatisch aangepast om het bedrijfsvermogen te bereiken.
De huidige waarde van de parameter Initieel vermogen en de waarde van de ingestelde parameter zijn alleen gelijk aan elkaar in de beginfase van de lasprocedure. Wanneer de procedure wordt gestart, wordt de positie van de uitgangscondensator automatisch aangepast om het bedrijfsvermogen te bereiken.
Bedrijfsvermogen [A] - deze parameter geeft de anodestroom Ia aan die wordt gebruikt voor het lassen. (Parameter uitgedrukt in ampèrewaarden variërend van 0 tot 4 A.)
![]() Waarden in groene kleur op de schaal van de anodestroommeter geven de aanvaardbare waarden van de anodestroom Ia aan.
Waarden in groene kleur op de schaal van de anodestroommeter geven de aanvaardbare waarden van de anodestroom Ia aan.
![]() Wanneer de lasprocedure wordt gestart, wordt de uitgangscondensator (aanvangsvermogen) automatisch aangepast om het bedrijfsvermogen te bereiken.
Wanneer de lasprocedure wordt gestart, wordt de uitgangscondensator (aanvangsvermogen) automatisch aangepast om het bedrijfsvermogen te bereiken.
Vertragingstijd [s] - deze parameter geeft de tijd aan waarin de elektrode zich aan het lasmateriaal heeft gehecht voordat de las werd geïnitieerd. (Parameter uitgedrukt in seconden, variërend van 0 tot 99 s.)
Lastijd [s] - deze parameter geeft de tijd aan die de machine nodig heeft om de hoogfrequente las te verwerken. (Parameter uitgedrukt in seconden, variërend van 0 tot 99 s.)
Afkoeltijd [s] - deze parameter geeft de tijd aan waarin de elektrode tegen het gelaste materiaal werd gedrukt nadat de lasnaad was beëindigd - het materiaal koelt af terwijl het tegen de tafel wordt gedrukt. (Parameter uitgedrukt in seconden, variërend van 0 tot 99 s).
Vermogensniveau [0-6] - is de belangrijkste instelling van het vermogen van de machine; aanpassing wordt uitgevoerd door de anodespanning te wijzigen Ua in het bereik van 1 tot 6, waarbij 1 staat voor laag vermogen en 6 voor maximaal vermogen:
0 - de anode transformator is uitgeschakeld;
1 - Ua = 3,4 kV;
2 - Ua = 3,95kV;
3 - Ua = 4,75kV;
4 - Ua = 5,87kV;
5 - Ua = 6,85kV;
6 - Ua = 8,2kV;
Druk [bar] - de parameter geeft de persluchtdruk in het pneumatische systeem van de elektrodespanning aan, uitgedrukt in bar; de parameter bepaalt de neerwaartse kracht van de elektrode ten opzichte van het materiaal tijdens het lassen.
Werk modus [0/1] - De parameter definieert de las werk modus. 0 waarde geeft aan dat de machine aan het werk is in 'Tijd' las modus. 1 waarde geeft aan dat de machine in de 'Current' lasmodus werkt. Een gedetailleerde beschrijving van de bedrijfsmodi "Time" en "Current" vindt u op op pagina's 71-72 van de documentatie.
Regeling modus [0/1] - De parameter definieert het bereik van automatische aanpassing modus van de uitgang condensator. Het typen van 1 waarde (MAX modus) schakelt het in volledige automatische aanpassing modus van de uitgang condensator. xm waarde (MIN-modus) betekent dat tijdens lassen, de uitgangscondensator alleen wordt aangepast wanneer de anodestroom hoger is dan de waarde ingevoegd in de parameter vermogen max . Een gedetailleerde beschrijving van de MAX en MIN werkingsmodi wordt gegeven op pagina 72 van de documentatie.
Opties:
Werkmodus stand-by / werk
 - groen knop
- groen knop  betekent dat de machine is draaide aan en klaar naar werk, werk tijdens normale werkzaamheden.
betekent dat de machine is draaide aan en klaar naar werk, werk tijdens normale werkzaamheden.
 - oranje knop
- oranje knop  betekent dat de machine is in stand-bymodus. Deze stand is tweedehands naar zwad: de machine naar stand slapen, die geeft de mogelijkheid om de verwarming van de elektrode voor de werkdienst.
betekent dat de machine is in stand-bymodus. Deze stand is tweedehands naar zwad: de machine naar stand slapen, die geeft de mogelijkheid om de verwarming van de elektrode voor de werkdienst.
Een referentiesituatie:
Een werkdienst duurt van 7:00 uur - 15:00 uur .
De operator beëindigt de shift om 15.00 uur moet NIET de machine uitschakelen op deHOOFDSCHAKELAAR en moet NIET de knop NOODGEVALLEN STOP indrukken; hij/zij mag alleen zet de machine in STANDBYxml-). ). De operator stelt de elektrode verwarming, inschakelen tijd in dit venster, in de tabel 'ELECTRODE VOOR VERWARMING INSTELLINGEN VOOR STANDBY MODE'; in ons geval, is verwarming te actief vanaf 6:40 xml-ph-0030@deepl.inter
De bediener verlaat dan de machine. Deze instelling zal ervoor zorgen dat de elektrode van de machine op 7 elke dag, zoals aangegeven, in volgorde om een efficiënte werking mogelijk te maken vanaf het begin van de dienst en daardoor vergemakkelijken lassen van herhaalbare xml-ph-0 De bovenstaande situatie wordt weergegeven in de volgende grafiek .
Fig. 21 Stand-bymodusvenster
|
|
Voor de stand-bymodus naar goed werken: Het moet zijn geschakeld op in de hoofdpagina raam met de oranje knop
|
|
|
|
Elektrode open / gesloten
 - een open hangslot op de rood achtergrond geeft aan dat het lassen elektrode was niet gesloten in zijn houder, wanneer jij druk op de grijs gesloten hangslot de houder wordt gesloten.
- een open hangslot op de rood achtergrond geeft aan dat het lassen elektrode was niet gesloten in zijn houder, wanneer jij druk op de grijs gesloten hangslot de houder wordt gesloten.
|
|
Bovendien, op het bericht zoals zoals ATTENTIE, ELECTRODE OPEN knippert, het ook betekent dat de elektrode houder is open is. |
 - a gesloten hangslot op de groen achtergrond geeft aan dat de lassen elektrode is gesloten in zijn houder, wanneer jij druk op op de grijs hangslot openen de houder zal open zijn.
- a gesloten hangslot op de groen achtergrond geeft aan dat de lassen elektrode is gesloten in zijn houder, wanneer jij druk op op de grijs hangslot openen de houder zal open zijn.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Temp. regeling uit / aan
 - drukknop
- drukknop  seinen dat de elektrode temperatuurstabilisator is geschakeld op, druk op
seinen dat de elektrode temperatuurstabilisator is geschakeld op, druk op  de drukknop draait uit temperatuurstabilisatie.
de drukknop draait uit temperatuurstabilisatie.
 - drukknop
- drukknop  seinen dat de elektrode temperatuurstabilisator is geschakeld op, druk op de
seinen dat de elektrode temperatuurstabilisator is geschakeld op, druk op de  drukknop draait uit temperatuurstabilisatie.
drukknop draait uit temperatuurstabilisatie.
 Draaien op temperatuur stabilisatie resultaten in de onderhouden van een stabiele temperatuurniveau en een herhaalbare laskwaliteit.
Draaien op temperatuur stabilisatie resultaten in de onderhouden van een stabiele temperatuurniveau en een herhaalbare laskwaliteit.
Licht uit/aan
 - a lamp die doet niet gloed op de rood achtergrond geeft aan dat de werk tabel verlichting in de lassen zone is geschakeld uit, wanneer u op de grijze gloeiende lamp, de verlichting zal worden geschakeld op.
- a lamp die doet niet gloed op de rood achtergrond geeft aan dat de werk tabel verlichting in de lassen zone is geschakeld uit, wanneer u op de grijze gloeiende lamp, de verlichting zal worden geschakeld op.
 - a gloeiend lamp op de groen achtergrond geeft aan dat de werk tabel verlichting in de lassen zone is geschakeld op, wanneer jij druk op de grijze lamp, de verlichting zal worden geschakeld uit.
- a gloeiend lamp op de groen achtergrond geeft aan dat de werk tabel verlichting in de lassen zone is geschakeld op, wanneer jij druk op de grijze lamp, de verlichting zal worden geschakeld uit.
Laser 1 uit / aan
 - drukknop
- drukknop  seinen dat de laser indicator 1 is geschakeld uit, druk op de drukknop
seinen dat de laser indicator 1 is geschakeld uit, druk op de drukknop  draait op de laser indicator 1.
draait op de laser indicator 1.
 - drukknop
- drukknop  seinen dat de laser indicator 1 wordt geschakeld op, druk op de drukknop
seinen dat de laser indicator 1 wordt geschakeld op, druk op de drukknop  draait de laserindicator uit 1.
draait de laserindicator uit 1.
Laser 2 uit / aan
 - drukknop
- drukknop  seinen dat de laser indicator 2 is geschakeld uit, druk op de drukknop
seinen dat de laser indicator 2 is geschakeld uit, druk op de drukknop  draait op de laser indicator 2.
draait op de laser indicator 2.
 - drukknop
- drukknop  seinen dat de laser indicator 2 wordt geschakeld op, druk op de drukknop
seinen dat de laser indicator 2 wordt geschakeld op, druk op de drukknop  draait de laserindicator uit 2.
draait de laserindicator uit 2.
 In de standaard, de laser indicator aangeduid als als Laser 1 is gevestigd op de links zijkant van de lassen hoofd en Laser 2 op zijn rechts kant, kijkend van de voorkant van de machine, dat is, van de bedieningspaneel zijde / kant van de operator.
In de standaard, de laser indicator aangeduid als als Laser 1 is gevestigd op de links zijkant van de lassen hoofd en Laser 2 op zijn rechts kant, kijkend van de voorkant van de machine, dat is, van de bedieningspaneel zijde / kant van de operator.
Werkmodus
Huidige / Tijd
 - de elektrische circuit op de groen achtergrond geeft aan dat de machine is werken in 'Actueel' lassen modus; druk op de grijs klok geeft aan dat de machine zal voer de 'Tijd lasmodus. 'Huidige' lasmodus geeft aan dat de machine teller heeft begonnen tellen hoog frequentielas tijd, die was ingevoerd in de Lassen tijd parameter, als binnenkort als de machine erkent de geschikt waarde van de la anode huidige die moeten ofwel hoger zijn dan of zijn gelijk naar de waarde ingevoerd in de Werk huidige parameter. Naar zet het anders, in Huidige lassen modus, de lassen tijd is gelijk aan de som van beide de waarde van de tijd de machine neemt naar produceren de anode stroom- die is, de waarde ingevoerd in de Werking stroom parameter- en de waarde van tijd ingevoerd in de Lastijd parameter.
- de elektrische circuit op de groen achtergrond geeft aan dat de machine is werken in 'Actueel' lassen modus; druk op de grijs klok geeft aan dat de machine zal voer de 'Tijd lasmodus. 'Huidige' lasmodus geeft aan dat de machine teller heeft begonnen tellen hoog frequentielas tijd, die was ingevoerd in de Lassen tijd parameter, als binnenkort als de machine erkent de geschikt waarde van de la anode huidige die moeten ofwel hoger zijn dan of zijn gelijk naar de waarde ingevoerd in de Werk huidige parameter. Naar zet het anders, in Huidige lassen modus, de lassen tijd is gelijk aan de som van beide de waarde van de tijd de machine neemt naar produceren de anode stroom- die is, de waarde ingevoerd in de Werking stroom parameter- en de waarde van tijd ingevoerd in de Lastijd parameter.
 Als de machine doet niet beheren naar produceren Werking stroom binnen 25 seconden, de bedrijfscyclus wordt stopgezet.
Als de machine doet niet beheren naar produceren Werking stroom binnen 25 seconden, de bedrijfscyclus wordt stopgezet.
 - de klok op de groen achtergrond geeft aan dat de machine is werken in 'Tijd lassen modus; druk op de grijs, elektrische circuit geeft aan dat de machine zal ga naar 'Huidige' lassen modus. De 'Tijd lassen stand geeft aan dat hoog frequentie las tijd is gelijk naar de waarde ingevoerd de recepten parameter onder de naam Lastijd.
- de klok op de groen achtergrond geeft aan dat de machine is werken in 'Tijd lassen modus; druk op de grijs, elektrische circuit geeft aan dat de machine zal ga naar 'Huidige' lassen modus. De 'Tijd lassen stand geeft aan dat hoog frequentie las tijd is gelijk naar de waarde ingevoerd de recepten parameter onder de naam Lastijd.
 Het is de moeite waard het opmerken van dat in 'Tijd, lassen modus, de plicht cyclus kunnen uitgevoerd zelfs als de machine heeft niet beheerd naar produceren Werking kracht. De resultaat van deze zal zijn dat de las bereikt kan worden van onregelmatige sterkte.
Het is de moeite waard het opmerken van dat in 'Tijd, lassen modus, de plicht cyclus kunnen uitgevoerd zelfs als de machine heeft niet beheerd naar produceren Werking kracht. De resultaat van deze zal zijn dat de las bereikt kan worden van onregelmatige sterkte.
Regelmodus min / max
 - drukknop
- drukknop  seinen dat de machine is werken in beperkt automatisch aanpassing stand van de uitgang condensator; druk op de drukknop
seinen dat de machine is werken in beperkt automatisch aanpassing stand van de uitgang condensator; druk op de drukknop  schakelaars het in volledig automatisch aanpassing stand van de uitgangscondensator. De min stand betekent dat tijdens lassen, de uitgang condensator wordt aangepast alleen wanneer de anode huidige is hoger dan de waarde ingevoegd in de Vermogen max parameter.
schakelaars het in volledig automatisch aanpassing stand van de uitgangscondensator. De min stand betekent dat tijdens lassen, de uitgang condensator wordt aangepast alleen wanneer de anode huidige is hoger dan de waarde ingevoegd in de Vermogen max parameter.
 - drukknop
- drukknop  dat de machine is werken in volledig automatisch aanpassing stand van de uitgang condensator; druk op de
dat de machine is werken in volledig automatisch aanpassing stand van de uitgang condensator; druk op de  drukknop schakelaars het in beperkt automatisch aanpassing stand van de condensator. De max. stand betekent dat tijdens lassen, de uitgang condensator is automatisch aangepast dus dat de anode huidige is op de niveau stel in in de Bedrijfsvermogen parameter.
drukknop schakelaars het in beperkt automatisch aanpassing stand van de condensator. De max. stand betekent dat tijdens lassen, de uitgang condensator is automatisch aangepast dus dat de anode huidige is op de niveau stel in in de Bedrijfsvermogen parameter.
Aandrijfmodus - de laskop kan werken in vijf doorgangsmodi :
 - operatie op de site stand - de machine werkt stationair (lassen in de dezelfde plaats zonder bewegend). Geen van de doorgangsparameters is actief.
- operatie op de site stand - de machine werkt stationair (lassen in de dezelfde plaats zonder bewegend). Geen van de doorgangsparameters is actief.
 - werken stand van links naar rechts zonder terugkeren - de machine maakt een las op de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de rechts en blijft op de plaats van de laatste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
- werken stand van links naar rechts zonder terugkeren - de machine maakt een las op de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de rechts en blijft op de plaats van de laatste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
 - werken stand van rechts naar links zonder terugkeren - de machine maakt een las op de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de links en blijft op de plaats van de laatste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
- werken stand van rechts naar links zonder terugkeren - de machine maakt een las op de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de links en blijft op de plaats van de laatste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
 - werken stand van links naar rechts met terugkeren - de machine voert lassen uit langs de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de rechts en geeft terug. automatisch naar de plaats van de eerste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
- werken stand van links naar rechts met terugkeren - de machine voert lassen uit langs de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de rechts en geeft terug. automatisch naar de plaats van de eerste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
 - werken stand van rechts naar links met terugkeren - de machine voert lassen uit langs de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de links en geeft terug. automatisch naar de plaats van de eerste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
- werken stand van rechts naar links met terugkeren - de machine voert lassen uit langs de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de links en geeft terug. automatisch naar de plaats van de eerste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
stel in op basis as X - de knop start het proces van homing de X as - de bepalen punt voor de reis van de kop. Om te starten, de knop ingedrukt houden. De xml-ph-0031@deepl.inte Wanneer de knop groen wordt en stopt met knipperen, is het proces beëindigd. Tijdens het proces homing, beweegt de laskop naar de links totdat de eindschakelaar bedient en van de eindschakelaar stuitert met de lengte die in het programma heeft ingesteld.
zet op basis as Y - de knop start het proces van homing de Y as - het bepalen van het nulpunt voor de reis van de kop. Om te starten, de knop ingedrukt houden. De xml-ph-0031@deepl.inte Wanneer de knop groen wordt en stopt met knipperen, is het proces beëindigd. Tijdens het proces homing, beweegt de laskop naar de voorkant totdat de eindschakelaar bedient en naar de basis gaat.
ALARM BERICHTEN MET DE MELDING: NIET KLAAR VOOR START LASCYCLUS:
LET OP, ELECTRODE OPEN - meldt dat de elektrode handgreep open is . Installeer de laselektrode correct en sluit de handgreep: HMI → Hoofdscherm→ Elektrode → gesloten.
NIET GEREED - geeft aan dat de machine niet niet correct opnieuw opstartte en er geen 30 seconden opstarttijd was. Druk op de knop RESTART op het bedieningspaneel .
Als een speciale elektrode is geïnstalleerd in de houder die lassen mogelijk maakt zonder het gebruik van een massa-elektrode , dan na het indrukken van de START knop op het bedieningspaneel , de aardelektrode zal blijven in de bovenste positie het zal niet lager. Na de installatie van dit type van elektrode, op de onderkant in het hoofdscherm van het HMI paneel zal het bericht " LASSEN ZONDER AARDINGSVOET!" weergeven.
6.6.6 Recepten databank
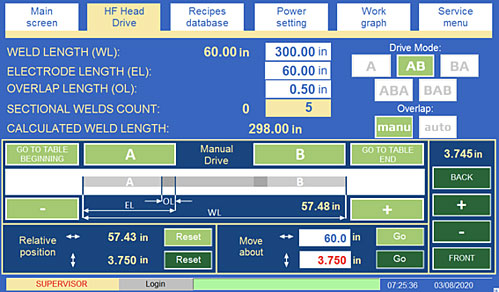
Fig. 22 HF-hoofdaandrijving
In het venster HF Kop Aandrijving zijn recept parameters die verwijzen naar de doorgang van de kop tijdens een automatische lascyclus :
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WELD LENGTE - gemarkeerd als WL geeft de laslengte aan (uitgedrukt in inch of centimeter afhankelijk van de positie van de eenheid schakelaar in het service menu).
ELECTRODE LENGTE - gemarkeerd als EL geeft de lengte van de elektrode gemonteerd in de lassen (uitgedrukt in inch of centimeter afhankelijk van de positie van de eenheid schakelaar in het servicemenu).
OVERLAP LENGTE - gemarkeerd als OL geeft overlap lengte aan. De overlap is de oppervlakte van het materiaal gelast waar de gedeeltelijke las overlapt de vorige een; dit betekent dat het materiaal is xml-ph-0030@deepl.int Er zijn twee mogelijke opties voor de berekeningen van de overlap gekozen door middel van van de Overlap drukknoppen:
 - de optimaal lengte van de overlap en de nummer van gedeeltelijk lassen wordt berekend automatisch op de basis van de totaal las lengte en de laselektrode lengte (gedeeltelijke las) invoer waarden.
- de optimaal lengte van de overlap en de nummer van gedeeltelijk lassen wordt berekend automatisch op de basis van de totaal las lengte en de laselektrode lengte (gedeeltelijke las) invoer waarden.
 - de las lengte is ingevoegd door de operator. Attentie moet zijn betaald naar invoer a lengte dat zal toestaan lassen van de materiaal langs zijn volledig lengte ingesteld; anders is de laatste las zullen moeten naar worden uitgevoerd handmatig.
- de las lengte is ingevoegd door de operator. Attentie moet zijn betaald naar invoer a lengte dat zal toestaan lassen van de materiaal langs zijn volledig lengte ingesteld; anders is de laatste las zullen moeten naar worden uitgevoerd handmatig.
SECTIEEL LASSEN TELLEN - het aantal gedeeltelijke lassen tot worden uitgevoerd door de machine in de automatische cyclus om het materiaal langs de volledige lengte te lassen. Het is niet mogelijk voor de operator om deze parameter in te stellen. Het is altijd automatisch berekend op de basis van de totale las lengte gegeven en de lengte van de las elektrode.
 Als de machine heeft zijn geweest gestopt met tijdens zijn automatisch cyclus door op de STOP knop op de controle paneel voor a minimum van 3 seconden dan de cyclus zal niet verder en de nummer van de gedeeltelijke lassen zal gereset.
Als de machine heeft zijn geweest gestopt met tijdens zijn automatisch cyclus door op de STOP knop op de controle paneel voor a minimum van 3 seconden dan de cyclus zal niet verder en de nummer van de gedeeltelijke lassen zal gereset.
 Als de machine heeft zijn geweest gestopt met tijdens zijn automatisch cyclus door op de STOP knop op de controle paneel en de operator beweegt de joystick dan de cyclus zal niet verder en het aantal van de gedeeltelijke lassen zal gereset.
Als de machine heeft zijn geweest gestopt met tijdens zijn automatisch cyclus door op de STOP knop op de controle paneel en de operator beweegt de joystick dan de cyclus zal niet verder en het aantal van de gedeeltelijke lassen zal gereset.
 Als de machine heeft zijn geweest gestopt met tijdens zijn automatisch cyclus door op de STOP knop op de controle paneel en de laskop is in de lassen positie (ongeacht van of het lassen proces heeft niet begonnen, is hardlopen of ingevuld) het is mogelijk naar verder de cyclus alleen als de START knop op het bedieningspaneel zal worden ingedrukt.
Als de machine heeft zijn geweest gestopt met tijdens zijn automatisch cyclus door op de STOP knop op de controle paneel en de laskop is in de lassen positie (ongeacht van of het lassen proces heeft niet begonnen, is hardlopen of ingevuld) het is mogelijk naar verder de cyclus alleen als de START knop op het bedieningspaneel zal worden ingedrukt.
 Als de machine heeft zijn geweest gestopt met tijdens zijn automatisch cyclus door op de STOP knop op de controle paneel en de laskop is in de aandrijving positie het is mogelijk naar verder de drukken op de cyclus de "Ga naar naar de volgende positie" knop in de HF hoofdaandrijvingsvenster.
Als de machine heeft zijn geweest gestopt met tijdens zijn automatisch cyclus door op de STOP knop op de controle paneel en de laskop is in de aandrijving positie het is mogelijk naar verder de drukken op de cyclus de "Ga naar naar de volgende positie" knop in de HF hoofdaandrijvingsvenster.
Aandrijfmodus - de laskop kan werken in vijf doorgangsmodi :
 - operatie op de site stand - de machine werkt stationair (lassen op dezelfde plaats zonder bewegen). Geen van de Doorgangsparameters zijn actief.
- operatie op de site stand - de machine werkt stationair (lassen op dezelfde plaats zonder bewegen). Geen van de Doorgangsparameters zijn actief.
 - werken stand van links naar rechts zonder terugkeren - de machine maakt een las op de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de rechts en blijft op de plaats van de laatste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
- werken stand van links naar rechts zonder terugkeren - de machine maakt een las op de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de rechts en blijft op de plaats van de laatste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
 - werken stand van rechts naar links zonder terugkeren - de machine maakt een las op de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de links en blijft op de plaats van de laatste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
- werken stand van rechts naar links zonder terugkeren - de machine maakt een las op de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de links en blijft op de plaats van de laatste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
 - werken stand van links naar rechts met terugkeren - de machine voert lassen uit langs de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de rechts en geeft terug. automatisch naar de plaats van de eerste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
- werken stand van links naar rechts met terugkeren - de machine voert lassen uit langs de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de rechts en geeft terug. automatisch naar de plaats van de eerste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
 - werken stand van rechts naar links met terugkeren - de machine voert lassen uit langs de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de links en geeft terug. automatisch naar de plaats van de eerste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
- werken stand van rechts naar links met terugkeren - de machine voert lassen uit langs de lengte stel in verhuizen naar de links en geeft terug. automatisch naar de plaats van de eerste las wanneer de taak is voltooid.
Handmatige aandrijving - een groep drukknoppen waarmee de machine kan worden bewogen:
De knoppen met een licht groen achtergrond verwijzen naar de machine reizen in de X-as (rechts / links).
 Alle drukknoppen voor handmatig doorgang werk met 0.5 sec vertraging om voorkomen elke per ongeluk indrukken.
Alle drukknoppen voor handmatig doorgang werk met 0.5 sec vertraging om voorkomen elke per ongeluk indrukken.
GO TO TABLE BEGINNING - Door op deze drukknop in te drukken, beweegt de laskop naar het begin van de bank.
GO TO TABLE END - Door op op deze drukknop te drukken, beweegt de laskop naar het einde van de bank.
Een - druk op deze drukknop beweegt de laskop naar de plaats van de eerste las.
B - door op op deze drukknop te drukken beweegt de laskop naar de plaats van de laatste las.
Relatieve positie - toont de positie van de machine ten opzichte van de positie in waar de Reset drukknop die ernaast zit werd ingedrukt .
Beweeg over - de operator voert de afstand in die de kop moet afleggen op deze plaats. Wanneer de Ga drukknop wordt ingedrukt , beweegt de machine en legt de afstand af die heeft ingesteld in het veld Beweeg over .
 Als de ingevoerd waarde is gemarkeerd in rood, het betekent dat de laskop kan niet zijn Verplaatst door de stel in waarde. Als de hoofd is niet op de rand van de tabel en het is fysiek mogelijk naar rijden, controleren of de tabel lengte heeft zijn geweest correct ingevoerd in de servicemenuvenster.
Als de ingevoerd waarde is gemarkeerd in rood, het betekent dat de laskop kan niet zijn Verplaatst door de stel in waarde. Als de hoofd is niet op de rand van de tabel en het is fysiek mogelijk naar rijden, controleren of de tabel lengte heeft zijn geweest correct ingevoerd in de servicemenuvenster.
 Wanneer de Ga naar drukknop is ingedrukt, de richting in die de machine verhuist hangt af van op de ingevoerd karakter, als daar is een positief waarde (zonder teken) de machine zal Ga naar naar de rechts, als de ingevoerd waarde is negatief, gaat de machine naar links.
Wanneer de Ga naar drukknop is ingedrukt, de richting in die de machine verhuist hangt af van op de ingevoerd karakter, als daar is een positief waarde (zonder teken) de machine zal Ga naar naar de rechts, als de ingevoerd waarde is negatief, gaat de machine naar links.
 - Als u op de knop "plus" knop stuurt de laskop naar rechts. De knop beweegt de laskop een millimeter (of een deel van een inch, afhankelijk van de positie van de eenheidsschakelaar in het servicemenu), ongeacht hoe lang de knop wordt vastgehouden.
- Als u op de knop "plus" knop stuurt de laskop naar rechts. De knop beweegt de laskop een millimeter (of een deel van een inch, afhankelijk van de positie van de eenheidsschakelaar in het servicemenu), ongeacht hoe lang de knop wordt vastgehouden.
 - Druk op de "min" knop zal aandrijving de lassen hoofd naar de links. De knop verhuist de lassen hoofd door a millimeter (of door a deel van een inch afhankelijk van op de positie van eenheid schakel in de servicemenu), ongeacht hoe lang het wordt vastgehouden.
- Druk op de "min" knop zal aandrijving de lassen hoofd naar de links. De knop verhuist de lassen hoofd door a millimeter (of door a deel van een inch afhankelijk van op de positie van eenheid schakel in de servicemenu), ongeacht hoe lang het wordt vastgehouden.
De knoppen met een donkere groene achtergrond verwijzen naar de machine reizen in de Y-as (vooruit/ achteruit).
 - Druk op de knop veroorzaakt de lassen hoofd naar bereiken de eindposities, dat is, naar de operator, als gespecificeerd in de bewegingen instellingen in de service menu.
- Druk op de knop veroorzaakt de lassen hoofd naar bereiken de eindposities, dat is, naar de operator, als gespecificeerd in de bewegingen instellingen in de service menu.
 - Druk op de min knop veroorzaakt de lassen hoofd naar rijd vooruit, dat is, naar de operator. De knop verhuist de lassen hoofd door een millimeter (of door a deel van een inch afhankelijk van op de positie van eenheid schakel in het servicemenu), ongeacht hoe lang het is gehouden.
- Druk op de min knop veroorzaakt de lassen hoofd naar rijd vooruit, dat is, naar de operator. De knop verhuist de lassen hoofd door een millimeter (of door a deel van een inch afhankelijk van op de positie van eenheid schakel in het servicemenu), ongeacht hoe lang het is gehouden.
 - Druk op de plus knop veroorzaakt de lassen hoofd naar aandrijving terug, dat is, weg van de operator. De knop verhuist de lassen hoofd door een millimeter (of door a deel van een inch afhankelijk van op de positie van eenheid schakel in het servicemenu) , ongeacht hoe lang het is gehouden.
- Druk op de plus knop veroorzaakt de lassen hoofd naar aandrijving terug, dat is, weg van de operator. De knop verhuist de lassen hoofd door een millimeter (of door a deel van een inch afhankelijk van op de positie van eenheid schakel in het servicemenu) , ongeacht hoe lang het is gehouden.
 - Druk op de knop veroorzaakt de lassen hoofd naar bereiken de eindposities, dat is, weg van de operator, als gespecificeerd in de bewegingen instellingen in de dienst menu.
- Druk op de knop veroorzaakt de lassen hoofd naar bereiken de eindposities, dat is, weg van de operator, als gespecificeerd in de bewegingen instellingen in de dienst menu.
Boven de donker groen knoppen en naar de links van de licht groen knop  de huidige positie van de elektrode wordt weergegeven, op de Y en X-as. De locatie van de weergave van de huidige positie van de elektrode is gemarkeerd met met pijlen in Fig. 23.
de huidige positie van de elektrode wordt weergegeven, op de Y en X-as. De locatie van de weergave van de huidige positie van de elektrode is gemarkeerd met met pijlen in Fig. 23.
Afb. 23 De huidige positie van de elektrode weergegeven in het gebied aangegeven door de rode pijlen.
6.6.7 Recepten databank
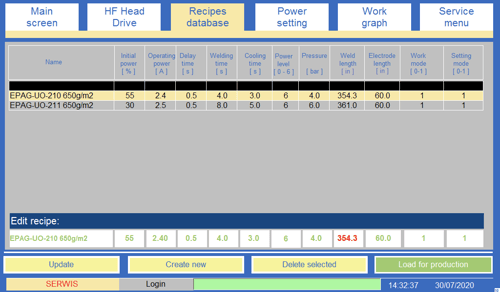 Fig. 24 Recepten Databank
Fig. 24 Recepten Databank
Alle recepten opgeslagen in de HMI geheugenkaart zijn opgenomen in de vorm van een grafiek. Elke rij bevat één recept en elke kolom bevat één van het recept parameters. De gedetailleerde beschrijving van de parameters werd geciteerd in het vorige hoofdstuk. De grafiek kan het onbeperkte aantal van recepten bevatten. Onder de grafiek is een rij getiteld Bewerk recept (op de witte achtergrond) gebruikt voor de editie en creatie van recepten.
NIEUW RECIPE
In volgorde naar maak een nieuwe recept vul in elk vak in de Bewerk recept rij en druk dan op Maak nieuwe toets. Systeem moet toevoegen de nieuw gemaakt recept naar de bestaande lijst xml-ph-0031@deepl.in
 In om sla die wijzigingen naar a recept die waren gemaakt met behulp van de Hoofd scherm, druk op de BESPAREN RECIPE knop naar kopie de parameters van de hoofdpagina scherm naar de Bewerk recept bar in de Recept database raam. De parameters gekopieerd mei zijn opgeslagen als a nieuw recept met de Maak nieuw knop of zij kan zijn gebruikt om update een bestaand recept met behulp van de Update knop.
In om sla die wijzigingen naar a recept die waren gemaakt met behulp van de Hoofd scherm, druk op de BESPAREN RECIPE knop naar kopie de parameters van de hoofdpagina scherm naar de Bewerk recept bar in de Recept database raam. De parameters gekopieerd mei zijn opgeslagen als a nieuw recept met de Maak nieuw knop of zij kan zijn gebruikt om update een bestaand recept met behulp van de Update knop.
RECIPE EDITIE
Voor om te bewerken een recept moeten we om klik op de receptnaam komen van de receptenlijst (geselecteerde recept moet gemarkeerd in geel en weergegeven in recept rij). Voor zover het als een wijziging van parameter waarde in Bewerk recept rij betreft, hebben we nodig om te klikken op het witte vak waar het moet worden weergegeven en voer een nieuwe waarde in. Zodra de editie procedure is afgerond , moet de Update toets worden ingedrukt en als een resultaat de ingevoerde wijzigingen in het aangegeven recept zal worden geaccepteerd, opgeslagen en bewaard.
VERWIJDERINGSPROCEDURE
In volgorde naar voer het recept verwijderen procedure klik op het recept naam afgeleid van de recepten lijst (geselecteerde recept moet gemarkeerd in geel en weergegeven in Bewerk recept rij) en druk vervolgens op verwijderen xml-ph-0029@deepl.intern
RECEPT SELECTIE PROCEDURE
In volgorde naar voer het recept selectie procedure voor productie doeleinden kies uit de lijst recepten het recept met waarden vereist voor dienst cyclus (geselecteerd recept moet gemarkeerd in gele en weergave rij) dan klik op Laad voor productie toets als een resultaat het recept zal worden geüpload naar het systeem en voorbereid voor gebruik in huidige productie met zijn parameters weergegeven in het hoofdscherm venster.
SORTEREN PROCEDURE
De recepten die gebruikt worden voor productie zijn opgesomd in een alfabetische volgorde. De verticaal scrollende balk waarmee de operator de grafiek meer soepel kan bekijken, verschijnt op de rechter zijde van de grafiek wanneer een groter aantal van recepten het systeem binnenkomt. Met het systeem kan de operator de recepten sorteren op naam of op elke waarde van een parameter (oplopend of aflopend). In volgorde naar voer een sorteerprocedure uit, zoek een rij van zwarte vakjes welke moet worden weergegeven in het bovenste deel van de grafiek en klik eenmaal op een zwart vakje gelegen precies over xml-ph-003 (Klik tweemaal op en de sorteerrichting wordt gewijzigd).
6.6.8 Instelling vermogen
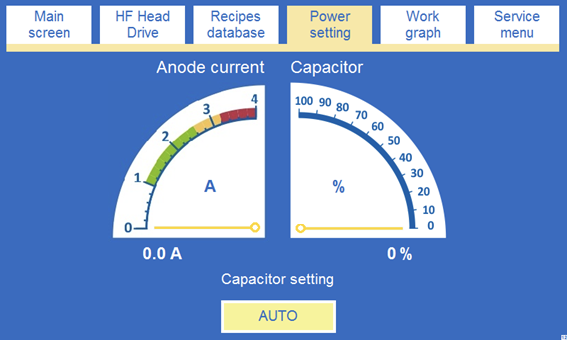
Fig.25 Instelling vermogen
Er zijn twee indicatoren in het venster (Afb.25):
Anode stroom - een indicator van de anode stroom intensiteit. Het geeft de La anode stroom intensiteit die moet gelijk zijn aan de stroom intensiteit van de analoge meter die te vinden is op het bedieningspaneel.
CAPACITOR - een tool die de positie van de uitgang condensator aangeeft (binnen het bereik van 0 tot 100%). Met de hulp van deze tool de instelling van het juiste niveau van vermogen kan plaats - als een regel hoe groter capaciteit, hoe hoger La anodestroom is.
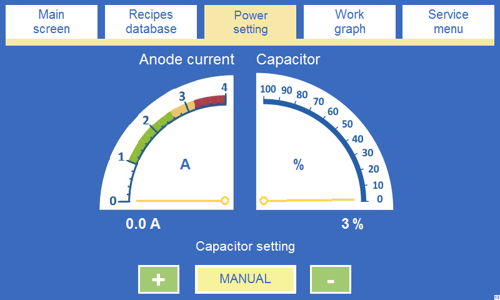
Fig. 26 Instelling vermogen
Een groep van toetsen onder de indicator (Fig.25 en Fig. 26) wordt gebruikt voor de afstelling van de anodecondensator . De afstelling kan op twee manieren worden uitgevoerd:
AUTO - vóór lassen de condensator wordt automatisch ingesteld op de positie correspondeert met de waarden ingevoerd in de Initiële vermogen parameter. Wanneer de lasprocedure wordt uitgevoerd , wordt de positie van de condensator automatisch aangepast zodat als het niveau van La anode stroom intensiteit kon stijgen tot de waarde ingeschreven in de Bedrijfsvermogen parameter.
 Kies AUTO instelling stand tijdens standaard plicht uitgevoerde cycli door de machine. HANDMATIG stand is tweedehands voor testprocedures.
Kies AUTO instelling stand tijdens standaard plicht uitgevoerde cycli door de machine. HANDMATIG stand is tweedehands voor testprocedures.
MANUAL - de hele condensator instelling procedure wordt uitgevoerd met de hand , wanneer de behoefte ontstaat kan de operator de positie van de condensator wijzigen met de hulp van "+" of "-" toetsen en op hetzelfde moment wordt de intensiteit van anode stroom aangepast.
6.6.9 Werkgrafiek
Afb. 28 Servicemenu
 Opening de service scherm is niet mogelijk tijdens de automatische cyclus.
Opening de service scherm is niet mogelijk tijdens de automatische cyclus.
In dit venster (Afb.28) worden de volgende stukjes informatie van statistische oorsprong weergegeven:
Cyclus telling - het is het totaal aantal van dienst cycli sinds de machine voor de eerste keer is ingeschakeld .
Werktijd - it is de totale tijd van machinewerk,
Anti-flash alarm - deze waarde geeft aan hoeveel keer sinds de dag toen de machine werd gefabriceerd, het beveiligingssysteem tegen vlamboogoverslag werd ingeschakeld .
Anode overbelasting alarm - deze waarde geeft aan hoeveel keer vanaf de dag toen de machine werd vervaardigd, het maximale niveau van stroom intensiteit in anode circuit werd overschreden en als een resultaat hoeveel keer het beschermingsmechanisme tegenanode overbelasting werd ingeschakeld .
Rooster overbelasting alarm - deze waarde geeft aan hoeveel keer vanaf de dag toen de machine werd vervaardigd, het maximale niveau van stroom intensiteit in netcircuit tijdens lassen werd overschreden en als gevolg daarvan hoeveel keer het beschermingsmechanisme tegen netoverbelasting werd ingeschakeld .
Buis temperatuur alarm - deze waarde geeft aan hoeveel keer sinds de dag waarop de machine werd geproduceerd, het buisbeschermingssysteem thermisch beveiligingssysteem automatisch werd geactiveerd.
De parameters hieronder zijn beschikbaar voor de fabrikant service technici en voor de supervisor. Om deze reden is een wachtwoord vereist om de parameters te bewerken.
Procesregeling actief- deze knop activeert de HF procesregeling algoritme. Elke lascyclus wordt gecontroleerd. Er wordt een alarm weergegeven op de HMI als het ingestelde lascriterium niet is bereikt . De regelparameters staan in het venster Procesregeling .
Statistieken actief - de actief statistieken knop maakt de gegevens, op elke deellas in de cyclus, welke is geweest gedaan op de machine, te worden verzameld en slaat het op in de statistieken De status van het lasproces , opgenomen in de statistieken, wordt verderop in de handleiding beschreven.
Weergave in inch - de knop gebruiken om te schakelen tussen eenheden (centimeters en inches ). De schakelaar is alleen actief voor de service.
Extra lassen starten optie - de schakelaar maakt het mogelijk om te starten de cyclus van het lassen met behulp van twee drukknoppen (of een van hen als een toets schakelaar tweehandbediening is uit positie) op de zwarte hand Fig. 7). De schakelaar is alleen actief voor de service.
Controlelampjes die de status van de sensoren van de machine (Sensoren) weergeven:
elektrode omhoog - het controlelampje , ingeschakeld , signaleert dat de grens schakelaar die de bovenste elektrode positie aangeeft, ingeschakeld is;
elektrode omlaag - het controlelampje , ingeschakeld , geeft aan dat de eindschakelaar die de positie van de onderste elektrode aangeeft, ingeschakeld is;
tabel aandrijving positie - de geactiveerde besturing signalen de aandrijving positie van de tafel en voorkomt zo het begin van het lassen;
noodgeval elektrode omhoog - de controle licht, ingeschakeld uit, signaleert dat de elektrode weerstand heeft ondervonden terwijl liet zakken (bijv. het is ingedrukt naar de bank) en de eindschakelaar is uitgeschakeld uit;
het passeren van begin - het controlelampje , ingeschakeld , geeft aan dat de laskop verplaatst is naar het begin van de bank en de grensschakelaar is ingeschakeld;
het passeren van einde - het controlelampje , ingeschakeld , signaleert dat de laskop naar het einde van de werkbank is verplaatst en de eindschakelaar is ingeschakeld .
De Alarm geschiedenis knop - opent het scherm met de opgeslagen geschiedenis van alarmen die hebben plaatsgevonden in de machine binnen het afgelopen jaar. De alarmgeschiedenis wordt opgeslagen in het geheugen van de De alarmgeschiedenis voor elke dag wordt opgeslagen als een bestand onder de naam EL gegevens, bijv. EL_20131122. Het is mogelijk om de geschiedenis bestanden te kopiëren van het touch paneel's geheugen naar een USB xml-ph-0031
 Alarm berichten zijn opgeslagen in de taal geselecteerd in de servicemenu.
Alarm berichten zijn opgeslagen in de taal geselecteerd in de servicemenu.
De knop gemarkeerd, Machine werk voorwaarden opent een venster (Fig. 29), waarin de individuele parameters van de lascyclus worden ingesteld, zoals:
 De stel in waarden van alle parameters in Machine werk voorwaarden zijn voorbeelden.
De stel in waarden van alle parameters in Machine werk voorwaarden zijn voorbeelden.
Druk max. = Druk + - deze door de gebruiker gedefinieerde parameter definieert de waarde van het bovenste downforce bereik; bij overschrijding van de drempel, wordt een alarm weergegeven op het HMI paneel. De drukregeling start wanneer het HF proces begint.
Druk min. = Druk - - deze door de gebruiker gedefinieerde parameter definieert de waarde van het onderste downforce bereik. Een alarm wordt weergegeven zodra de drempelwaarde op het HMI-paneel is overschreden; de drukregeling begint wanneer het HF-proces begint.
Tabel vertraging tijd [s] - vertraging tijd tussen het stoppen van de laskop en het instellen van de tafel op de laspositie .
Druk op vertraging tijd - deze waarde geeft de hoeveelheid van tijd die verstrijkt sinds het moment de onderste grens schakelaar (aangegeven de onderste positie van de elektrode) wordt geactiveerd tot het moment de elektrode wordt tegen het materiaal gedrukt met volle kracht
Wacht tijd tot bereiken instellenstroom (in huidige las modus) - de parameter die de tijd aangeeft het systeem nodig heeft om een gegeven waarde voor de anodestroom te bereiken. Als de stroom niet is bereikt, binnen die tijd, zal de lascyclus onderbreken en de boodschap, 'WELDING PARAMETERS NIET GEREIKT' zal worden weergegeven. Deze parameter is alleen belangrijk in 'stroom' lassen modus.
Vermogen max = Operationeel vermogen + ... - Deze parameter wordt alleen gebruikt voor het regelen van het lasproces en voor het bepalen van het bovenste bereik van de stroomtolerantie. De parameter is instelbaar in het bereik van 0 - 1A.
Vermogen min = Werkend vermogen - ... - Deze parameter wordt alleen gebruikt voor het regelen van het lasproces en voor het bepalen van het bovenste bereik van stroomtolerantie . De parameter is instelbaar in het bereik van 0 xml-ph-0
Afb. 29 Venster Werkomstandigheden machine
Bewegingen instellingen knop opent het venster (Fig. 30), in waarin de specifieke parameters voor de aandrijving van de drukplaat, worden ingesteld, zoals :
![]() De stel in waarden van alle parameters in Bewegingen instellingen zijn voorbeelden.
De stel in waarden van alle parameters in Bewegingen instellingen zijn voorbeelden.
De lengte van tafel tussen stoppers - een parameter tot invoeren de lengte van de gemonteerde tafel op waarop de las kop beweegt. De ingevoerde afstand moet de werkende lengte van de tafel uitdrukken (vanaf de linker tafelstopper vanaf de rechter tafelstopper).
Machine las kop breedte tussen limiet schakelaars [cm] - een parameter om de machine kopbreedte tussen schakelaarlimieten in te voeren.
Minimale overlaplengte [mm] - de minimale overlaplengte die de gebruiker kan instellen in de modus handmatig en automatisch overlap .
X - Aandrijving snelheid AUTO - de parameter bepaalt de snelheid van passage in X-as de machine werkt in de automatische cyclus (uitgedrukt als een percentage van de maximale snelheid).
X - Aandrijving snelheid HANDMATIG - LAAG - de parameter bepaalt de snelheid van passage in X-as wanneer de operator de machine beweegt handmatig - licht indrukken van de joystick (uitgedrukt als een percentage van de maximale spe
X - Aandrijving snelheid HANDMATIG - SNEL - de parameter bepaalt de snelheid van doorgang in X-as wanneer de operator de machine beweegt handmatig - sterk drukken op de joystick (uitgedrukt als een percentage van de maximale spee
Y - Aandrijving snelheid AUTO - de parameter bepaalt de snelheid van passage in Y-as de machine werkt in de automatische cyclus (uitgedrukt als een percentage van de maximale snelheid).
Y - Aandrijving snelheid HANDMATIG - LAAG - de parameter bepaalt de snelheid van doorgang in Y-as wanneer de operator de machine beweegt handmatig - licht indrukken van de joystick (uitgedrukt als een percentage van de maximale spe
Y - Aandrijving snelheid HANDMATIG - SNEL - de parameter bepaalt de snelheid van passage in Y-as wanneer de operator de machine beweegt handmatig - sterk drukken op de joystick (uitgedrukt als een percentage van de maximale spee
Stel in op basis as X - de knop start het proces van homing de X as - het bepalen van het nulpunt voor de verplaatsing van de kop. Om te starten, de knop ingedrukt houden. De xml-ph-0031@deepl.inte Als de knop uitgaat is het proces beëindigd . Tijdens het proces homing, de laskop beweegt naar de links totdat de eindschakelaar werkt en stuitert van de eindschakelaar met de lengte die in het programma is ingesteld.
Stel in op basis as Y - de knop start het proces van homing de Y as - het bepalen van het nulpunt voor de verplaatsing van de kop. Om te starten, de knop ingedrukt houden. De xml-ph-0031@deepl.inte Wanneer de knop uitgaat is het proces beëindigd . Tijdens het proces homing, beweegt de laskop naar de voorkant totdat de eindschakelaar werkt en gaat naar de basispositie (ongeveer het midden van as).
![]() Tijdens de naar proces, de lassen hoofd verhuist binnen het assortiment van de geselecteerd basis as. Er moet zijn geen hindernis op het rijpad van de machine.
Tijdens de naar proces, de lassen hoofd verhuist binnen het assortiment van de geselecteerd basis as. Er moet zijn geen hindernis op het rijpad van de machine.
![]() Asinstelling moeten gedragen uit tijdens:
Asinstelling moeten gedragen uit tijdens:
- de eerste na-service opstarten,
- op het moment van het veranderen van de positie van de eindschakelaar,
- wanneer de plaats van het element / machine is fysiek veranderd (verandering van spanketting).
![]() Tijdens de naar proces, de lassen hoofd verhuist binnen het assortiment van de geselecteerde basisas.
Tijdens de naar proces, de lassen hoofd verhuist binnen het assortiment van de geselecteerde basisas.
Omvormer regeling versterking - een parameter met een direct effect op de snelheidsregeling van de omvormer.
Stel positie invoor breekafstand [cm] - De parameter bepaalt de remafstand van de laskop , voordat de gewenste positie bereikt (uitgedrukt in inch of centimeter afhankelijk van de positie van de eenheid schakelaar in het service menu).
As Y ondergrens [mm] - de parameter specificeert de minimale afstand waarmee de aandrijving met de kop achteruit kan bewegen, in de richting van de Y-as (uitgedrukt in inch of centimeter afhankelijk van de positie van de eenheidsschakelaar in het menu service ).
As Y bovengrens [mm] - de parameter specificeert de maximale afstand waarmee de aandrijving met de kop achteruit kan bewegen, in de richting van de Y-as (uitgedrukt in inch of centimeter afhankelijk van de positie van de eenheidsschakelaar in het menu service ).
Fig. 30 Instellingenvenster Bewegingen
Knop Proces controle - deze opent het venster (Afb. 31 ) voor het definiëren van de parameters van het lasproces . Er wordt een alarm weergegeven op de HMI als de lascriteria ingestelde niet is bereikt. De operator kan de individuele parameters in xml-ph-0030@deepl.inte instellen.
Vermogen max = Bedrijfsvermogen + ... - Deze parameter wordt alleen gebruikt voor het regelen van het lasproces en voor het bepalen van het bovenste bereik van de stroomtolerantie . De parameter is instelbaar in het bereik van 0 - 1A.
Vermogen min = Operationeel vermogen - ... - Deze parameter wordt alleen gebruikt voor het regelen van het lasproces en voor het bepalen van het bovenste bereik van de stroomtolerantie . De parameter is instelbaar in het bereik van 0 - 0,5A.
Setpoint % voor de huidige die is te zijn in tolerantie - deze parameter specificeert het percentage waarde van de tijd voor die de huidige is vereist te zijn binnen tolerantie. Wanneer het voorgeschreven percentage drempel niet is bereikt, zal een alarm worden weergegeven op het HMI paneel om aan te geven dat de lasparameters niet zijn bereikt. De parameter wordt uitgedrukt als een percentage, in het bereik van 0-100%.
Gemeten totaal lassen tijd [s]: - deze parameter toont de totale tijd die in beslag heeft genomen door de laatste las. De tijd wordt geteld vanaf het moment dat de stroom opgeslagen in het recept is bereikt.
Gemeten lassen tijd wanneer de stroom was binnen de tolerantie [s]: - Deze parameter toont de tijd van de laatste las, echter het is alleen geteld voor de stroom binnen de tolerantie bereik +/- (Vermogen max/min) voorgeschreven in de bovenstaande parameters.
Berekende waarde voor waarbij de stroom binnen de tolerantie [%]: - Deze parameter toont het percentage van de tijd gedurende welke de stroom binnen het tolerantiebereik +/- was gedurende de gehele cyclus.
Druk max. = Druk + - deze door de gebruiker gedefinieerde parameter definieert de waarde van het bovenste downforce bereik; bij overschrijding van wordt een alarm weergegeven op het HMI paneel. De druk xml-ph-0030@deepl.int
Druk min. = Druk - - deze door de gebruiker gedefinieerde parameter definieert de waarde van het onderste downforce bereik. Een alarm wordt weergegeven zodra de drempelwaarde op het HMI-paneel is overschreden; de drukregeling begint wanneer het HF-proces begint.

Fig. 31 Lasprocesbesturingsvenster
De knop Statistieken - opent een venster (Afb. 32), in waarin de statistieken van de werking van de machine wordt verzameld . Elke rij in de tabel heeft betrekking op een van de gedeeltelijke las van de machine, terwijl de kolommen tonen details van de las, zoals wanneer het werd gemaakt, welk recept werd gebruikt, welke operator xml-ph-... Gedetailleerde informatie over elke las maakt het mogelijk het volledige proces van één enkele lascyclus te traceren en te weten te komen welke waarden van anode stroomsterkte en druk werden bereikt. Daarnaast toont de tabel eerder geregistreerde gegevens. Aan de rechterkant is een keuzelijst van data met elke datum toont een dag van de machine werking. Om de gegevens te bekijken voor een gegeven
Tijd - tijd van de opname van de cyclus;
Datum - datum van de registratie van de cyclus;
1 - Recept- de naam van het recept gebruikt in de geregistreerde cyclus;2 - Operator - de naam van de operator die is aangemeld tijdens de uitvoering van de cyclus;
3 – Condensatorpositie [%] - start positie van de condensator;4 - Vertragingstijd [ s ] - vertragingstijd instellen;
5 - Lasduur [ s ] lasduur instellen ;
6 - Koeltijd [ s ] - koeltijd instellen;
7 – Vermogen [ 1 - 6 ] - stel in vermogensniveau;8 – Anode instellen huidige [A] - anodestroom stel in tijdens het lassen proces;
9 – Druk instellen [bar ] - stel in druk tijdens het lasproces;
10 – Werk stand [0-1] - de parameter definitie van de lassen werk modus. A gedetailleerd beschrijving van de "Tijd" en "Huidige" werking modi is vindt u op pagina's 71-72 van de documentatie;
11 – Regeling stand 0-1] - de parameter definitie van de bereik van automatische aanpassing stand van de uitgang condensator. A gedetailleerd beschrijving van de 1 (MAX) en 0 (MIN) werking modi is voorzien op pagina's 73-74 van de documentatie;
12 – Aandrijving stand - lassen hoofd aandrijving stand op de werktafel. A gedetailleerde beschrijving van de alle aandrijving modi is op op pagina's 74,77 van de documentatie;
13 – Auto overlap [0-1] - een van twee mogelijk opties voor de berekeningen van de overlapping gekozen door betekent van de Overlap drukknoppen. 1 betekent auto overlapping, 0 betekent manu overlappen (zie documentatie op pagina 76);
14 – Laslengte - de laslengte;
15 – Lengte elektrode - de elektrode lengte gebruikt in de cyclus;
18 – Gedeeltelijk lasnummer - de aantal doorsnede lassen;
19 – Proces controle actief [0-1] - activeert of deactiveert de HF algoritme voor procesregeling (zie documentatie op pagina's 91-93);
20 – Proces status [0-1] - status van de proces, waarbij 0 geeft aan een fout - een onderbroken processor of lassen parameters dat hebben niet zijn geweest bereikt, 1 geeft aan succes - de lassen proces liep volgens naar de vooraf ingestelde parameters;
21 – Huidige in tolerantie [0-1] - parameter definitie van of de huidige waarde was binnen of uit van tolerantie De anode huidige verkregen moet zijn binnen +/- van de tolerantie bereik van de anode huidige waarde voor a gegeven percentage van de tijd voor de duur van het lassen. 1 middelen dat een tolerantie anode stroom werd verkregen tijdens lassen. 0 betekent bereiken de anode huidige buiten het tolerantiebereik;
22 – Druk in tolerantie [0-1] - parameter definitie van of de druk was binnen of uit van tolerantie De druk verkregen moet zijn binnen +/- van het tolerantiebereik van de drukwaarde. 1 betekent dat een tolerantiedruk werd bereikt tijdens het lassen. 0 betekent dat de anodestroom buiten het tolerantiebereik is bereikt;
23 - Gemiddelde anodestroom [A] - gemiddelde anodestroom tijdens doorsnede lassen;
24 - Gemiddelde druk [bar] - gemiddelde druk tijdens doorsnede lassen;
25 - Cyclusteller - de cyclusteller vanaf de eerste keer dat de machine is opgestart.
![]() De procesregistratie vindt alleen plaats in de automatische modus.
De procesregistratie vindt alleen plaats in de automatische modus.
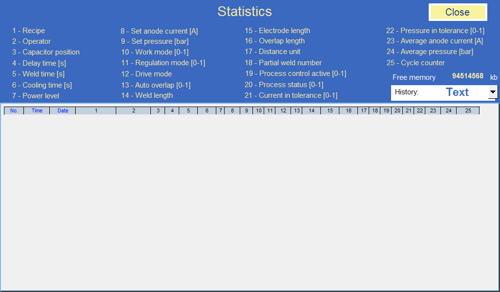
Afb. 32 Statistiekenvenster
Knop Stand-by modus - instellingen - opent een venster (Fig. 21) met tabellen Elektrode verwarming instellingen voor stand-by modus. Een gedetailleerde beschrijving van de Stand-by modus is te vinden op pagina 69-70 van de documentatie.
6.7 Geschiedenis en receptenbestanden
De volgende software is vereist voor het lezen van en het converteren van geschiedenis bestanden en recepten op een computer met Windows besturingssysteem:
de gratis, EasyBuider Pro software, die kan zijn gedownload van de HMI paneel van de fabrikant webpagina: http://www.weintek.com/ of vertegenwoordiger in Polen http://www.multiprojekt.pl/ftp/weintek_hmi/easy_builder_pro/Microsoft Excel of andere spreadsheet programma.
6.7.2 Conversie van geschiedenisbestanden in xlsx.
Om historische gegevens te lezen, moet deze worden gedownload van het geheugen van het touch panel op de PC; deze moeten worden ingevoerd in de juiste map; dubbelklik op het bestand met de datum in vraag; een xlsx (Excel) bestand zal dan worden gegenereerd. Het bestand presenteert de historische gegevens van belang op een duidelijke en transparante manier.
6.7.3 De computer verbinden met de machine via WiFi
Elke machine is uitgerust met een WiFi router, die, op zijn beurt, is verbonden met het bedieningspaneel. Om uw computer aan te sluiten op dit netwerk volgt u deze stappen:
Op de computer uitgerust met a draadloos netwerk kaart, selecteer de netwerk met a naam overeenkomstig naar de fabriek aantal de machine zoals opgeslagen op het typeplaatje, bijvoorbeeld: D650-QE-104.6.7.4 Het IP adres van de machine om recepten en geschiedenis te kopiëren bestanden
Het touch paneel krijgt een vast IP adres toegewezen. Om dit te lezen, moet je:
- Druk op het pictogram met een pijl in de rechterbenedenhoek van het aanraakpaneel

- Dit opent het contextmenu van het paneel
- Druk op het tweede pictogram vanaf de links, een kaart met de letter 'i'. Dit opent het venster 'Systeem Informatie'; het IP adres dat nodig is om een netwerkverbinding met het paneel te maken, wordt daar weergegeven.
- Na het opslaan van het IP adres, druk op OK - het venster zal sluiten.
6.7.5 Geschiedenis kopiëren bestanden vanaf het HMI-paneel via het WiFi-netwerk netwerkAls je computer is verbonden met een WiFi-netwerk:
- Open Windows Verkenner in elke map en ga naar de volgend op formule in de adres bar waarbij de IP adres is gevestigd, voor voorbeeld: 192.168.189.10; de adres lees van de aanraken paneel moet worden ingevoerd:ftp://uploadhis:111111@192.168.189.10/
- Klik dan op 'Enter
- Er wordt een venster geopend met het geheugen van het aanraakscherm
- De volledige inhoud van elke map kan gekopieerd worden . Het is ook mogelijk om individuele bestanden te kopiëren die opgeslagen zijn in de mappen.
6.7.6 Gegevens gearchiveerd in het geheugen van het HMI touch panelRecepten kopiëren, werkgeschiedenis en alarmgeschiedenis op a USB-apparaat:
1. Steek een USB geheugen apparaat in de poort van het HMI touch paneel.
2. Klik op OK. Op het scherm van het HMI-paneel verschijnt een venster , druk op Upload.
3. In het volgende venster, selecteer geschiedenis bestandenuploaden, voer het wachtwoord in: 111111 en druk op OK.
4. Open de map gemarkeerd "usbdisk" en selecteer de map "disk_a_1", druk vervolgens op OK.
In het USB geheugen wordt de"geschiedenis" opgeslagen, met daarin de mappen:
- "datalog"→ "trend" - de map "trend" bevat bestanden met records van de werkende parameters van de machine. Elke dag wordt één bestand opgeslagen onder de overeenkomstige datum. Om historische gegevens te lezen, plaatst u het USB-geheugen in de computer, vervolgens in de map "TREND" , dubbelklik op het vereiste bestand om te genereren een bestand in het xls formaat (Excel) in volgorde om duidelijk te zien de geschiedenis van de werking van de machine of om te genereren een grafiek voor een bepaalde xml-ph-0 Om xls bestanden te genereren, is de gratis software programma EasyBuider Pro nodig ; deze moet worden gedownload van de website van de fabrikant van het HMI-paneel: http://www.weintek.com/.
- "eventlog" - de map "eventlog" bevat bestanden met records van de geschiedenis van alarmen die hebben plaatsgevonden tijdens de werking van de machine . De geschiedenis van alarmen voor elke dag wordt opgeslagen als een bestand met de naam EL_data, bijvoorbeeld EL_20131122. Om historische gegevens te lezen, de USB geheugen in de computer, dan dubbelklik op de vereiste bestand te genereren een bestand in de xls formaat (Excel) om duidelijk zien de alarm geschiedenis xml-ph-0030@deepl.inte Voor het genereren van xls bestanden is de gratis software programma EasyBuider Pro nodig; deze moet worden gedownload van de website van de fabrikant van het HMI-paneel: http://www.weintek.com/.
- "recept" - de map "recept" bevat twee bestanden met recepten gekopieerd van het HMI paneel: "recipe.db" en "recipe_a.rcp". De bestanden kunnen worden gebruikt als back-up voor de recepten of om de recepten xml-ph-0030@deepl.i op te slaan. Het is ook mogelijk om recepten te bewerken op de computer.
Recepten bewerken gekopieerd van het HMI-paneel:
Om recepten te bewerken, is de gratis software programma EasyBuider Pro nodig ; deze moet gedownload worden van de website van de fabrikant van het HMI paneel: http://www.weintek.com/.
1. Plaats het USB-geheugen- met gekopieerde recepten -in de computer en open de toepassing Utility Manager . Kies in de toepassing Recipe Database Editor in het gedeelte Data Conversion .
2. In de toepassing Recept Database Editor klik op Import... en selecteer de bestanden met gekopieerde recepten"recipe.db".
3. Het venster voor het bewerken van recepten wordt geopend .
4. Wanneer het bewerken van klaar is , klik op Exporteren... en sla het bestand op in zijn vorige locatie.
Recepten kopiëren vanaf een USB-geheugen:
- Steek het USB-apparaat in de poort van het HMI-aanraakpaneel.
- Op de scherm van de HMI paneel, a raam zal verschijnen, klik op op Downloaden.
-
In het venster volgende , selecteer Download geschiedenis bestanden, voer het wachtwoord in: 111111 en klik op OK.
4. Open de map "usbdisk" en selecteer de map "disk_a_1", dan klik op OK.
Recepten worden geladen in het geheugen van het HMI touch paneel. Zet de machine uit en vervolgens aan.
Het aanraakpaneel kan ook worden beveiligd tegen onbevoegde toegang. Het is niet mogelijk om op de machine te werken zonder dat de gebruiker inlogt op het aanraakpaneel.
1. Nadat u de machine hebt aangezet, klikt u op de knop "Log-in" op het venster van het touch panel, op de status balk onderaan.

2. Er wordt een contextvenster geopend om in te loggen.
Afb. 33 Aanmeldingsvenster
3. Selecteer een geschikt gebruiker van de vervolgkeuzelijst.4. Voer de geschikt wachtwoord.
5. Druk op de Aanmelden knop.
6. De gebruikersnaam zal verschijnen in de veld 'Aangemeld gebruiker".
7. Druk op OK en het venster zal sluiten.
 In de hoofdpagina raam, volgende naar de inloggen knop, de naam van de De gebruiker die momenteel is ingelogd is weergegeven.
In de hoofdpagina raam, volgende naar de inloggen knop, de naam van de De gebruiker die momenteel is ingelogd is weergegeven.
 Na de machine is geschakeld uit, de gebruiker is gelogd automatisch uit.
Na de machine is geschakeld uit, de gebruiker is gelogd automatisch uit.
Het wachtwoord wijzigen dat aan de gebruiker is toegewezen.
1. Meld u aan als een gebruiker met de bevoegdheid om wachtwoorden te wijzigen .
2. Druk op de knop'Pas wijzigen'.
4. Voer de Nieuw wachtwoord.
5. Druk op 'Verander'.
6. Druk op OK en het venster zal sluiten.
Fabriek aangemaakte gebruikers en hun toegewezen wachtwoord(en)
GEBRUIKERSNAAM - WACHTWOORD
SERVICE - BEDOELD VOOR SERVICE DOOR DE FABRIKANT;
Operator - 100
Supervisor - 111 Machtigingen:
OPERATOR - kan werken op de machine, kan recepten selecteren, kan geen recepten bewerken en de geavanceerde opties machine op het venster van het Servicemenu.
Supervisor - kan werken op de machine, recepten selecteren, recepten bewerken, parameters wijzigen, de wachtwoorden van andere gebruikers wijzigen.
6.9 Aansluiting op stroombron
 ONDER GEEN OMSTANDIGHEDEN moet de machine zijn bediend door ongekwalificeerd personeel. De machine operators moeten zijn vertrouwd met de beroeps veiligheid en gezondheidsregels.
ONDER GEEN OMSTANDIGHEDEN moet de machine zijn bediend door ongekwalificeerd personeel. De machine operators moeten zijn vertrouwd met de beroeps veiligheid en gezondheidsregels.
Voordat de machine wordt aangesloten op een voedingsbron moeten de volgende procedures worden uitgevoerd :
- Zorg ervoor dat de werkomgeving van de machine (de omgeving van de machine en ) schoon is en in orde is of er geen obstakels zijn die een negatieve invloed kunnen hebben op de standaard bedrijfscyclus van de machine; en
- Zorg ervoor dat de adequate hoeveelheid van ruw materiaal (teststukjes ) wordt voorbereid ; en
- Zorg ervoor dat de afvalbakken en containers voor gelaste producten op de juiste plaats zijn geplaatst maar in dicht bij de machine als gevolg van de eisen van Bayer toepassen op de productiecyclus indien van toepassing; en
- Zorg ervoor dat alle afschermingen goed zijn bevestigd aan de machine en zijdeuren van een schakelkast gesloten zijn; en
 ATTENTIE ! Schakelkast deuren moet zijn altijd gesloten zelfs als de machine is gestopt.
ATTENTIE ! Schakelkast deuren moet zijn altijd gesloten zelfs als de machine is gestopt.
 De machine herstart procedure is onmogelijk naar zijn uitgevoerd wanneer de schild is ongepast bijgevoegd naar de machine of de deuren van de schakelkast open zijn
De machine herstart procedure is onmogelijk naar zijn uitgevoerd wanneer de schild is ongepast bijgevoegd naar de machine of de deuren van de schakelkast open zijn
5. Controleer of de knop NOODGEVALLEN STOP is losgemaakt. Als de drukknop met paddestoelvormige kop vastzit, draai hem naar rechts.
 De herstart procedure kan niet zijn artiest wanneer de NOODSTOP knop is vastgelopen (stuck).
De herstart procedure kan niet zijn artiest wanneer de NOODSTOP knop is vastgelopen (stuck).
7. Maak zeker de handbediend gecomprimeerd lucht uitschakeling ventiel (Afb.9) is uitgeschakeld, in het geval dat de klep moet worden ingeschakeld - draai deze naar de linker - ON positie; en
8. Maak zeker de niveau van druk in de pneumatisch systeem is tussen 0,4 en 0.8 MPa (de gewaardeerd werking druk van de machine komt naar 0,6 MPa) als de heeft nodig ontstaat gedrag instelling procedure met de help van de gecomprimeerde lucht afsluitklep (Fig.9). en
9. Maak zeker de HOOFD SWITCH is stel in naar 1-AAN positie en als a resultaat het POWER-lampje begint te knipperen op het bedieningspaneel; en
 LET OP: NOODGEVALLEN STOP knop kan zijn ingedrukt op elk moment van werk cyclus vooral wanneer de noodgevallen uitschakeling is onmiddellijk nodig.
LET OP: NOODGEVALLEN STOP knop kan zijn ingedrukt op elk moment van werk cyclus vooral wanneer de noodgevallen uitschakeling is onmiddellijk nodig.
10. Zorg ervoor dat de machine opnieuw wordt gestart met de hulp van de blauwe RESTART toets, dan wacht gedurende 30 seconden binnen die de machine volledig moet worden geactiveerd en maak klaar voor werk als de indicator in het licht signaal kolom begint groen te knipperen en de voortgangsbalk gevonden in het hoofdscherm van het HMI paneel volledig groen is.
 ATTENTIE ! Na druk op de RESTART (na draaien op de machine) zal zijn basing lassen hoofd - de as motie achterwaarts / vooruit.
ATTENTIE ! Na druk op de RESTART (na draaien op de machine) zal zijn basing lassen hoofd - de as motie achterwaarts / vooruit.
 In geval de alarm bericht is weergegeven zelfs als de machine was opnieuw opgestart zie hoofdstuk 6.6.2.
In geval de alarm bericht is weergegeven zelfs als de machine was opnieuw opgestart zie hoofdstuk 6.6.2.
11. Zorg ervoor dat de elektrode is gemonteerd op de houder.
 ATTENTIE ! Een elektrode moet zijn altijd gemonteerd op de houder wanneer het gaat naar gesloten zijn.
ATTENTIE ! Een elektrode moet zijn altijd gemonteerd op de houder wanneer het gaat naar gesloten zijn.
 Zie hoofdstuk 6.13. voor meer informatie toepassen naar de Procedure voor gereedschap Vervanging en Omgeving.
Zie hoofdstuk 6.13. voor meer informatie toepassen naar de Procedure voor gereedschap Vervanging en Omgeving.
- Til de elektrode naar de bovenste positie.
- Zet de HOOFDSCHAKELAAR in de stand 0-UIT - dit betekent dat de machine is uitgeschakeld.
- Zet de handbediende persluchtafsluiter uit (om de procedure uit te voeren - draai de klep naar rechts - UIT-stand)
- Breng de werkomgeving rond de machine in orde.
- Zowel de stekker van de stroomtoevoer als die van het persluchtsysteem moeten uit het stopcontact worden getrokken in geval van langdurige werkonderbreking (beide stekkers moeten uit het stopcontact worden getrokken).
6.11 Test- en instelprocedure
 LET OP! De testprocedure kan worden uitgevoerd zolang de machine op de juiste manier is opgestart - zie hoofdstuk 6.5.9.
LET OP! De testprocedure kan worden uitgevoerd zolang de machine op de juiste manier is opgestart - zie hoofdstuk 6.5.9.De test- en instelprocedure moet in de praktijk worden gebracht wanneer:
- de machine voor het eerst is ingeschakeld,
- het vervangen van gereedschap nodig is (wanneer dit nodig is),
- de onderhoudsprocedure is voltooid,
- De operators moeten bekend zijn met de functionaliteit van de machine.
Om de genoemde procedure uit te voeren, moet de operator:
1. Stel de temperatuur in die moet worden gehandhaafd door de elektrode tijdens het lassen (bijv. 40oC voor testen) met behulp van ELECTRODE TEMPERATUUR thermo-regelaar.
2. Ga naar het aanraakgevoelige paneel: HMI → Venster voor vermogensinstelling → stel de instelmodus van de condensator in op HANDMATIG → controleer met behulp van de toetsen "-" en "+" of de procedure voor het wijzigen van de positie van de condensator soepel verloopt bij elk vermogensniveau van 0 tot 100%. Zodra de controleprocedure is voltooid, zet u de instelmodus van de condensator op AUTO.
3. Zet de HF OFF/ON-schakelaar in de stand OFF.
4. Upload het juiste recept uit het geheugen van het aanraakgevoelige paneel: HMI → Receptendatabasevenster → markeer het gewenste recept in de grafiek → klik vervolgens op Laad voor productie toets of vul de volgende vakjes in van de lascyclusparameters in het hoofdscherm:
- Initieel vermogen;
- Bedrijfsvermogen;
- Vertragingstijd;
- Lastijd;
- Afkoeltijd;
- Vermogensniveau;
6. Druk op op het HMI-paneel: HMI → Venster HF-kopaandrijving → Rijmodus
→ A;
7. Druk op op het HMI-paneel: HMI → Hoofdscherm → Opties → Temperegeling → aan;8. Druk op op het HMI-paneel: HMI → Hoofdscherm → Werkmodus → 0 ;
9. Druk op op het HMI-paneel: HMI → Hoofdscherm → Regelmodus→ 1;
10. Zorg ervoor dat een isolatiekussentje op de werktafel of op het tussenschot van aluminiumplaat schoon is - het mag niet vuil of mechanisch beschadigd zijn op de plaats waar de elektrode tegen het lasmateriaal wordt gedrukt;
 ATTENTIE ! De isolerende onderlegger moet zijn geplaatst worden direct onder de gelast materiaal als het is verondersteld om beschermen de operator tegen een elektrische vlamboog gevormd tussen de lassen elektrode en de werktafel.
ATTENTIE ! De isolerende onderlegger moet zijn geplaatst worden direct onder de gelast materiaal als het is verondersteld om beschermen de operator tegen een elektrische vlamboog gevormd tussen de lassen elektrode en de werktafel.
 ATTENTIE ! Als de verdeler was overdekt met de isolerend pad het moet plakken naar de tabel strak - in dergelijke a weg dat geen onzuiverheden tussen de verdeler en de werktafel kon worden gevonden.
ATTENTIE ! Als de verdeler was overdekt met de isolerend pad het moet plakken naar de tabel strak - in dergelijke a weg dat geen onzuiverheden tussen de verdeler en de werktafel kon worden gevonden.
12. Voer het homing in de X- en Y-as uit. Tijdens het homingproces beweegt de laskop. Het homingproces wordt gesignaleerd door de achtergrondverlichting van de knop.
13. De werking van de joystick testen
 te vinden op de bedieningspreekstoel. Beweeg de machine naar rechts en vervolgens naar links. Bij een lichte druk op de joystick moet de machine langzaam bewegen; bij een sterkere druk moet de machine sneller bewegen.
te vinden op de bedieningspreekstoel. Beweeg de machine naar rechts en vervolgens naar links. Bij een lichte druk op de joystick moet de machine langzaam bewegen; bij een sterkere druk moet de machine sneller bewegen.14. De werking van de joystick testen
 te vinden op de bedieningspreekstoel. Beweeg de koplassen naar voren en vervolgens naar achteren. Met een lichte druk op de joystick moet de machine langzaam bewegen; met een sterkere druk - moet de machine sneller bewegen.
te vinden op de bedieningspreekstoel. Beweeg de koplassen naar voren en vervolgens naar achteren. Met een lichte druk op de joystick moet de machine langzaam bewegen; met een sterkere druk - moet de machine sneller bewegen.15. Gebruik de knop
16. Controleer in het venster Servicemenu of de elektrode naar beneden indicator brandt.
17. Als de veiligheidsmaatregel, aangegeven door het bericht NOODELEKTRODE UP wordt geactiveerd - de elektrode die op het materiaal is neergelaten, komt spontaan omhoog. In het bovenstaande geval moet de eindschakelaar die de onderste elektrodepositie aangeeft, worden afgesteld zoals beschreven in hoofdstuk 6.4.
18. Gebruik de knop
19. Controleer in de Service menu venster om te zien of de elektrode op indicator brandt.
20. Test het omhoog en omlaag bewegen van de elektrode meerdere keren om te controleren of het soepel beweegt.
21. Laat de laselektrode op het materiaal zakken en druk op de START knop - de automatische lascyclus moet worden uitgevoerd met de hoogfrequente generator uitgeschakeld.
23. Zet de schakelaar HF OFF/ON in de stand ON ,
2. Druk op op het HMI-paneel: HMI → Hoofdscherm → Regelmodus → 1 of 0;
 Werk stand huidige / tijd (1/0) en Regeling Modus min / max (0/1) zijn beschreven in detail in hoofdstuk 6.6.5.
Werk stand huidige / tijd (1/0) en Regeling Modus min / max (0/1) zijn beschreven in detail in hoofdstuk 6.6.5.
3. Laat de laselektrode zakken op het materiaal precies in de plaats van de las.
 LET OP: Het is mogelijk naar stop de lassen proces herhaaldelijk op elk gewenst moment met behulp van de STOP drukknop.
LET OP: Het is mogelijk naar stop de lassen proces herhaaldelijk op elk gewenst moment met behulp van de STOP drukknop.
4. Druk op de knop START - een automatische lascyclus volgens de parameters aangegeven in het venster van het hoofdpaneel HMI zal starten. Indicaties van de ANODE STROOM meter moeten worden geobserveerd - tijdens lassen; de stroom moet toenemen binnen het bereik groen gemarkeerd op de schaal van de meter.
5. Als het hele proces is afgerond , moet de kwaliteit van de las worden beoordeeld . Praktische kennis is onontbeerlijk voor een correcte beoordeling; daarom is het het beste om het advies van het personeel van de contractor in te winnen en de eerste machine opstart met hem uit te voeren .
6. Als de afdichting naad geproduceerd is ongelijk langs de hele uitbreiding, moet je het hoofdstuk 6.14 lezen.
7. Afhankelijk van het effect van het lassen (gelast, niet gelast, oververhit) lassen parameters moeten dienovereenkomstig worden aangepast :
- Initieel vermogen;
- Bedrijfsvermogen;
- Vertragingstijd;
- Lastijd;
- Afkoeltijd;
- Vermogensniveau;
- Druk.
8. Zorg ervoor dat de volgende parameters ondergingen vele uren van testen met betrekking tot: werken op dezelfde soort van materiaal, werkcyclus van de machine en functionaliteit, ergonomie van de machine normen die zijn cruciaal voor het voorkomen van ernstig letsel tijdens productiecyclus;
9. Zodra de parameters esthetiek en sterkte zijn bereikt moeten de waarden worden opgeslagen als recept: HMI → Hoofdscherm → klik op de knop RECIPE OPSLAAN → Recepten database venster → voer de naam van het recept in de rij met de titel Recept bewerken → druk op de toets Create new .
10. Zet de schakelaar HF OFF/ON in de stand OFF ,
11. Breng de elektrode omhoog naar de bovenste positie .
12. Druk op op het HMI-paneel: HMI → Hoofdscherm → Werk modus → 0 ;
13. Druk op op het HMI paneel: HMI → HF Head Drive venster → Drive Mode → AB;
14. Druk op op het HMI paneel: HMI → HF Head Drive venster → Overlap → auto;
15. Spreid het te lassen materiaal uit op de werkbank.
16. Voer las lengte in op het touch-panel: HMI → HF Kop Rijden venster → WELD LENGTE(WL).
17. Plaats elektrode lengte op het touch-panel: HMI → HF Kop Aandrijvingsvenster → ELECTRODE LENGTE (EL).
18. gebruiken de joystick  verplaatsen het naar de positie in die de lassen moet beginnen en druk op knop
verplaatsen het naar de positie in die de lassen moet beginnen en druk op knop ![]() naar lager de elektrode op de gelaste materiaal. Ervoor zorgen dat de materiaal wordt verspreid correct;
naar lager de elektrode op de gelaste materiaal. Ervoor zorgen dat de materiaal wordt verspreid correct;
19. Druk op de knop START op het bedieningspaneel - een automatische lascyclus begint met de hoogfrequente generator uitgeschakeld .
20. De machine last langs de ingevoegde lengte en stopt dan.
21. Druk op en houd ingedrukt: HMI → HF Kop Aandrijving venster → Handmatig Aandrijving → A op het touch-panel - de laskop zal verplaatsen naar de positie boven de eerste las.
22. Druk op en houd ingedrukt: HMI → HF Kop Aandrijving venster → Handbediening → B op het touch-panel - de laskop beweegt naar de positie boven de laatste las.
23. Druk op en houd ingedrukt: HMI → HF Kop Aandrijving venster→ Handmatige aandrijving → GO TO TABLE END on the touch-panel - the welding head will move to the end of the bench.
24. Controleer of de pass einde controle is ingeschakeld op in het Service menu venster.
25. Druk op en houd ingedrukt: HMI → HF Kop Aandrijving venster → Handmatige aandrijving → GO TO TABLE BEGINNING on the touch panel - the laskop will move to the beginning of the bench.
26. Controleer of de passerende beginnende controle lampje is ingeschakeld in het venster Servicemenu .
27. Schrijven: HMI → HF Hoofd Aandrijving raam → Handmatig Aandrijving → Verplaats over  , voor voorbeeld 100cm (of 39 inch als de eenheid schakel op de servicemenu is op inch positie) op de aanraakpaneel en dan druk op de Ga naar Drukknop naast het - de laskop beweegt 100cm (of 39 inch als de apparaatschakelaar op de het servicemenu is op inch positie) naar rechts.
, voor voorbeeld 100cm (of 39 inch als de eenheid schakel op de servicemenu is op inch positie) op de aanraakpaneel en dan druk op de Ga naar Drukknop naast het - de laskop beweegt 100cm (of 39 inch als de apparaatschakelaar op de het servicemenu is op inch positie) naar rechts.
 Als de ingevoerd waarde is gemarkeerd in rood, het betekent dat de laskop kan niet zijn Verplaatst door de stel in waarde. Als de hoofd is niet op de rand van de tabel en het is fysiek mogelijk naar rijden, controleren of de tabel lengte heeft zijn geweest correct ingevoerd in de servicemenuvenster.
Als de ingevoerd waarde is gemarkeerd in rood, het betekent dat de laskop kan niet zijn Verplaatst door de stel in waarde. Als de hoofd is niet op de rand van de tabel en het is fysiek mogelijk naar rijden, controleren of de tabel lengte heeft zijn geweest correct ingevoerd in de servicemenuvenster.
 Wanneer de Ga naar drukknop is ingedrukt, de richting in die de machine verhuist hangt af van op de ingevoerd karakter, als daar is een positief waarde (zonder teken) de machine zal Ga naar naar de rechts, als de ingevoerd waarde negatief is, gaat de machine naar links.
Wanneer de Ga naar drukknop is ingedrukt, de richting in die de machine verhuist hangt af van op de ingevoerd karakter, als daar is een positief waarde (zonder teken) de machine zal Ga naar naar de rechts, als de ingevoerd waarde negatief is, gaat de machine naar links.
28. Schrijven: HMI → HF Hoofd Aandrijving raam → Handmatig Aandrijving → Verplaats over  , voor voorbeeld 50 mm (of 1,95 inch als de eenheid schakel op de servicemenu is op inch positie) op de aanraakpaneel en dan druk op de Ga naar drukknop naast het - de lassen hoofd zal verplaatsen 50 mm (of 1,95 inch als de apparaat inschakelen de servicemenu staat aan inch positie) naar de terug.
, voor voorbeeld 50 mm (of 1,95 inch als de eenheid schakel op de servicemenu is op inch positie) op de aanraakpaneel en dan druk op de Ga naar drukknop naast het - de lassen hoofd zal verplaatsen 50 mm (of 1,95 inch als de apparaat inschakelen de servicemenu staat aan inch positie) naar de terug.
29. Druk op en houd ingedrukt: HMI → HF Kop Aandrijving venster → Handmatige aandrijving → Een op het touch-panel - de laskop zal verplaatsen naar de positie boven de eerste las.
30. Zet de schakelaar HF OFF/ON in de stand ON ,
31. Gebruik de knop om de elektrode op het gelaste materiaal te laten zakken en zorg ervoor dat het materiaal correct wordt verdeeld,32. Druk op de START-knop op het bedieningspaneel - een automatische lascyclus met hoge frequentie begint.
Als er een speciale elektrode in de houder is geïnstalleerd die lassen zonder gebruik van een massa-elektrode mogelijk maakt, druk dan na het indrukken van de knop START knop op het bedieningspaneel te drukken, blijft de aardelektrode in de bovenste positie - hij zakt niet naar beneden. Na het installeren van dit type elektrode, zal in het hoofdscherm de melding " LASSEN ZONDER AARDINGSTOF! ".
33. Controleer na het maken van een volledige las of de deellassen elkaar op de juiste plaats overlappen.34. Nadat de hele sealnaad is gemaakt, moet worden gecontroleerd of de deelnaden elkaar in het overlappende gebied goed overlappen. Als dit niet het geval is, moet de parallelle positie van de elektrode worden aangepast zoals beschreven in hoofdstuk 6.14.
De eerste dienstcyclus van de operator is gebaseerd op op de volgende activiteiten:
1. Start de machine op volgens de procedure in hoofdstuk 6.9.
 LET OP! Zodra de opstartprocedure in hoofdstuk 6.5.9 met succes is uitgevoerd, begint het lasapparaat met zijn routinewerkzaamheden.
LET OP! Zodra de opstartprocedure in hoofdstuk 6.5.9 met succes is uitgevoerd, begint het lasapparaat met zijn routinewerkzaamheden. Lassen zonder isolatiekussen of wanneer het oppervlak versleten is, wordt afgeraden omdat dit kan leiden tot een boogoverslag met schade aan het machinepark tot gevolg.
Lassen zonder isolatiekussen of wanneer het oppervlak versleten is, wordt afgeraden omdat dit kan leiden tot een boogoverslag met schade aan het machinepark tot gevolg.- Initieel vermogen;
- Bedrijfsvermogen;
- Vertragingstijd;
- Lastijd;
- Koeltijd
- Machtsniveau
- Druk
- WELD LENGTH (WL) in het venster RF Head Drive;
- ELECTRODE LENGTE (EL) in het venster RF Head Drive;
- OVERLAP LENGTH (OL) (optioneel) in het venster RF Head Drive. Selecteer de automatische overlapping (druk
 knop)
knop)
8. Druk op op het HMI-paneel: HMI → Hoofdscherm → Werkmodus → 0 of 1;
9. Druk op op het HMI-paneel: HMI → Hoofdscherm → Regelmodus→ 1 of 0;
10. Klik vervolgens opnieuw op het HMI-paneel: HMI → Energie-instellingsvenster → stel de regelmodus van de condensator in op de stand AUTO ;
11. Prepareer materiaal voor het lassen op de werktafel waar de procedure moet worden uitgevoerd;
12. Beweeg de joystick in de positie waar het lassen moet beginnen en gebruik de knop om de elektrode op het gelaste materiaal te laten zakken. Zorg ervoor dat het materiaal correct geplaatst is;
13. Druk op de START-knop op het bedieningspaneel - een automatische cyclus van lassen met hoge frequentie volgens de parameters in het venster van het HMI-paneel zal starten. Let op de uitlezing van de ANODE CURRENT-meter; tijdens het lassen moet de stroom worden verhoogd binnen het groen gemarkeerde bereik op de schaalverdeling van de meter.
De laszone wordt beschermd tegen niet-ioniserende straling door de beweegbare aardelektrode die tijdens het lassen tegen de tafel wordt gedrukt, waardoor een soort condensator ontstaat die de niet-ioniserende straling moet beperken. De aardelektrode zakt boven het gelaste materiaal wanneer de hoge frequentie wordt ingeschakeld door op de START-knop op het bedieningspaneel te drukken.
 Bijzonder attentie moet zijn besteed aan de feit dat de oppervlak van de materiaal naar worden gelast is gelijkmatig verdeeld op de werk tafel en is niet gegolfd.
Bijzonder attentie moet zijn besteed aan de feit dat de oppervlak van de materiaal naar worden gelast is gelijkmatig verdeeld op de werk tafel en is niet gegolfd.
 Bijzonder attentie moet zijn besteed dat er zijn geen metaal objecten in de buurt van de aarding elektrode en eronder.
Bijzonder attentie moet zijn besteed dat er zijn geen metaal objecten in de buurt van de aarding elektrode en eronder.
Als een speciale elektrode is geïnstalleerd in de houder die lassen mogelijk maakt zonder het gebruik van een massa-elektrode , dan na het indrukken van de START knop op het bedieningspaneel , de aardelektrode zal blijven in de bovenste positie - het zal niet onderste. Na het installeren van dit type van elektrode, in het hoofdscherm zal het bericht "xml-ph-0030@deepl.
14. Wanneer de werkzaamheden beëindigd zijn, de machine uitschakelen volgens de procedure beschreven in hoofdstuk 6.10.
De laselektrodehouder is uitgerust met het automatische snelspansysteem dat wordt bediend via het aanraakgevoelige HMI-paneel. Hierdoor kan de operator tijd besparen en de elektrode verwisselen zonder instrumenten te gebruiken.
![]() LET OP! Let op het gewicht van de elektrode tijdens het verwisselen. Als de elektrode groot en zwaar is, is het ten zeerste aan te raden dat twee personen de elektrode verwisselen. Ondeskundig omgaan met de elektrode kan ertoe leiden dat de operator in zijn handen knijpt wanneer de zware elektrode uit de klem wordt gehaald.
LET OP! Let op het gewicht van de elektrode tijdens het verwisselen. Als de elektrode groot en zwaar is, is het ten zeerste aan te raden dat twee personen de elektrode verwisselen. Ondeskundig omgaan met de elektrode kan ertoe leiden dat de operator in zijn handen knijpt wanneer de zware elektrode uit de klem wordt gehaald.
Voer de volgende stappen uit om de procedure voor het vervangen van de elektrode uit te voeren:
- Sluit de machine aan op de elektrische en pneumatische voeding - de machine moet klaar zijn voor het uitvoeren van de routine bedrijfscyclus (wat betekent dat de alarmmeldingen niet mogen worden weergegeven en dat de elektrode zich in de bovenste positie moet bevinden),
- Instellen in het hoofdscherm van het paneel: HMI → Opties → elektrode → open,
- Beweeg de elektrode naar links of naar rechts (afhankelijk van de uitvoering van de machine) - de elektrode moet uit de houders glijden;
- Schuif een nieuwe elektrode over de houders die gebruikt zijn voor het vastklemmen, verplaats de elektrode naar links of naar rechts (dit hangt af van de uitvoering van de machine).
- Instellen in het hoofdscherm van het paneel: HMI → Opties → elektrode → gesloten.
6.14 Afstellen van de parallelle positie van de laselektrode ten opzichte van de tafel en de lasnaadas

Fig. 34. Elektrodegreep
Benodigd gereedschap:
Sleutel 30
Inbussleutel 4
1. Start de machine op, start hem opnieuw op en bereid hem voor op normale werking, dat wil zeggen dat er geen alarmberichten worden weergegeven op het bedieningspaneel en 'gereed aan'. Een beschrijving voor het starten van de machine is te vinden in het hoofdstuk: 6.6.2. Controleer of het afdichtingsoppervlak van de elektrode vlak is en controleer ook of de elektrode:
a. gebogen is;
b. is gedraaid;
c. inkepingen heeft;
d. uitsteeksels heeft.
Elk van de bovenvermelde defecten zal resulteren in een ongelijkmatige naad, tenzij ze expliciet werden gecreëerd, zoals voor het overtrekken van een patroon op het afdichtingsoppervlak van de elektrode.
In het geval van een dergelijk defect moet de elektrode worden gerepareerd.
3. Plaats de afdichtelektrode in de handgreep en sluit de handgreep (zie hoofdstuk 6.12.).4. Leg het te sealen materiaal klaar op de werktafel.
5. Laat de elektrode met de joystick zakken op het af te dichten materiaal.
6. Controleer in het venster van het servicemenu of de indicator voor de elektrode naar beneden brandt.
7. Als het veilig is om verder te gaan, zoals wordt aangegeven door de melding NOOD-ELEKTRODE OMHOOG - diewordt weergegeven nadat de elektrode op het materiaal is neergelaten - gaat hij automatisch omhoog. Men moet dan de eindschakelaar afstellen die naar de onderste positie van de elektrode wijst, zoals beschreven in hoofdstuk 6.4.
8. Til de elektrode op en breng hem naar de bovenste positie.
9. Controleer in het Servicemenu of de indicator voor elektrode omhoog brandt.
10. Test de elektrode verschillende keren door hem te laten zakken en op te tillen om te controleren of hij soepel beweegt.

Afb. 35. Naad met een foutief afgesteld parallelle positie van de elektrode in relatie tot de afdichtende naad as.
- Til de elektrode omhoog om de bovenste positie.
- Maak een voorbeeldnaad gemaakt van ten minste twee deelnaden.
- Controleer wanneer de naad klaar is:
- Voor gelijkmatigheid langs de gehele oppervlak - als het is ongelijkmatig, dan een moet iets lager de greep met de elektrode, met behulp van moeren B en C in die gebieden waar de elektrode doet niet xml-ph (eerst draai de relevante moer op B en vervolgens draai de corresponderende moer op C).
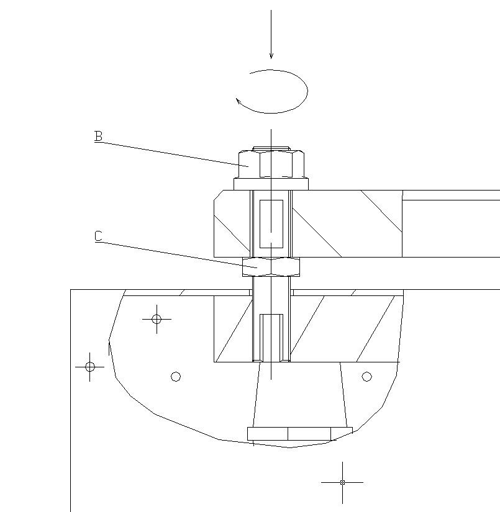
Afb. 36. Regeling van de parallelle positie van de elektrode in relatie tot de tafel met het gebruik van moeren B en C (vooraanzicht van de elektrode greep).
- Controleer of het begin van de tweede naad gedeeltelijk het einde van de eerste naad overlapt - Fig. 35. Als ze niet overlappen, moet een aanpassen de greep met de elektrode, parallel aan de naad as, xml-ph-0030@deep (iets losdraaien de moeren op B en dan iets losdraaien de schroeven op A op de kant waar de elektrode niet overlapt met de naad en vastdraaien de relevante schroeven op A op xml-ph-0031@
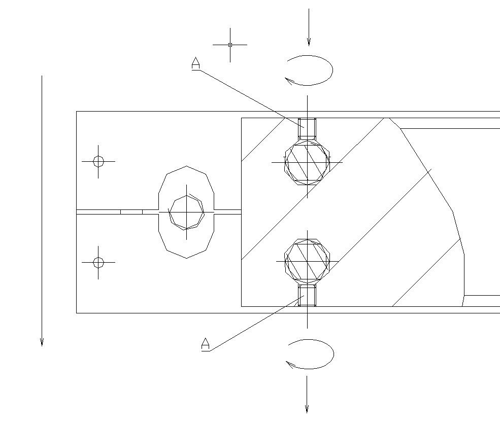
Afb. 37. Aanpassing van de parallelle positie van de elektrode in relatie tot de naad as met de gebruik van de schroeven op A (verticaal aanzicht van een doorsnede van de elektrode greep).
7.0 Selectie van lasparameters
 LET OP: De machine moet niet uitvoeren de lassen procedure zonder een isolerend pad onder de elektrode. Due naar de juiste toegepast isolerend pad de nummer van de overspanningsverschijnselen die zich vormen op het oppervlak van de elektrode is verminderd.
LET OP: De machine moet niet uitvoeren de lassen procedure zonder een isolerend pad onder de elektrode. Due naar de juiste toegepast isolerend pad de nummer van de overspanningsverschijnselen die zich vormen op het oppervlak van de elektrode is verminderd.
7.2 Selectie van uitgangsvermogen
Om te het hoogste niveau van productiviteit te bereiken bij het relatief lage niveau van defecte lassen moet de machinebediener de instelprocedure vermogen uitvoeren voor elke vervangen elektrode. De genoemde procedure wordt uitgevoerd met de hulp van de Ua INSTELLING bediening en de parameter Bedrijfsvermogen .
Zodra het vermogen is ingesteld en het lasproces is gestart de indicaties van de ANODE CURRENT ampèremeter zijn onderworpen aan visuele inspectie. Wanneer de metingen op de toename betekent dit dat op dit specifieke moment het lasproces begint. De parameter van de las tijd moet overeenkomen met de waarde van de parameter als gevolg van waardoor de hoge frequentie lasprocedure zal worden gestopt als gevolg van het stoppen van de aanwijsnaald van de ampèremeter .
Wanneer het lasproces eindigt moet de kwaliteit van las de visuele inspectie ondergaan. Als de kwaliteit van de las onvoldoende is moet het niveau van vermogen worden verhoogd. In het geval dat de bovengenoemde oplossing geen vruchtbare resultaten oplevert, dan kan de parameter van tijd verhoogd worden. Echter, de waarde van het vermogen moet niet te hoog zijn omdat het kan leiden tot producten, isolerende pad en de elektrode schade veroorzaakt door een arc-over.
7.3 Selectie van lastijdparameters
Als regel voor geldt dat de lastijd voor materialen gemaakt van hard PVC niet langer dan 4-5 sec. mag zijn. Door de ervaring van de fabrikant hogere waarden van de genoemde parameters hebben geen invloed op de kwaliteit van de bereikte naad maar verslechtert het proces efficiëntie. Als het lasproces langer duurt tijdens test procedures betekent dit dat de instelling van het vermogen moet worden geregeld .
7.4 Instelling elektrode druk
Om te kunnen lassen de PVC folie het materiaal moet worden aangedrukt door de elektrode met de druksterkte varieert van 0,5 tot 3 kg/cm2. Het meten van van druksterkte terwijl de meest geschikte waarde selecteert, zou te tijdrovend zijn en bovendien zou in de praktijk deze methode nutteloos blijken. In het algemeen, om om uit te voeren de instelling procedure met succes, de operator moet merken sommige onregelmatigheden die komen bestaan tijdens lasprocedure en in naad verschijning. Wanneer de druk te laag is ontstaan de volgende onregelmatigheden :
- Gevoeligheid voor vonkontladingen die optreden tussen twee elektroden als de lucht, die zou moeten zijn uitgeperst, optreedt in tussen twee lagen folie en als een resultaat wordt een onregelmatige stroomsterkte gevormd;
- voorkomen van lucht bellen in de naad;
- uiterlijk van naad sterkte die klein is
If the pressure is particularly low, there can occur something usually called “film boiling”. When the film is welded under very low pressure, it can be deformed into a foamy product of very low resistance. Applying excessive pressure is also inappropriate, as it can make the film very thin along the place of welding and thus also result in lower resistance of the welded material. Therefore, it is recommended to follow the principle saying that the thickness of film after welding should be equal to at least half the initial thickness of both layers of film. The appearance and proper shape of characteristic leakage that is usually formed along both edges of the welded place has also significant influence on the resistance properties of the welded material. If such a leakage does not appear, it usually indicates insufficient resistance of the welded place, which can be very easily tested. The lack of the leakage after the welding process can be caused by applying too low output power or insufficient pressure. If you use electrodes with cutting edges, it is very important to position the cutting edge correctly. It is usually assumed that the cutting edge of the electrode should protrude from the welding plane by about half the thickness of welded film. In order to check the operation of the cutting edge, it is necessary to make several test welding cycles and remove the film scraps. The result of tests can be considered satisfactory when removing the film scraps along the line of welding takes no more than one cut with scissors.
8.0 Onderhoud
Dankzij de toegepaste constructieoplossingen en ongecompliceerde structuur van de machine zijn zowel preventieve als noodonderhouds- en controleactiviteiten relatief eenvoudig en vereisen ze geen lange onderbrekingen in de werking van de machine.
De lasmachine vereist een kleine hoeveelheid werk in verband met de machine
werking en onderhoud, op voorwaarde dat de juiste gebruiksomstandigheden worden gehandhaafd. Het is noodzakelijk om regelmatig de technische staat van de aansluiting van de machine op het elektriciteitsnet te controleren, met name de staat van het elektrische schokbeveiligingssysteem.
Alle onderdelen van de hoogfrequent generator, met name alle isolerende elementen, moeten schoon worden gehouden. De binnenkant van het uitvoersysteem van de generator moet minstens om de drie maanden grondig worden gereinigd. Na deze reiniging moet de toestand van de generatorcomponenten en de eenheden die rechtstreeks samenwerken met de generator worden gecontroleerd en moeten alle verbindingen worden aangedraaid.
Vanwege de specifieke eigenschappen van de machine wordt aanbevolen dat sommige van de bovengenoemde taken worden uitgevoerd door bevoegd en goed gekwalificeerd technisch onderhoudspersoneel van de fabrikant (dit geldt met name voor noodsituaties). De bovengenoemde taken vereisen bijzondere zorg en aandacht.
 ATTENTIE: Tijdens de werking van de generator hebben de componenten ervan, evenals de componenten van het uitgangscircuit, een spanning tot 8 kV gelijkstroom en een hoogfrequente spanning tot 480 V (27,12 MHz ).
ATTENTIE: Tijdens de werking van de generator hebben de componenten ervan, evenals de componenten van het uitgangscircuit, een spanning tot 8 kV gelijkstroom en een hoogfrequente spanning tot 480 V (27,12 MHz ).
 LET OP: De condensatoren van de anodegenerator kunnen elektrische lading vasthouden met een spanning tot 8000 VDC, zelfs nadat het lasapparaat is losgekoppeld van de voeding. Voordat de onderdelen van de hoogfrequentiegenerator worden aangeraakt, moeten deze condensatoren altijd worden ontladen.
LET OP: De condensatoren van de anodegenerator kunnen elektrische lading vasthouden met een spanning tot 8000 VDC, zelfs nadat het lasapparaat is losgekoppeld van de voeding. Voordat de onderdelen van de hoogfrequentiegenerator worden aangeraakt, moeten deze condensatoren altijd worden ontladen.
De aarding van de machinestructuur moet met bijzondere zorg worden uitgevoerd. Vergeet niet dat de generator nooit mag werken wanneer de beschermschermen verwijderd zijn, ook niet tijdens technische service- en onderhoudswerkzaamheden, wanneer het veiligheidsniveau van de machine lager kan zijn als gevolg van de uitgevoerde reparatie.
Voor alle onderhoudstaken en reparaties is een vergunning van de bevoegde personen vereist.
U moet een MACHINERECORD BIJHOUDENmet de data en types van uitgevoerde preventieve activiteiten of reparaties.
Betreed tijdens onderhoudstaken of andere vereiste handmatige handelingen nooit het gebied dat blootgesteld is aan potentiële en voorspelbare gevaren en plaats er geen lichaamsdelen in om het risico op potentiële en voorspelbare gevaarlijke situaties te elimineren.
 ATTENTIE: Alle werkzaamheden binnen de zone van de actieve perseenheid van de machine, d.w.z. het vervangen van het apparaat, mogen alleen worden uitgevoerd met speciale voorzorgsmaatregelen door een getraind serviceteam.
ATTENTIE: Alle werkzaamheden binnen de zone van de actieve perseenheid van de machine, d.w.z. het vervangen van het apparaat, mogen alleen worden uitgevoerd met speciale voorzorgsmaatregelen door een getraind serviceteam.Draag altijd beschermende kleding en antislipschoenen om het risico op vallen te verkleinen. Zorg er altijd voor dat je mouwen goed om je polsen zitten of goed opgerold zijn.
Gebruik altijd werkhandschoenen bij het werken met onderdelen met scherpe randen.
Al het personeel dat verantwoordelijk is voor de bediening en het onderhoud van de machine moet goed worden opgeleid en geïnstrueerd.
Alle onderhouds- of reparatiewerkzaamheden mogen uitsluitend worden uitgevoerd door bevoegd en gekwalificeerd personeel dat in staat is defecten en storingen correct te interpreteren en installatieschema's en technische tekeningen te lezen, zodat alle demontage- en montagewerkzaamheden die verband houden met standaard onderhoudsprocedures op een professionele en - wat het belangrijkst is - veilige manier worden uitgevoerd.
Alle taken die worden uitgevoerd in het werkgebied van de perseenheid, d.w.z. montage en demontage van de elektrode, uitgevoerd wanneer de voeding van de machine is ingeschakeld, kunnen uitsluitend worden uitgevoerd door personeel dat goed is opgeleid in Arbo & veiligheid, met name wat betreft de risico's die gepaard gaan met de werking van de perseenheid.
Je moet ook rekening houden met mogelijk afwijkend gedrag van de machine als het pneumatische systeem van de lasmachine of de persluchttoevoerkanalen niet zijn afgedicht. Dit zal resulteren in het langzaam automatisch laten zakken van de perseenheid van de lasmachine.
Het personeel moet over een dergelijk risico worden geïnformeerd tijdens de training in gezondheid en veiligheid op het werk.
 ATTENTIE: Tijdens elk van de bovengenoemde handelingen moet de machine worden stopgezet.
ATTENTIE: Tijdens elk van de bovengenoemde handelingen moet de machine worden stopgezet.
8.2 Preventief programma - Periodieke controles
AAN HET BEGIN VAN ELKE DIENST
- Controleer of het werkgebied van de machine schoon en netjes is;
- Controleer visueel of de schermen vergrendeld zijn;
- Controleer de verlichting van het werkgebied;
- Controleer of de NOODSTOP-knop goed werkt;
- Controleer de hoofdbeveiliging in de elektrische installatie;
- Controleer de staat van de koperen en messing geleidende elementen in het gebied van de elektrodehouder en de aardingselementen van de zijbeschermingsschermen.
ELKE 100 BEDRIJFSUREN VAN DE MACHINE (MINSTENS ÉÉN KEER PER WEEK):
- Controleer of de lastdragende schroeven (met name de schroeven waarmee de gereedschappen zijn bevestigd) goed vastzitten en goed zijn aangedraaid;
- Controleer het condenswaterniveau in het persluchtfilterreservoir; als er water in zit, leegt u het reservoir; als er grote hoeveelheden vaste verontreinigingen in zitten, demonteert u het reservoir en wast u het;
ELKE 500 BEDRIJFSUREN VAN DE MACHINE (MAAR TEN MINSTE ELKE TWEE WEKEN)
- Controleer of de radiator van de anodelamp schoon is;
- Controleer de hoeveelheid vaste verontreinigingen en stof in de generatorkamer; als het nodig is, reinigt u de kamer met een stofzuiger of een persluchtpistool;
- Controleer of bewegende elementen (waaronder met name de gereedschappen en geleiders) schoon zijn;
- Smeer bewegende elementen - met name de geleiders; als het nodig is, gebruik dan vast vet op lithiumbasis en een smeermiddel;
- Controleer en test de alarmunit.
ELKE 1000 BEDRIJFSUREN VAN DE MACHINE (MAAR TEN MINSTE ELKE ZES MAANDEN)
- Controleer de toestand van de mechanische elementen visueel;
- Draai alle schroeven vast;
- Controleer of de beveiliging tegen elektrische schokken goed werkt;
- Controleer of de geleiders goed gesmeerd zijn;
- Controleer de toestand van de hoofdcontactelementen - hoofdcontacten of andere contactelementen van het systeem, zoals contacten of relais van overmatig versleten oppervlakken moeten worden vervangen.
ELKE 5000 UREN VAN MACHINE BEDIENING (MAAR OP MINSTENS ELKE ZES MAANDEN)
- vervang olie verwarming elektrode - olie type L-LH-46.
 LET OP: Schakel vóór elk onderhoud de machine uit met behulp van de HOOFDSCHAKELAAR en koppel de hoofdstroom los.
LET OP: Schakel vóór elk onderhoud de machine uit met behulp van de HOOFDSCHAKELAAR en koppel de hoofdstroom los.
 het is verboden om smeer de machine tijdens gebruik.
het is verboden om smeer de machine tijdens gebruik.
9.0 Gezondheid en veiligheid op het werk
9.1 Basisvereisten
- De machine mag uitsluitend worden gebruikt op een manier die geschikt is voor het doel dat expliciet is beschreven in punt 1.
- De toegepaste constructieoplossingen met betrekking tot veiligheid beperken zowel het niet-standaard gedrag van de machine als de gevaren voor de bedieners en andere personen die in contact komen met de machine tot een minimum, op voorwaarde dat de principes van veilig werken worden nageleefd. De machine is uitgerust met sleutelschakelaars op beschermende schermen, waarvan de demontage specifiek gereedschap vereist, waaronder de schakelaar op de deur van de laskamer, NOODSTOP-knop en bewegende beschermende schermen die het lasgebied omsluiten gedurende het lasproces.
- De kwesties die verband houden met gezondheid en veiligheid op het werk en de beoordeling van risico's tijdens het contact van een persoon met de machine zijn in detail beschreven in de vorige hoofdstukken van deze handleiding.
- Omdat deze kwestie uiterst belangrijk is, worden sommige instructies in dit gedeelte herhaald.
- Elke nieuwe werknemer die in contact komt met de lasmachine moet worden getraind op het gebied van de basisprincipes van gezondheid en veiligheid op het werk en vertrouwd worden gemaakt met de soorten gevaren die gepaard gaan met de bediening van de lasmachine, tenzij de operator de verplichte voorschriften en principes volgt.
- Het personeel dat verantwoordelijk is voor de bediening van het lasapparaat moet een grondige kennis hebben van eerste hulp bij elektrische schokken en brandwonden. In het geval van personen die werken met apparaten die elektromagnetische golven met een frequentie in het bereik van 0,1 - 300 MHz gebruiken, is periodiek medisch onderzoek vereist.
- Na de installatie van het lasapparaat is het noodzakelijk om de elektromagnetische veldemissie te meten en de grenzen van de gevaarlijke zone vast te stellen.
- Op basis van de meetresultaten worden het risiconiveau en de tijd dat operators in de gevaarlijke zone mogen blijven, bepaald in overeenstemming met de geldende normen.
- De gevaarlijke zone mag alleen worden betreden door operators die op basis van gespecialiseerde medische onderzoeken de juiste goedkeuring hebben voor het werken in de zone die blootgesteld is aan elektromagnetische velden en die goed zijn opgeleid in het veilig bedienen van apparaten die elektromagnetische velden uitzenden.
- De bovengenoemde metingen moeten worden uitgevoerd door een bevoegd instituut. Gedetailleerde instructies met betrekking tot dergelijke metingen worden gespecificeerd door de toepasselijke regelgeving in het land waar de machine wordt gebruikt.
- Machinebedieners moeten altijd standaard werkkleding, handschoenen, hoofddeksels en antislipschoenen dragen.
- De werkomgeving van de machine, de vloer en de handmatige houders en handgrepen moeten altijd schoon en vrij van verontreiniging, vet of modder zijn om het risico van uitglijden of vallen tot een minimum te beperken.
- Gebruik de machine nooit in de automatische bedrijfsmodus zonder de vaste of mobiele beveiligingselementen. Controleer regelmatig of alle noodschakelaars en alle andere beveiligingselementen goed gemonteerd zijn en goed functioneren.
- Iedere bediener van de machine moet instructies krijgen over de functies van de beveiligingselementen van de machine en het juiste gebruik ervan.
- In de omgeving van het apparaat (ongeveer 1,5 m rond het apparaat) mogen zich geen voorwerpen bevinden die de werking van het apparaat kunnen verstoren. Dit gebied moet schoon worden gehouden en goed verlicht zijn.
- Gebruik de manipulators of flexibele leidingen van de machine nooit als houders. Onthoud dat elke onopzettelijke beweging van de manipulator van de machine per ongeluk de werking van de machine kan starten.
- Stel de supervisor en/of het verkeerspersoneel altijd op de hoogte van onjuiste bediening van de machine.
- Voor alle onderhoudstaken en reparaties is een vergunning van de bevoegde personen vereist.
- U moet een Machinerecordmet de datums en types van uitgevoerde preventieve activiteiten of reparaties.
- Betreed tijdens onderhoudstaken of andere vereiste handmatige handelingen nooit het gebied dat blootgesteld is aan potentiële en voorspelbare gevaren en plaats er geen lichaamsdelen in om het risico op potentiële en voorspelbare gevaarlijke situaties te elimineren.
 GEBRUIK HET LASAPPARAAT NOOIT ALS DE VEILIGHEIDSSCHERMEN VERWIJDERD ZIJN OF ALS DE SLEUTELSCHAKELAARS GEBLOKKEERD ZIJN. DIT GELDT MET NAME VOOR DE BEVEILIGINGSSCHERMEN VAN DE GENERATOR.
GEBRUIK HET LASAPPARAAT NOOIT ALS DE VEILIGHEIDSSCHERMEN VERWIJDERD ZIJN OF ALS DE SLEUTELSCHAKELAARS GEBLOKKEERD ZIJN. DIT GELDT MET NAME VOOR DE BEVEILIGINGSSCHERMEN VAN DE GENERATOR.
Deze beveiligingsschermen verminderen de emissie van elektromagnetische velden en voorkomen dat de elementen van het elektrische circuit met een voedingsspanning of een hoogspanning tot 8000 V per ongeluk worden aangeraakt.
- Draag altijd beschermende kleding en antislipschoenen om het risico op vallen te verkleinen. Zorg er altijd voor dat je mouwen goed om je polsen zitten of goed opgerold zijn.
- Gebruik altijd werkhandschoenen bij het werken met hete onderdelen of onderdelen met scherpe randen.
- Men moet ook onthouden dat op de onderdelen die om ergonomische redenen niet achter een afscherming zijn afgedekt, d.w.z. de elektrode en de geleidende onderdelen van de elektrodehouder, hoogfrequente spanning staat. RAAK DEZE ONDERDELEN NOOIT AAN TIJDENS HET LASPROCES..
- Het aanraken van deze onderdelen tijdens het lasproces resulteert in verbranding van de huid door hoogfrequente spanning. Dit is echter niet gevaarlijk voor het leven of de gezondheid.
- De gebruikte methode van stroomtoevoer van de lasmachine houdt een potentieel risico in van het samendrukken of verpletteren van ledematen in de ruimte tussen het samendrukken van de elektroden. Alle werkzaamheden in het werkgebied van de perseenheid, d.w.z. het monteren en demonteren van elektroden of het verspreiden en verwijderen van materiaal en afval, die worden uitgevoerd wanneer de lasmachine is aangesloten op de stroomvoorziening, mogen uitsluitend worden uitgevoerd door werknemers die zijn opgeleid op het gebied van gezondheid en veiligheid op het werk, inclusief de informatie over de risico's die de perseenheid met zich meebrengt.
- Tijdens het gebruik van de machine moet de bediener zich in het onderstaande gebied bevinden
Afb. 38. ZDWA-15-C-3 - veiligheidswerkgebied (kleur groen )
9.3 Voorwaarden voor arbeidsveiligheid van personeel dat verantwoordelijk is voor onderhoud en reparatie van de lasmachine- Deze werkzaamheden vereisen bijzondere zorgvuldigheid. Men moet altijd onthouden dat condensatoren van de anodegenerator elektrische lading met een spanning van 8000 V kunnen vasthouden, zelfs nadat het lasapparaat is losgekoppeld van het voedingsnetwerk. Voordat de onderdelen van de hoogfrequente generator worden aangeraakt, moeten deze condensatoren altijd worden ontladen.
- Tijdens de werking van de generator staan de componenten en de componenten van het uitgangscircuit onder hoogfrequente spanning. De aarding van de machinestructuur moet met bijzondere zorg worden uitgevoerd. Men moet ook onthouden dat de tijd dat de generator in werking is terwijl de beschermkappen verwijderd zijn, tot een minimum beperkt moet worden.
- Alle reparaties moeten worden uitgevoerd in overeenstemming met de geldende principes voor het repareren en bedienen van apparaten door een persoon met een geschikt certificaat dat is afgegeven door de betreffende vereniging van elektriciens (in Polen: SEP).
- Al het personeel dat verantwoordelijk is voor de bediening en het onderhoud van de machine moet goed worden opgeleid en geïnstrueerd.
- Elke onderhouds- of reparatiehandeling mag uitsluitend worden uitgevoerd door bevoegd en gekwalificeerd personeel dat in staat is defecten en storingen correct te interpreteren en installatieschema's te lezen, zodat alle demontage- en montagehandelingen die verband houden met standaard onderhoudsprocedures op een professionele en - wat het belangrijkst is - veilige manier worden uitgevoerd.
- Tijdens elk van de bovengenoemde handelingen moet de machine worden stopgezet.
ALLE NODIGE STAPPEN ONDERNEMEN OM DIT TE VOORKOMEN:
- Het apparaat op een andere manier gebruiken dan beschreven in deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding,
- Verkeerde installatie, niet uitgevoerd volgens de procedures die in deze handleiding worden beschreven,
- Onjuiste bediening van de machine of bediening door personeel zonder de juiste training,
- Machinetoevoer van onjuiste parameters,
- Onvoldoende onderhoud van de machine,
- Onbevoegde wijzigingen of ingrepen door personen zonder de vereiste licenties, vergunningen of training,
- Gebruik van andere dan originele reserveonderdelen,
- Handelingen door personen die niet in overeenstemming zijn met de principes die in deze Bedienings- en Onderhoudshandleiding en waarschuwingsinformatie zijn gespecificeerd.
10.0 Elektrische documentatie
10.1 Parameters voeding - Technische gegevens
|
Stroomvoorziening |
3 x 220 VAC; 50/60 Hz |
|
Geïnstalleerde capaciteit |
22 kVA |
|
HF-vermogen |
15 kW |
|
Bedrijfsspanning |
24 VDC |
|
Werkfrequentie |
27,12 MHz |
|
Hoofdoverstroombeveiliging |
63A |
|
Frequentiestabiliteit |
+/- 0.6 % |
|
Generatorlamp (metaal-keramische triode) |
ITL 12-1 |
|
PLC-besturingssysteem |
DELTA |
|
Systeem met ontladingscircuit |
complete ANTIFLASH met HF-filter |
10.2 Conceptontwerptekeningen elektrische installatie
Zie bijlagen
11.0 Pneumatische documentatie
11.1 Technische gegevens
|
Bedrijfsdruk |
0,4 - 0,8 MPa |
|
Persluchtverbruik |
Max. 70 nl (standaard) per cyclus |
|
Luchtzuiverheid |
volgens ISO8573-1:4-4-4 |
|
Filterprestaties |
20 um (ISO8573-1 4-4-4) |
11.2 Werkingsprincipe
- aandrijving van de pneumatische houders van de elektrode;
- aandrijving van de geaarde elektrode;
- perseenheid;
- houders voor elektrode.
Verder bestaat het pneumatische systeem uit een luchtvoorbereidingssysteem: drukfilter en reduceerventiel, zachte aanloop, verbindingselementen, uitblaasventiel en smoorkleppen. De lucht wordt via het uitblaasventiel naar de VFRL-unit gevoerd, voorgefilterd en gereduceerd tot het vereiste volume. Vervolgens wordt de lucht via elektrisch of elektropneumatisch geregelde verdeelkleppen naar de juiste pneumatische aandrijvingen geleid, waardoor deze in beweging komen. De dynamiek van de beweging van de actuators kan worden aangepast met behulp van smoorkleppen die op de actuators zijn gemonteerd. De volgorde van de beweging van de actuators wordt geregeld door de besturing van de lasmachine.
11.3 Bedieningshandleiding BELANGRIJK: De aanwezigheid van het luchtbehandelingssysteem in de machine ontslaat de klant niet van de verplichting om te zorgen voor luchtzuiverheid conform Klasse 4-4-4 volgens ISO8573-1.
BELANGRIJK: De aanwezigheid van het luchtbehandelingssysteem in de machine ontslaat de klant niet van de verplichting om te zorgen voor luchtzuiverheid conform Klasse 4-4-4 volgens ISO8573-1.ZIE BIJLAGEN
12.0 Verwijdering
12.1 Algemene instructies
De toegepaste constructieoplossingen en de hoogwaardige componenten maken een goede werking van de machine voor een periode van ongeveer 30 jaar mogelijk. Er kunnen zich echter veranderingen voordoen in de behoeften van de klant of veranderingen in de principes of normen die op dit moment niet te voorspellen zijn, waardoor het nodig kan zijn om de machine voor het einde van de bovengenoemde periode weg te doen. Dit geldt ook voor vervangen of gerepareerde onderdelen of componenten van de lasmachine.
De Klant is verplicht om ervoor te zorgen dat de verwijdering van de machine of de onderdelen ervan wordt uitgevoerd in overeenstemming met de toepasselijke wettelijke vereisten die op een bepaald moment en op een bepaalde plaats gelden.
Alle onderdelen van de machine zijn recyclebaar.
Verwijdering van gevaarlijk afval moet altijd worden uitgevoerd door gespecialiseerde bedrijven.
Soorten afval die ontstaan tijdens de levenscyclus van het apparaat worden hieronder beschreven in punt 12.2.
12.2 Afval
- Stukken doek of papier verzadigd met stoffen die worden gebruikt voor het reinigen van de machineonderdelen;
- Gebruikte reserveonderdelen van de generator, afhankelijk van het materiaal waarvan ze gemaakt zijn;
- Vloeibaar of vast vetafval;
- Vet dat overblijft na het smeren of na onderhoud van de machine;
- Generatorlamp.
 LET OP: de lamp bevat zeldzame aardmetalen en zeldzame aardmetaaloxiden die zeer giftig zijn. In geval van breuk moet de lamp met de grootste zorg en met de hulp van gespecialiseerde diensten worden verwijderd.
LET OP: de lamp bevat zeldzame aardmetalen en zeldzame aardmetaaloxiden die zeer giftig zijn. In geval van breuk moet de lamp met de grootste zorg en met de hulp van gespecialiseerde diensten worden verwijderd.
Al het afval dat vrijkomt bij vervangings- of technische onderhoudsactiviteiten en dat vervuild is met vet, mag niet samen met industrieel afval worden verwijderd.
 HET IS VERBODEN om afval in de vuilnisbak te gooien, het op een andere manier rechtstreeks weg te gooien of het weg te gooien door standaard vuilnisophaaldiensten.
HET IS VERBODEN om afval in de vuilnisbak te gooien, het op een andere manier rechtstreeks weg te gooien of het weg te gooien door standaard vuilnisophaaldiensten. 12.3 Procedure voor het demonteren van de machine vóór verwijdering
- Plaats het apparaat zo dat het onbeweeglijk staat.
- Koppel de voeding van de machine los.
- Koppel de persluchttoevoer van de machine los.
- Verwijder flexibele plastic of rubberen leidingen en laat deze afvoeren door een gespecialiseerd bedrijf.
- Koppel draden en elektrische apparaten los, verwijder ze en laat ze afvoeren door een gespecialiseerd bedrijf.
- Scheid stalen onderdelen en onderdelen van non-ferrometalen en laat ze afvoeren door een gespecialiseerd bedrijf.
13.0 Bijlagen
13.1 Label met model- en serienummer
Elke Miller Weldmaster machine heeft deze sticker op de achterkant van de machine. Hierop staat het model- en serienummer van elk lasapparaat.
Het zal ook de spanning en de hertz aangeven die nodig zijn voor de werking.



 LET OP! De beschermende behuizing van de machine en de geïnstalleerde sleuteleindschakelaars minimaliseren de emissie van niet-ioniserende elektromagnetische energie. Het is ten strengste VERBODEN om aan het HF-lasapparaat te werken zonder deze beschermingsmiddelen!!!
LET OP! De beschermende behuizing van de machine en de geïnstalleerde sleuteleindschakelaars minimaliseren de emissie van niet-ioniserende elektromagnetische energie. Het is ten strengste VERBODEN om aan het HF-lasapparaat te werken zonder deze beschermingsmiddelen!!! LET OP!!!
LET OP!!! De laserhendels en de lasers zelf, als ze zich in
De laserhendels en de lasers zelf, als ze zich in Operatie
Operatie

 Het is mogelijk om de STAND-BY modus op elk moment en ga
Het is mogelijk om de STAND-BY modus op elk moment en ga .
. Wanneer
Wanneer ATTENTIE
ATTENTIE LET OP! Let vooral op het gewicht van de
LET OP! Let vooral op het gewicht van de Er
Er Een gedeeltelijke las is een gelast materiaaloppervlak gelijk aan het oppervlak
Een gedeeltelijke las is een gelast materiaaloppervlak gelijk aan het oppervlak Als de ingevoerde waarde rood gemarkeerd is, betekent dit dat het lassen
Als de ingevoerde waarde rood gemarkeerd is, betekent dit dat het lassen De stel in waarden van alle parameters in HF Hoofd Aandrijving zijn voorbeelden.
De stel in waarden van alle parameters in HF Hoofd Aandrijving zijn voorbeelden.

